Rep:MOD:JHworkbook
Introduction
Using the program Gaussian, the following calculations and pictures have been generated. This information has been used to describe the following molecules: NH3, H2, N2 and BH3.
NH3 Molecule
Summary Information
N-H Bond distance = 1.01798 A
N-H Bond Angle = 105.741 degrees
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p)
Spin = Singlet
Final Energy E(RB3LYP) = -56.55776678 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00053995 a.u.
Point Group = C3v
Item
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Structure and Vibrations
Ammonia Molecule |
Access the file using this link

From the 3N-6 rule we expect 6 different vibrations.
Modes 2 and 3 are degenerate and so too are modes 5 and 6.
Modes 1,2 and 3 are bending and modes 4, 5 and 6 are stretching.
Mode 4 is highly symmetric and mode 1 is known as the "umbrella" mode.
There are 4 different frequencies of vibration for the 6 vibrations due to some being degenerate. Therefore we would see 4 bands on an experimental spectrum. However, due to small movements in the dipole moment, 2 of the peaks are so small (the peak for 4 and the peak for 5 and 6) it is not possible to see them on a regular scale.
Charges

The charge on a hydrogen atom in NH3 is +0.375. The charge on a nitrogen atom in NH3 is -1.125.
I would expect these charges in the ammonia molecule because nitrogen is more electronegative and so withdraws the electrons from the covalent bond more than the hydrogen. This happens in every bond equally and so the nitrogen has three times the charge of each hydrogen.
H2 Molecule
Summary Information
H-H Bond distance = 1.01798 A
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p)
Spin = Singlet
Final Energy E(RB3LYP) = -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00000017 a.u.
Point Group = D∞h
Item
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Structure, Charge and Vibration
Hydrogen Molecule |
Access the file using this link
The charge on both molecules is 0.
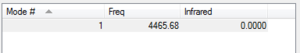
The peak for this vibration is not visible because there is no movement of the dipole moment.
N2 molecule
Summary Information
N-N Bond distance = 1.09200 A
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p)
Spin = Singlet
Final Energy E(RB3LYP) = -109.52412868 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00000060 a.u.
Point Group = D∞h
Item
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Structure, Charge and Vibration
Nitrogen Molecule |
Access the file using this link
The charge on both molecules is 0.

The peak for this vibration is not visible because there is no movement of the dipole moment.
Haber-Bosch Process Energy Change
E(NH3)= -56.55776678 au
2*E(NH3)= -112.8879438 au
E(N2)= -109.52412868 au
E(H2)= -1.17853936 au
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 au
ΔE=2*E(NH33)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557868 au = -146.47 KJ/mol (2dp)
The reaction is exothermic so the products of the reaction are of a lower energy than the reactants. Therefore the ammonia is more stable than the gaseous reactions of nitrogen and hydrogen molecules.
BH3 Molecule
Summary Information
B-H Bond distance = 1.18000 A
B-H Bond Angle = 120.000 degrees
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p)
Spin = Singlet
Final Energy E(RB3LYP) = -26.61511243 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00305259 a.u.
Point Group = D3h
Item
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000017 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000011 0.001200 YES
Structure and Vibrations
Borontrihydride Molecule |
Access the file using this link
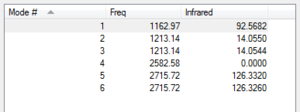
From the 3N-6 rule we expect 6 different vibrations.
Modes 2 and 3 are degenerate and so too are modes 5 and 6.
Modes 1,2 and 3 are bending, modes 4, 5 and 6 are stretching and also mode 4 is also a highly symmetric stretching vibration. There are 2 sets of degenerate vibrations, therefore we would see 4 bands on an experimental spectrum. However, due to small movements in the dipole moment, 2 of the peaks are so small, it is not possible to see them on a regular scale.
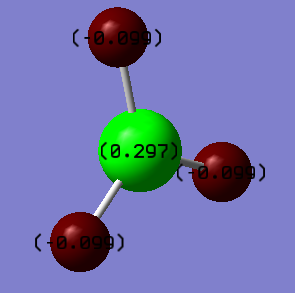
The charge on a boron atom in BH3 is +0.297. The charge on a hydrogen atom in BH3 is -0.099.
The hydrogen atoms are more electronegative than the boron atom and so in each of the bonds the electrons are withdrawn closer to the hydrogen atoms. The boron has 3 bonds and so 3 times more than charge each of the hydrogen atoms.
Molecular Orbitals of BH3
B2H6
Problems on Gaussview
B2H6 is a the dimer of borontrihydride and shows a more stable electronic configuration. This is due to the boron atom no longer having an empty p orbital. The optimization of borane on Gaussview was repeatedly unsuccessful because Gaussview struggled to optimize the 3 center, 2 electron bond. Changes the starting structure, bonds lengths, bond angles, the optimizing basis set were made. The following images are different starting and end points to finally achieve a successful optimization.



Successful Optimization
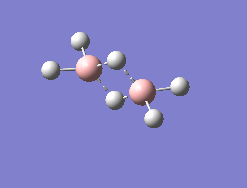
Borane Dimer (The jmol image has added a bond between the two boron atom, showing the optimization, although still slightly successful, contains errors) |
Access the file using this link
Summary Information
B-H Bond distance = 1.30976 A (central bonds), 1.19000 A (outside bonds)
B-H Bond Angle = 94.256 degrees (angle in the center), 123.076 (angle on the outside)
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p)
Spin = Singlet
Final Energy E(RB3LYP) = -53.29472232 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00007400 a.u.
Point Group = C1
Item
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000073 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000037 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.007007 0.001800 NO
RMS Displacement 0.002133 0.001200 NO
Although the structure appears to be very similar to that of the accepted structure of the borane dimer there was no convergence in the last 2 rows of the item table. Thus showing, the difficulties of using Gaussview for a slightly abnormal molecule.