MRD:wm814mrd
H+ H2 system
Dynamics from the Transition state region
The gradient of the potential surface at minimum and transition state are both zero. The minimum and transition state can be distinguished by second derivative. The minimum will have a positive value of second derivative. The transition state will have a negative second derivative.
(There is more than one direction to take the second derivatives in Tam10 (talk) 16:03, 8 June 2017 (BST))

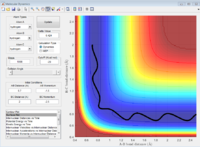
Trajectories form r1 =r2:locating the transition state
The estimated transition state position rts = 0.9077 At bond distance 0.9077, the internulear distance vs time diagram became a straight line, which means at that point, there was not vibration occur. Therefore transition state found.

Trajector from r1 = rts+δ, r2=rts
The difference between MEP and dynamics is that MEP set the velocity to zero at every steps. The momentum A-B atoms under dynamics calculation approached 2.5 but never reached 2.5. The momentum of B-C atoms under dynamics calculation vibrated. However, under MEP calculation, the momentum stayed constant.
(More importantly, the momentum is zero in the MEP Tam10 (talk) 16:03, 8 June 2017 (BST))


Trajector from r1 = rts, r2+δ=rts
When set r2+0.01, the sign has reversed with the same value.

Reactive and Unreactive Trajectories
There are two assumption made in the transition state theory. The first one is that atoms obey Newton' s law of motion. The second one is that there is enough energy for the reaction to cross transition state after collision.
(How does the rules about recrossing in transition state theory relate to this lab? Tam10 (talk) 16:03, 8 June 2017 (BST))
In this experiment, the collision angle is always 180 degrees, but in real life, this is not always. Thus the experiment results obtained in this lab is faster than real life experiment.
F-H-H System
PES inspection
When B-C bond was shorter, the energy was approximately -103.8Kcal/mol, this is the F-H2 case. When A-B bond was shorter, the energy was approximately -133.6Kcal/mol, this is the H-HF case. The energy when from high to low in the reaction, therefore the reaction is exothermic. As the forward reaction was exothermic, the backward reaction mush be endothermic.

Forwards Reaction energy barrier: 103.8-103.3=0.5 kcal/mol
Backwards Reaction energy barrier: 133.6-103.3= 30.3 Kcal/mol
(How did you get these values? Tam10 (talk) 16:03, 8 June 2017 (BST))

Reaction Dynamics
F-H2
When momentum between F-H was low (P=-0.5), changing the momentum of H-H do not dominate the results of reaction. i.e.sometimes reactive, sometime not. However, when the momentum of F-H was high (p=-0.8), even if the momentum of H-H was low (p=0.1), the reaction still occurred. From this, we can conclude that the momentum between H and F is what dominates the reaction.
(Be careful making conclusions with only 3 trajectories. These are empirical rules, which will be an average across many trajectories. Tam10 (talk) 16:03, 8 June 2017 (BST))
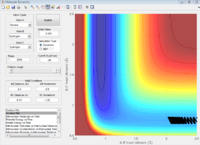


HF-H
When the momentum between H-F is high enough, no matter what values of H-H momentum, the reaction will still proceed. When the vibrational energy of H-F is high enough, the transnational energy of H does not matter. Therefor the momentum of H-F dominated the reaction
(You starting geometry is not inside the reactant channel - it has far too much potential energy as a result. Tam10 (talk) 16:03, 8 June 2017 (BST))


(A bit bare and missing some answers. Tam10 (talk) 16:03, 8 June 2017 (BST))