Mod:Hunt Research Group/PlotCube.py
CubePy is under CC BY-NC-SA license
PlotCube.py is a collection of functions that plot data from cube files.
Requirements
- Python
- Matplotlib
- NumPy
- scipy
- gistfile1
ReadCube.pyCalculateCube.py
An easy way to obtain Python with the required modules is by installing Anaconda.
Anaconda comes with Spyder, which is a Python editor that you can use to write and run Python codes (Applications Anaconda Navigator spyder Launch)
Instructions
Running the code
The plotting functions can be run from the terminal window by typing:
python ReadCube.py function_name cube_file_path arg1=val1 arg2=val2...
Functions
PlotMesh
This function creates an interactive plot of the cube file values.
Required arguments
fpath(string) = path for a cube file
Optional arguments
xlim(list,default=[None, None]) = a list of two values to be used as the lower and upper limit for the x values (by default all the x values from the cube file are plotted)ylim(list,default=[None, None]) = a list of two values to be used as the lower and upper limit for the y values (by default all the y values from the cube file are plotted)zlim(list,default=[None, None]) = a list of two values to be used as the lower and upper limit for the z values (by default all the z values from the cube file are plotted)alpha(float, default=0.1) = transparency value (between 0 and 1)size(float, default=0.05) = marker sizelower_cutoff(float, default=None) = the lower limit of the values to be plotted (by default all the values from the cube file are plotted)upper_cutoff(float, default=None) = the upper limit of the values to be plotted (by default all the values from the cube file are plotted)axes(boolean, default=False) = if True, show axes; if False, hide axescolour(string, default='rainbow') = colour scheme ('rainbow' by default, change it to 'bwr' for blue-white-red) - full list herebkg(tuple/list/string, default=(1, 1, 1)) = background colour (RGB tuple/list or name - each value between 0 and 1, white by default)minmax(boolean, default=True) = if True, show minima and maxima; if False, hide minima and maximaminmax_range(float, default=0.01) = the value range to consider for the minima and maxima (i.e. ±0.01 by default)cb_lim(list, default=None) = limits for the colour bar (list of two floats; if not specified, the limits will be the min and max of the values; if the limits do not cover the whole range of values, a warning is printed)au(boolean, default=False) = if True, use atomic units (i.e. bohr for coordinates); if False, use Angstroms for coordinates andunitsfor valuesdensity(integer, default=1) = an integer number n which indicates that the number of points stored along each axis is reduced by the density value n (therefore the total number of points is reduced by n3)value_type(string, default='esp') = can be ‘esp’/’potential’ or ‘dens’/’density’ (or any uppercase version of the aforementioned); used in conjunction with the keywordsauandunitsin order to convert the values to the appropriate unitsunits(string, default=None) = the units to be used for the value; currently supports ‘V’ for ESP and ‘A’/‘angstrom’, ’nm’, ’pm’, ’m’ for density (or any lowercase/uppercase version of these). In the case of the density, the actual units are the specified units ^(-3). The keywordsvalue_typeandauoverrideunits. Ifauis True, the values will be in atomic units regardless of the value passed forunits. Ifvalue_typeis ‘dens’, the values will be read as density values even if theunitsargument has a valid ESP value (such as ‘V’). The default unit for ESP is V and for density 1/Å3.log(boolean, default=True) = if True, it saves a .log file of the command used to run the functions (the command is tidied-up before saving i.e. unnecessary spaces are removed, argument values are converted to their usual uppercase/lowercase versions, file lists are explicit - instead of using wildcard symbols such as *)logfile(string, default=None) = the name of the log file (iflogis True); by default the file name is the input file name followed by the function name
Calls
ExtractData(fromReadCube.py)Axes(fromReadCube.py)ValuesAsDictionary(fromReadCube.py)
Sliders

- lower cutoff value
- upper cutoff value
- alpha
- size
Buttons
- axes: on/off
- minima and maxima: on/off
- colour: 'rainbow', 'bwr' and the value passed for the
colourparameter (if different from 'rainbow' and 'bwr') - background colour: 'white', 'black' and the value passed for the
bkgparameter (if different from white and black)
Observations
- SLOW
- ONLY WORKS FOR ORTHONORMAL GRIDS
- If you click on a point, it will be highlighted and its value will be displayed in the upper right corner.
Example
python PlotCube.py PlotMesh test_emim_oac_esp.cube colour='plasma' axes=True
Plot shown in figure 1.
PlotSurface
This function creates an interactive plot of all the points which reside within +/- a fractional distance from the surface defined in terms of the Van der Waals radii of the atoms in the molecule (the fractional distance represents 30% of the distance between two diagonally adjacent points in the grid).
Required arguments
fpath(string) = path for a cube file
Optional arguments
factor(float, default=1) = factor by which to multiply the VdW radiialpha(float, default=1) = transparency value (between 0 and 1)size(float, default=1) = marker sizeaxes(boolean, default=False) = if True, show axes; if False, hide axescolour(string, default='rainbow') = colour scheme ('rainbow' by default, change it to 'bwr' for blue-white-red) - full list herebkg(tuple/list/string, default=(1, 1, 1)) = background colour (RGB tuple/list or name - each value between 0 and 1, white by default)minmax(boolean, default=False) = if True, show minima and maxima; if False, hide minima and maximaminmax_range(float, default=0.05) = the value range to consider for the minima and maxima (i.e. ±0.05 by default)cb_lim(list, default=None) = limits for the colour bar (list of two floats; if not specified, the limits will be the min and max of the values; if the limits do not cover the whole range of values, a warning is printed)atoms(boolean, default=True) = if True, show atoms; if False, hide atomsau(boolean, default=False) = if True, use atomic units (i.e. bohr for coordinates); if False, use Angstroms for coordinates andunitsfor valuescurvature(boolean, default=False) = if True, plots curvature points (either based on cv_lim if given, or cv_pts)cv_lim(float, default=None) = the upper limit of the curvature for the low curvature points to be plotted (it overrides cv_pts if given)cv_pts(integer, default=5) = the number of low curvature points to be plotted (the points will be chosen in increasing order of their absolute curvaturesave(boolean, default=False) = if True, it saves a .txt file with a summary of the results (minimum, maximum and lowest curvature)grey_surf(boolean, default=False) = if True, it plots a grey surface just below the van der Waals surfacedensity(integer, default=1) = an integer number n which indicates that the number of points stored along each axis is reduced by the density value n (therefore the total number of points is reduced by n3)value_type(string, default='esp') = can be ‘esp’/’potential’ or ‘dens’/’density’ (or any uppercase version of the aforementioned); used in conjunction with the keywordsauandunitsin order to convert the values to the appropriate unitsunits(string, default=None) = the units to be used for the value; currently supports ‘V’ for ESP and ‘A’/‘angstrom’, ’nm’, ’pm’, ’m’ for density (or any lowercase/uppercase version of these). In the case of the density, the actual units are the specified units ^(-3). The keywordsvalue_typeandauoverrideunits. Ifauis True, the values will be in atomic units regardless of the value passed forunits. Ifvalue_typeis ‘dens’, the values will be read as density values even if theunitsargument has a valid ESP value (such as ‘V’). The default unit for ESP is V and for density 1/Å3.thickness(float, default=0.3) = represents the fractional thickness of the van der Waals surface (by default, the points that are within 0.3=30% of the surface defined by the van der Waals radii of the constituent atoms are selected as part of the van der Waals surface)log(boolean, default=True) = if True, it saves a .log file of the command used to run the functions (the command is tidied-up before saving i.e. unnecessary spaces are removed, argument values are converted to their usual uppercase/lowercase versions, file lists are explicit - instead of using wildcard symbols such as *)logfile(string, default=None) = the name of the log file (iflogis True); by default the file name is the input file name followed by the function name
Calls
ExtractData(fromReadCube.py)Axes(fromReadCube.py)ValuesAsDictionary(fromReadCube.py)GetVdWPoints(fromReadCube.py)VdWLaplacian(fromCalculateCube.py)
Sliders

- azimuth
- elevation
- alpha
- size
- zoom
Buttons
- axes: on/off
- minima and maxima: on/off
- atoms: on/off
- colour: 'rainbow', 'bwr' and the value passed for the
colourparameter (if different from 'rainbow' and 'bwr') - background colour: 'white', 'black' and the value passed for the
bkgparameter (if different from white and black) - curvature: on/off
Example
python PlotCube.py PlotSurface test_emim_oac_esp.cube bkg=[0.2,0.2,0.3]
The resulting plot, shown after changing the alpha and zoom values using the slider, is shown in figure 2.
PlotIsosurface
This function creates an interactive plot of all the points which are within a specified value range from a given value.
Required arguments
fpath(string) = path for a cube file
Optional arguments
factor(float, default=1) = factor by which to multiply the VdW radiialpha(float, default=1) = transparency value (between 0 and 1)size(float, default=4) = marker sizeaxes(boolean, default=True) = if True, show axes; if False, hide axescolour(string, default='rainbow') = colour scheme ('rainbow' by default, change it to 'bwr' for blue-white-red) - full list herebkg(tuple/list/string, default=(1, 1, 1)) = background colour (RGB tuple/list or name - each value between 0 and 1, white by default)minmax(boolean, default=True) = if True, show minima and maxima; if False, hide minima and maximaminmax_range(float, default=0) = the value range to consider for the minima and maximacb_lim(list, default=None) = limits for the colour bar (list of two floats; if not specified, the limits will be the min and max of the values; if the limits do not cover the whole range of values, a warning is printed)atoms(boolean, default=False) = if True, show atoms; if False, hide atomsau(boolean, default=False) = if True, use atomic units (i.e. bohr for coordinates); if False, use Angstroms for coordinates andunitsfor valuescurvature(boolean, default=False) = if True, plots curvature points (either based on cv_lim if given, or cv_pts)cv_lim(float, default=None) = the upper limit of the curvature for the low curvature points to be plotted (it overrides cv_pts if given)cv_pts(integer, default=5) = the number of low curvature points to be plotted (the points will be chosen in increasing order of their absolute curvaturezoom(float, default=1) = how large the plot is displayed with respect to the default sizedensity(integer, default=1) = an integer number n which indicates that the number of points stored along each axis is reduced by the density value n (therefore the total number of points is reduced by n3)iso(float, default=None) = the value of the points to be plottediso_range(float, default=0.01) = the value range to consider when selecting the points (i.e.iso±0.01 by default)value_type(string, default='esp') = can be ‘esp’/’potential’ or ‘dens’/’density’ (or any uppercase version of the aforementioned); used in conjunction with the keywordsauandunitsin order to convert the values to the appropriate unitsunits(string, default=None) = the units to be used for the value; currently supports ‘V’ for ESP and ‘A’/‘angstrom’, ’nm’, ’pm’, ’m’ for density (or any lowercase/uppercase version of these). In the case of the density, the actual units are the specified units ^(-3). The keywordsvalue_typeandauoverrideunits. Ifauis True, the values will be in atomic units regardless of the value passed forunits. Ifvalue_typeis ‘dens’, the values will be read as density values even if theunitsargument has a valid ESP value (such as ‘V’). The default unit for ESP is V and for density 1/Å3.thickness(float, default=0.3) = represents the fractional thickness of the van der Waals surface (by default, the points that are within 0.3=30% of the surface defined by the van der Waals radii of the constituent atoms are selected as part of the van der Waals surface)log(boolean, default=True) = if True, it saves a .log file of the command used to run the functions (the command is tidied-up before saving i.e. unnecessary spaces are removed, argument values are converted to their usual uppercase/lowercase versions, file lists are explicit - instead of using wildcard symbols such as *)logfile(string, default=None) = the name of the log file (iflogis True); by default the file name is the input file name followed by the function name
Calls
ExtractData(fromReadCube.py)Axes(fromReadCube.py)ValuesAsDictionary(fromReadCube.py)GetVdWPoints(fromReadCube.py)
Sliders
- value
- azimuth
- elevation
- alpha
- size
- zoom
Buttons
- axes: on/off
- minima and maxima: on/off
- atoms: on/off
- colour: 'rainbow', 'bwr' and the value passed for the
colourparameter (if different from 'rainbow' and 'bwr') - background colour: 'white', 'black' and the value passed for the
bkgparameter (if different from white and black) - curvature: on/off
Example
python PlotCube.py PlotIsosurface test_emim_oac_esp.cube iso=0.01 iso_range=0.02
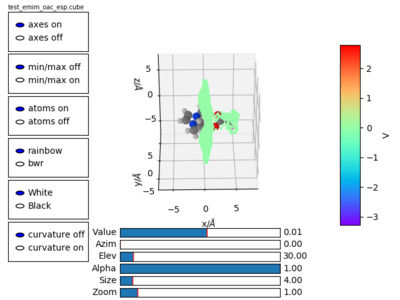
The resulting plot after rotation is shown in figure 3.
PlotSlice
This function generates an interactive plot of all the points which reside within +/- a fractional distance from a plane defined in terms of a normal vector and an origin (the fractional distance represents 30% of the distance between two diagonally adjacent points in the grid).
Required arguments
fpath(string) = path for a cube file
Optional arguments
factor(float, default=1) = factor by which to multiply the VdW radiialpha(float, default=1) = transparency value (between 0 and 1)size(float, default=4) = marker sizeaxes(boolean, default=True) = if True, show axes; if False, hide axescolour(string, default='rainbow') = colour scheme ('rainbow' by default, change it to 'bwr' for blue-white-red) - full list herebkg(tuple/list/string, default=(1, 1, 1)) = background colour (RGB tuple/list or name - each value between 0 and 1, white by default)minmax(boolean, default=False) = if True, show minima and maxima; if False, hide minima and maximaminmax_range(float, default=0) = the value range to consider for the minima and maximacb_lim(list, default=None) = limits for the colour bar (list of two floats; if not specified, the limits will be the min and max of the values; if the limits do not cover the whole range of values, a warning is printed)atoms(boolean, default=False) = if True, show atoms; if False, hide atomsau(boolean, default=False) = if True, use atomic units (i.e. bohr for coordinates); if False, use Angstroms for coordinates andunitsfor valuescurvature(boolean, default=False) = if True, plots curvature points (either based on cv_lim if given, or cv_pts)cv_lim(float, default=None) = the upper limit of the curvature for the low curvature points to be plotted (it overrides cv_pts if given)cv_pts(integer, default=5) = the number of low curvature points to be plotted (the points will be chosen in increasing order of their absolute curvaturezoom(float, default=1) = how large the plot is displayed with respect to the default sizea(float, default=0) = the x component of the normal vector defining the planeb(float, default=0) = the y component of the normal vector defining the planec(float, default=1) = the z component of the normal vector defining the planex0(float, default=None) = the x coordinate of the origin for the normal vector defining the planey0(float, default=None) = the y coordinate of the origin for the normal vector defining the planez0(float, default=None) = the z coordinate of the origin for the normal vector defining the planedensity(integer, default=1) = an integer number n which indicates that the number of points stored along each axis is reduced by the density value n (therefore the total number of points is reduced by n3)contour(boolean, default=True) = if True, show van der Waals contour; if False, hide van der Waals contourvalue_type(string, default='esp') = can be ‘esp’/’potential’ or ‘dens’/’density’ (or any uppercase version of the aforementioned); used in conjunction with the keywordsauandunitsin order to convert the values to the appropriate unitsunits(string, default=None) = the units to be used for the value; currently supports ‘V’ for ESP and ‘A’/‘angstrom’, ’nm’, ’pm’, ’m’ for density (or any lowercase/uppercase version of these). In the case of the density, the actual units are the specified units ^(-3). The keywordsvalue_typeandauoverrideunits. Ifauis True, the values will be in atomic units regardless of the value passed forunits. Ifvalue_typeis ‘dens’, the values will be read as density values even if theunitsargument has a valid ESP value (such as ‘V’). The default unit for ESP is V and for density 1/Å3.thickness(float, default=0.3) = represents the fractional thickness of the van der Waals surface (by default, the points that are within 0.3=30% of the surface defined by the van der Waals radii of the constituent atoms are selected as part of the van der Waals surface)log(boolean, default=True) = if True, it saves a .log file of the command used to run the functions (the command is tidied-up before saving i.e. unnecessary spaces are removed, argument values are converted to their usual uppercase/lowercase versions, file lists are explicit - instead of using wildcard symbols such as *)logfile(string, default=None) = the name of the log file (iflogis True); by default the file name is the input file name followed by the function name
Calls
ExtractData(fromReadCube.py)Axes(fromReadCube.py)ValuesAsDictionary(fromReadCube.py)GetVdWPoints(fromReadCube.py)
Sliders
- a
- b
- c
- x0
- y0
- z0
- zoom
Buttons
- axes: on/off
- minima and maxima: on/off
- atoms: on/off
- colour: 'rainbow', 'bwr' and the value passed for the
colourparameter (if different from 'rainbow' and 'bwr') - background colour: 'white', 'black' and the value passed for the
bkgparameter (if different from white and black) - curvature: on/off
Example
python PlotCube.py PlotSlice test_emim_oac_esp.cube colour='plasma'
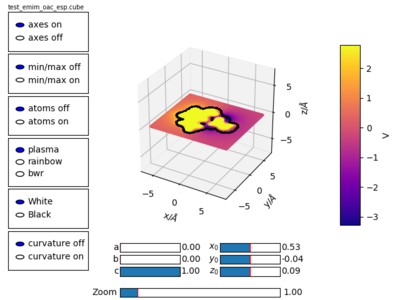
The resulting plot is shown in figure 4.
PlotHistogram
Required arguments
fpath(string) = path for a cube file
Optional arguments
factor(float, default=1) = factor by which to multiply the VdW radiibins(integer/None/string, default=30) = the number of bins in the histogram (see here for details)hist(boolean, default=True) = if True, it plots the histogram; if False, it does not plot the histogram (only the KDE)kde(boolean, default=True) = if True, it plots a gaussian kernel density estimate (KDE = a way to estimate the probability density function of a variable); if False, it does not plot the KDEnorm_freq(boolean, default=False) = if True, it plots a histogram with normalised frequency (without KDE, because the KDE has a normalised area, not normalised bin heights)norm_hist(boolean, default=True) = if True, it normalises the histogram (i.e. integral=1) - this happens by default for plots including KDEau(boolean, default=False) = if True, use atomic units (i.e. bohr for coordinates); if False, use Angstroms for coordinates andunitsfor valuesdensity(integer, default=1) = an integer number n which indicates that the number of points stored along each axis is reduced by the density value n (therefore the total number of points is reduced by n3)value_type(string, default='esp') = can be ‘esp’/’potential’ or ‘dens’/’density’ (or any uppercase version of the aforementioned); used in conjunction with the keywordsauandunitsin order to convert the values to the appropriate unitsunits(string, default=None) = the units to be used for the value; currently supports ‘V’ for ESP and ‘A’/‘angstrom’, ’nm’, ’pm’, ’m’ for density (or any lowercase/uppercase version of these). In the case of the density, the actual units are the specified units ^(-3). The keywordsvalue_typeandauoverrideunits. Ifauis True, the values will be in atomic units regardless of the value passed forunits. Ifvalue_typeis ‘dens’, the values will be read as density values even if theunitsargument has a valid ESP value (such as ‘V’). The default unit for ESP is V and for density 1/Å3.colour(string, default='rainbow') = colour scheme ('rainbow' by default, change it to 'bwr' for blue-white-red) - full list herecb_lim(list, default=None) = limits for the colour bar (list of two floats; if not specified, the limits will be the min and max of the values; if the limits do not cover the whole range of values, a warning is printed)

xlim(list, default=None) = x axis limitsylim(list, default=None) = y axis limitssave(boolean, default=True) = if True: ifhistis also True, a file <original_file_name>_hist.out is created, containing the bin edges values and the frequency for each bin as shown in the histogram; ifkdeis also True, a file <original_file_name>_kde.out is created, containing the range of values used for plotting the KDE and the corresponding KDE value. The file ends with two separate sections: peak values and minimum valuescat(boolean, default=False) = if True, it only plots the histogram and/or KDE for the points that correspond to the cation (the condition for which atoms belong to the cation has to be changed manually insideGetVdWPoints)an(boolean, default=False) = if True, it only plots the histogram and/or KDE for the points that correspond to the anion (the condition for which atoms belong to the cation has to be changed manually insideGetVdWPoints; the atoms belonging to the anion are the remaining ones)thickness(float, default=0.3) = represents the fractional thickness of the van der Waals surface (by default, the points that are within 0.3=30% of the surface defined by the van der Waals radii of the constituent atoms are selected as part of the van der Waals surface)log(boolean, default=True) = if True, it saves a .log file of the command used to run the functions (the command is tidied-up before saving i.e. unnecessary spaces are removed, argument values are converted to their usual uppercase/lowercase versions, file lists are explicit - instead of using wildcard symbols such as *)logfile(string, default=None) = the name of the log file (iflogis True); by default the file name is the input file name followed by the function namecb_sym(boolean, default=False) = if True, the colour bar limits are chosen to be symmetric around 0 (cb_lim, if specified, overridescb_sym)
Calls
ExtractData(fromReadCube.py)Axes(fromReadCube.py)ValuesAsDictionary(fromReadCube.py)GetVdWPoints(fromReadCube.py)
Observations
- if you only want to specify one limit for either of the axis, use None for the other (e.g. xlim=[None,3.5])
Example
python PlotCube.py PlotHistogram test_emim_oac_esp.cube
The resulting plot is shown in figure 5.
