Rep:MOD:JDN15
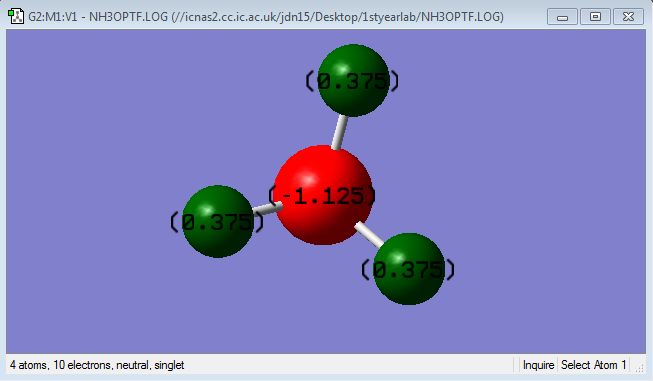
NH3
Calculation Method : RB3LYP
Basic Set : 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E (RB3LYP) : -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS gradient : 0.00000485 a.u.
Point Group : C3V
N-H Bond Length: 1.3
H-N-H Bond Angle: 109.47
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986267D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
NH3 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Display Vibrations :
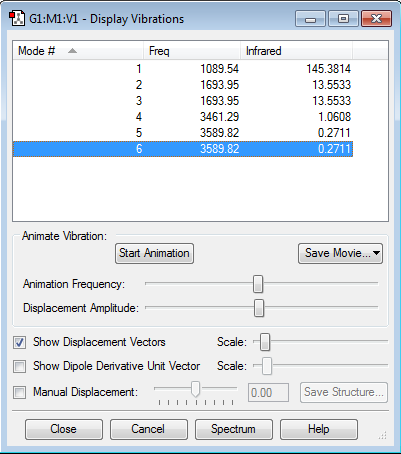
Vibrational modes expected from 3(N)-6 Rule : 3(4) - 6 = 6
Modes that are degenerate : 2&3, 5&6
Bending modes : 1,2,3
Stretching modes : 4,5,6
Highly Symmetric Mode: 4
Umbrella mode : 1
Bands observed in an experimental spectrum of NH3(g): 4
N is expected to be negatively charged as it is a more electronegative atom compared to H
N2
Calculation Method : RB3LYP
Basic Set : 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E (RB3LYP) : -109.52412868 a.u.
RMS gradient : 0.00000003 a.u.
Point Group : D∞h
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.076410D-15
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
The optimisation file is linked to here
Display Vibrations :
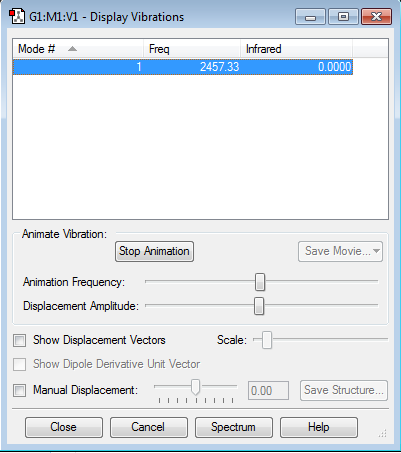
Vibrational modes expected from 3(N)-5 Rule : 3(2) - 5 = 1
Bands observed in an experimental spectrum of N2(g): 1
Confirmed : No negative frequencies
H2
Calculation Method : RB3LYP
Basic Set : 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E (RB3LYP) : -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS gradient : 0.00002276 a.u.
Point Group : D∞h
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000039 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000039 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000052 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000073 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.043043D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
The optimisation file is linked to here
Display Vibrations :
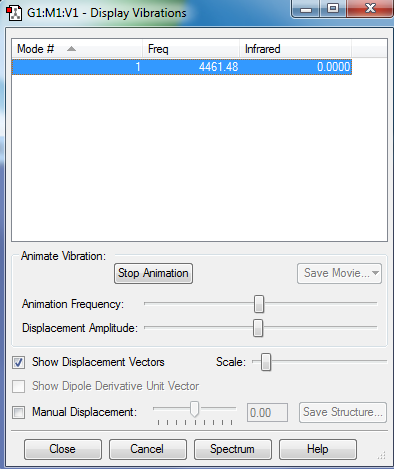
Vibrational modes expected from 3(N)-5 Rule : 3(2) - 5 = 1
Bands observed in an experimental spectrum of H2(g): 1
Confirmed : No negative frequencies
Energy Values
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)=-113.11553746 a.u.
E(N2)=-109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)=-1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -113.11553746 - [ (-109.52412868) + (-3.53561808) = -0.0557907 a.u. = -146.47849401kJ/mol
As reaction is exothermic, the product will be more stable.
CH4
Calculation Method : RB3LYP
Basic Set : 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E (RB3LYP) : -40.52401404 a.u.
RMS gradient :0.00003263 a.u.
Point Group : Td
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000063 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000034 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000179 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000095 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.256043D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
The optimisation file is linked to here
Display Vibrations :
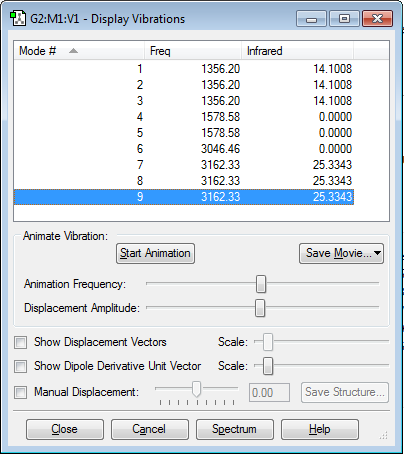
Vibrational modes expected from 3(N)-6 Rule : 3(5) - 6 = 9
Number of vibrational modes: 9
Degenerate modes : 1,2,3 & 4,5 & 7,8,9
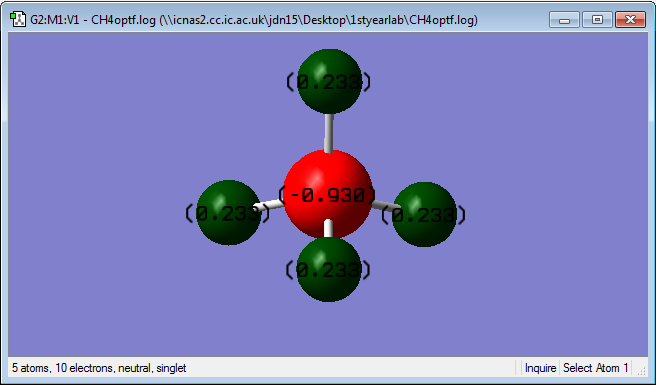
C is expected to be negatively charged as it is more electronegative than H
MO

This MO is very deep (-10.16707 a.u.), the AOs hardly overlap and are not very involved with chemical bonding.
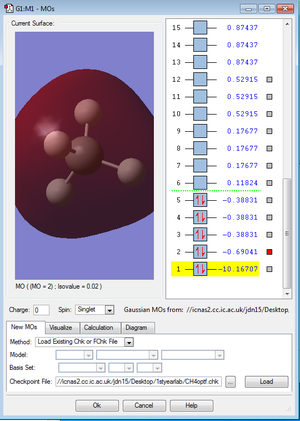
MOs 2 has stronger overlap and is very extensive. The energy is also at a higher level compared to MO1 (-0.69 compared to -10.17)

These MOs are formed by the valence 2s and 2p orbitals of C and 1s valence electron of H. They are bonding MOs
