MODSNA17
All the calculations were made by using following settings in Gaussian:
Calculation Method: B3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
NH3
About the molecule
Name: Ammonia
Point group: C3v
N-H Bond distance : 1.01798 Å
H-N-H Bond angle : 105.741°
Final energy E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 a.u.
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986265D-10 Optimization completed.
Link to the *.log file: here
Link to the summary: here
Dynamic image
Ammonia |
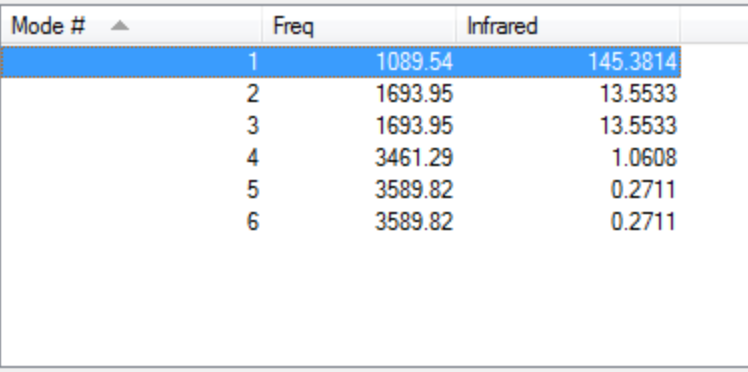
Vibrational modes
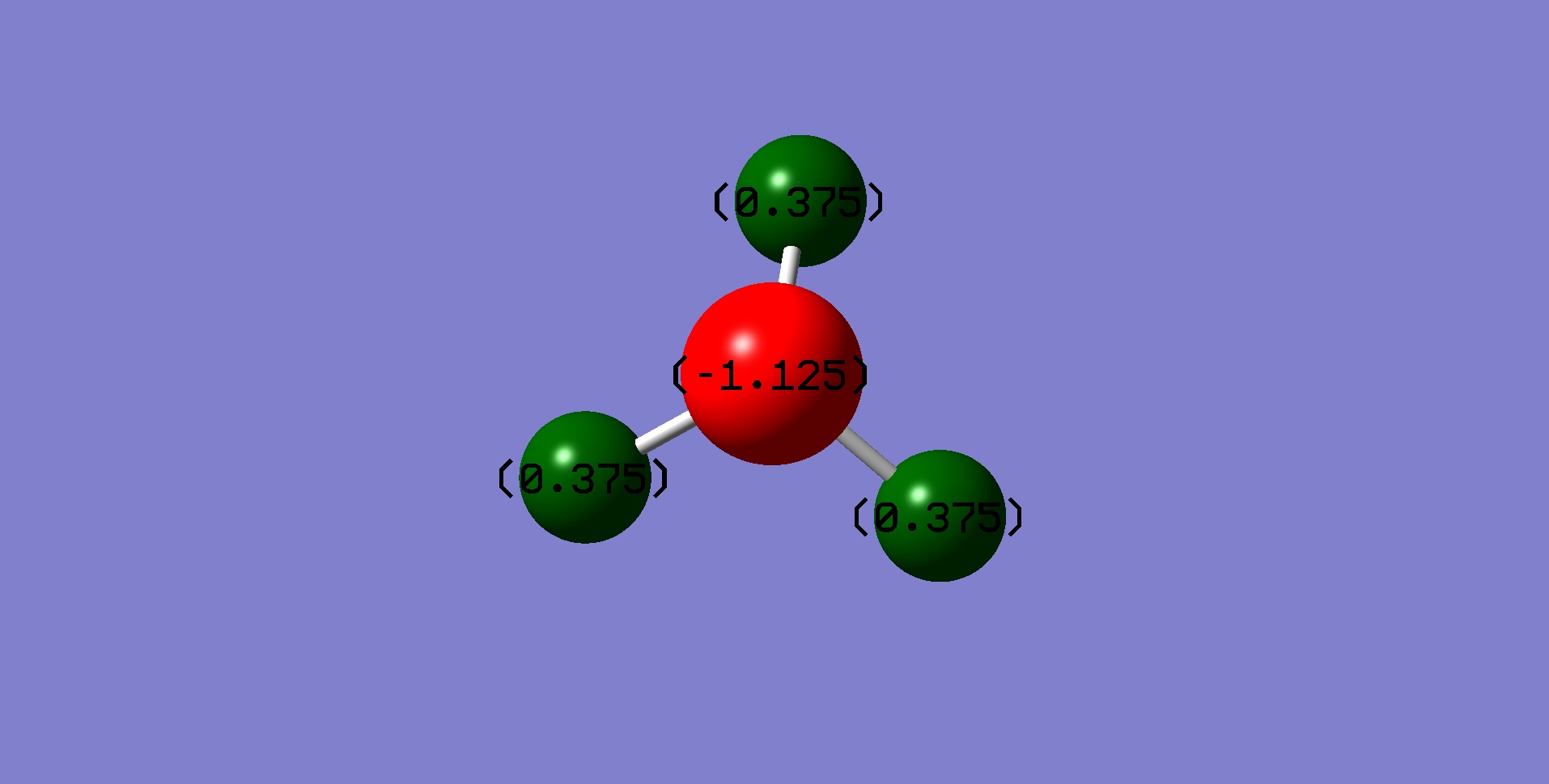
Charge distribution
Questions
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? - Since N=4 I would expect 6 modes
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? - Modes 2 and 3 and modes 5 and 6 seem to be degenerate.
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Bond Stretch: 1, 4, 5, 6 / Bending: 2, 3
Which mode is highly symmetric? - Mode 4 is highly symmetric.
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? - Mode 1 is known as the "umbrella" mode.
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? - I would expect 2 bands.
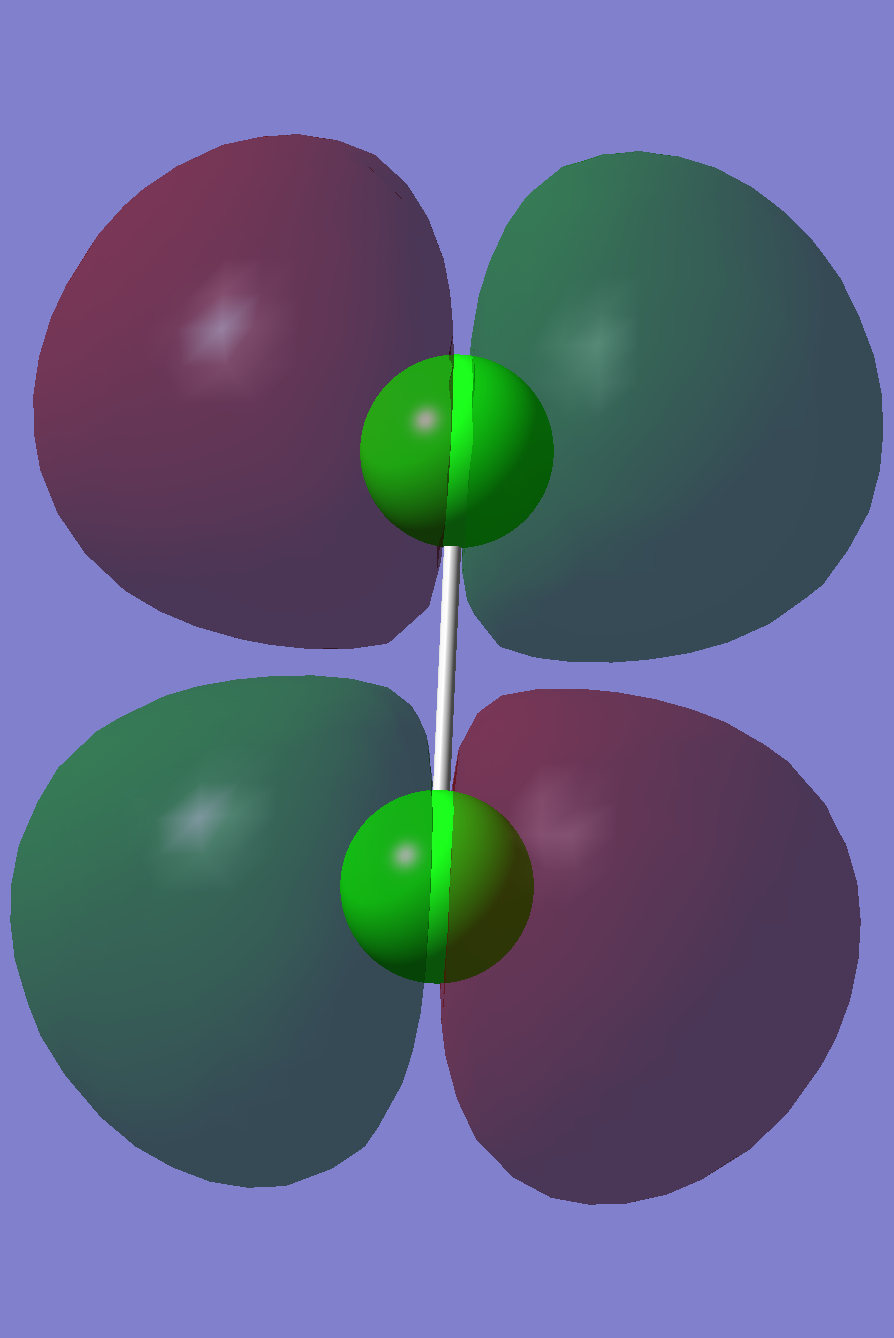
H2
About the molecule
Name: (Di-)Hydrogen
H-H bond length: 0.74279 Å
Point group: D∞h
Final energy E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936 a.u.
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
Link to the *.log file: here
Link to the summary: here
Dynamic image
Hydrogen |
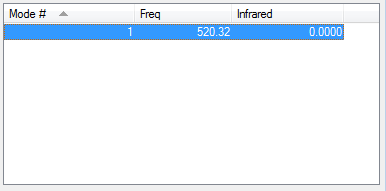
Vibrational modes
N2
About the molecule
Name: Nitrogen
N-N bond length: 1.1055 Å
Point group: D∞h
Final energy E(RB3LYP): -109.5241287 a.u.
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.401204D-13 Optimization completed.
Link to the *.log file: here
Link to the summary: here
Dynamic image
Nitrogen |
Vibrational modes
Question
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? N = 2 --> 1 mode expected
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? The mode is a “bond stretch” vibration
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous nitorgen? 0, as the vibration is symmetrical there is no change in dipole moment
Haber Bosch Reaction
The Haber-Bosch process is the industrial means by which nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas are converted to ammonia. Ammonia is crucially important as a fertilizer. The reason we can support so many people in a limited area is that almost all farms in the western world use fertilizers extensively. [1]
N2 + 3 H2 → 2 NH3
E(NH3) = -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3) = -113.11553746 a.u.
E(N2) = -109.52412867 a.u.
E(H2) = -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2) = -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE = 2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)] = -113.11553746 a.u. - [-109.52412867 a.u. + (-3.53561808 a.u.)] = -0.05579071 a.u.
ΔE = -146.478520263 kJ/mol
Cl2
About the molecule
Name: Chlorine
Cl-Cl bond length: 1.98Å
Point group: D∞h
Final energy E(RB3LYP): -920.3499 a.u.
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.277167D-09 Optimization completed.
Link to the *.log file: here
Link to the summary: here
Dynamic image
Chlorine |
Vibrational modes
Charge distribution
Molecular orbitals
All the orbitals shown are occupied.