ModBB:916
BB916 Wiki Page
NH3 Molecule
What is the molecule? NH3
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -56.55776873au
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00000485au
What is the point group of your molecule? C3V
Bond Length 1.01798
Bond Angle 105.741 degrees (H-N-H)
Optimisation Proof
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Vibrations
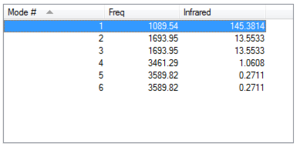
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 6 modes are expected
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? Vibrational modes 2 and 3 are degenerate as are vibrational modes 5 and 6 from our table of vibrations.
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? Vibrational modes 1,2 and 3 are all bending vibrations and vibrational modes 4,5 and 6 are all bond stretching vibrations.
Which mode is highly symmetric? The most highly symmetric vibrational mode is number 4.
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? Vibrational mode 1 can be known as the "umbrella" mode as it looks to almost invert.
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? There will be 4 peaks present in the IR spectrum of gaseous ammonia. This is due to degeneracy of some vibrations. The last peak will also have a very small intensity (0.2711) and so may be difficult to distinguish from the base line.
Charges

In NH3 the Nitrogen adopts a negative charge of -1.125 whilst each of the three Hydrogens adopts a positive charge of +0.375. This is as expected as Nitrogen is more electronegative than Hydrogen so draws the electrons towards itself and away from the Hydrogens. This entire effect adds electron density to the Nitrogen and takes electron density away from the Hydorgens, resulting in them being positive. The Nitrogen also has a lone pair which makes it even more negative. Also the net charge of the molecule is 0 as the negativity of the Nitrogen is cancelled out by the combined positivity of the Hydrogens.
N2 Molecule
What is the molecule? N2
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -109.52412868au
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00000060au
What is the point group of your molecule? D*H
Bond Length 1.10550
Bond angle 180 degrees
Optimisation Proof
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Vibrational Modes
There is only one frequency of vibration at 2457.33cm-1, meaning there are no negative freqencies.
The optimisation file is liked to here
H2 Molecule
What is the molecule? H2
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -1.17853936au
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00000017au
What is the point group of your molecule? D*H
Bond Length 0.74279
Bond angle
180 degrees
Optimisation Proof
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Vibrational Modes
There is only one frequency of vibration at 2457.33cm-1, meaning there are no negative freqencies.
The optimisation file is liked to here
Haber-Bosch process
N2+3H2=NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 au 2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 au E(N2)= -109.52412868 au E(H2)= -1.1785396 au 3*E(H2)= -3.53591808 au ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05549074 au = -145.690948961 kJ/mol
The products are more stable as the enthalpy is more negative, as the ΔE is negative. [1]
Project Molecule-CN-
What is the molecule? CN-
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -92.82453153au
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00000704au
What is the point group of your molecule? C*V
Bond Length 1.18489
Bond angle 180 degrees
Optimisation Proof
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000012 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000012 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000005 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000008 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is liked to here
CN molecule |
Vibrational Modes
There is only one frequency of vibration at 2139.19cm-1, meaning there are no negative freqencies. This one vibration is a bond stretching vibration.
Charges

In the CN-, the nitrogen and carbon are both negatively charged due to the overall negative charge of the molecule. Of the two the nitrogen is the more negative atom due to it being more electronegative than carbon so draws the electrons towards itself and away from the carbon. This entire effect adds electron density to the Nitrogen and takes electron density away from the carbon, resulting it being more positive.
CN- MOs

The first molecular orbital is most likely the pi orbital within the CN- triple bond. It is formed from the overlap of p orbitals.

The second molecular orbital looks almost exactly like a d orbital

The third molecular orbital looks like a pi* antibonding orbital.

The fourth molecular orbital appears to have antibonding contribution on the carbon atom whereas on the nitrogen atom it looks like a pi orbital, so maybe there is some antibonding which occurred on the carbon and made the orbital smaller.

The fifth molecular orbital looks like the second molecular orbital apart from it looks like all of the electron density is on the Nitrogen. You could also look at it like it is a d orbital on the Nitrogen.
