Pc2715
Ammonia
Optimized Ammonia Molecule
N-H bond distance = 1.01798
H-N-H bond angle = 105.741
Summary
Molecule = NH3
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basic Set = 6-31G(d.p)
Final Energy E(RG3LYP) = -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norn = 0.00000485
Point Group = C3V
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986280D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The optimisation file is liked to here
Ammonia |
Animating Vibration
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
= 6
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
= 2 and 3, 5 and 6
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
=The bond stretch vibration modes are 4,5 and 6, while the bending vibration modes are 1, 2 and 3.
Which mode is highly symmetric?
= 4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
= 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 2 Because there are only 2 visible peaks in the IR spectrum.
Charge Distribution of Ammonia
N = -1.125
H = 0.375
Nitrogen atom is more negative because it is more electronegative atom than the hydrogen.
Haber-Bosch Process
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
N2 summary
What is the molecule? = N2
What is the calculation method? = RB3LYP
What is the basis set? = 6-31G(d,p0
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? = -109.52412868 a.u.
What is the RMS gradient? = 0.00000060
What is the point group of your molecule? = Dinf H
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401050D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The optimisation file is liked to here
Nitrogen |
List Of Frequency- Display Vibrations
| Mode | Freq | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2457.33 | 0.0000 |
Charge Distribution of Nitrogen
N = 0
Charge Distribution is zero because the molecule is non polar.
H2 summary
What is the molecule? = H2
What is the calculation method? = RB3LYP
What is the basis set? = 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? = -1.17853936 a.u.
What is the RMS gradient? = 0.00000017
What is the point group of your molecule? = Dinf H
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164079D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The optimisation file is liked to here
Hydrogen |
List Of Frequency- Display Vibrations
| Mode | Freq | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4465.68 | 0.0000 |
Charge Distribution of Hydrogen
H = 0
Charge Distribution is zero because the molecule is non polar.
Energy
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579070 a.u
Therefore, ΔE is -146.48 kJ/mol. The ammonia product is more stable than gaseous reactants.
Methane
Optimized Methane Molecule
C-H bond distance = 1.09197
H-C-H bond angle = 109.47122
Methane summary
molecule name = Methane CH4
calculation method = RB3LYP
basis set = 6-31G(d,p)
final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? = -40.52401404 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00003263 a.u.
the point group of your molecule = TD
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000063 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000034 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000179 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000095 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.255986D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R4 R(1,5) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(3,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(4,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,5,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(2,1,5,4) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(3,1,5,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The optimisation file is liked to here
List Of Frequency- Display Vibrations
| Mode | Freq | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1356.20 | 14.1008 |
| 2 | 1356.20 | 14.1008 |
| 3 | 1356.20 | 14.1008 |
| 4 | 1578.58 | 0.0000 |
| 5 | 1578.58 | 0.0000 |
| 6 | 3046.46 | 0.0000 |
| 7 | 3162.33 | 25.3343 |
| 8 | 3162.33 | 25.3343 |
| 9 | 3162.33 | 25.3343 |
Animating Vibration

Methane |
Charge distribution of Methane
C = -0.930
H = 0.233
The carbon atom is more negative because it is more electronegative atom than the hydrogen. However, the molecule is a non polar molecule because the charges canceled out.
Molecular Orbitals
1s bonding orbital
The energy level of this orbital is at -10.16707 which is too low to form bond with other orbital. It doesn't involve in any chemical bonding.
2s bonding orbital
2s orbital is larger than the 1s orbital, Therefore, it can overlap with other orbital.
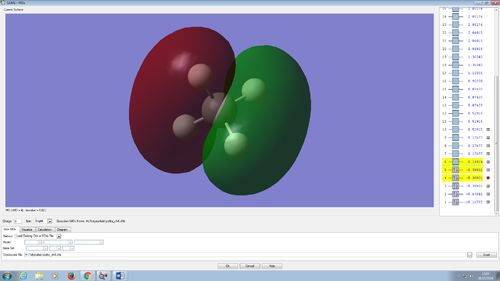
2p bonding orbital.
Methane contain 3 of this p orbitals. They all located at the same energy level of -0.38831. The 3 orbitals orientate in 3 different direction; x, y or z. The p orbital of the carbon overlap with the 1s orbital of the hydrogen; the AO that contributed to this orbital is 1s from hydrogen and 2p from carbon giving this MO.
However, the 2s and the three 2p can mixed to form 4 sp3 orbitals. The MO of the 4 sp3 orbitals were not shown as the program did not show the hybridised orbital formed.
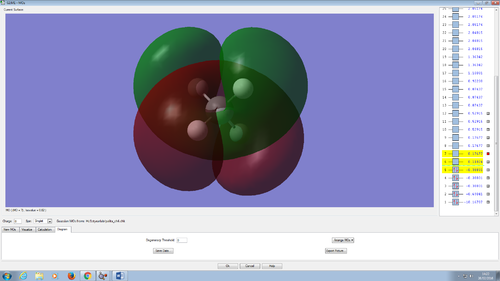
2s antibonding orbital.
This is the antibonding orbital of this orbital. The energy level is higher than the bonding orbital, it is at 0.11824.
2p antibonding orbital.
This is the antibonding orbital of this orbital. The energy level of this orbital is at 0.17677.