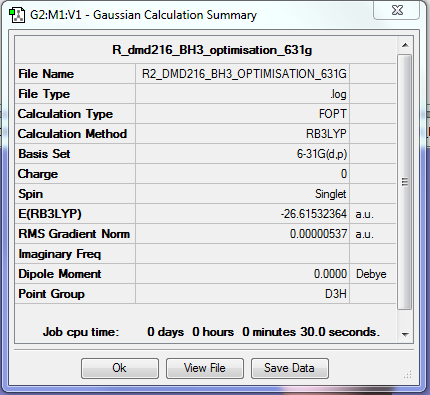
MMdmd216
BH3
Calculation Method/Basis Set = RB3LYP/6-31G Level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000011 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000007 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000043 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000028 0.001200 YES
Frequency Analysis Log File: DMD216_BH3_FREQ.LOG
Low frequencies --- -7.5936 -1.5614 -0.0055 0.6514 6.9319 7.1055 Low frequencies --- 1162.9677 1213.1634 1213.1661
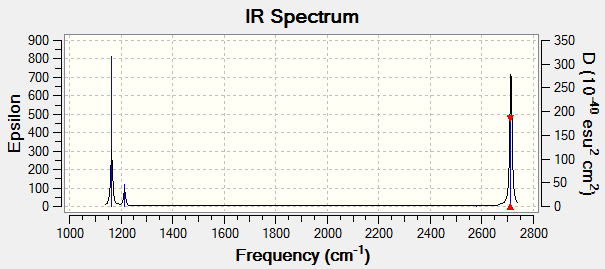
BH3 |
| wavenumber (cm-1 | Intensity (arbitrary units) | symmetry | IR active? | type |
| 1163 | 93 | A2" | yes | out-of-plane stretch |
| 1213 | 14 | E' | slight | bend |
| 1213 | 14 | E' | slight | bend |
| 2582 | 0 | A1' | no | symmetric stretch |
| 2716 | 126 | E' | yes | asymmetric stretch |
| 2715.6 | 126 | E' | yes | asymmetric stretch |
Although there are 6 vibrational modes of BH3, there are only 3 peaks in the IR spectrum. This is due to the two sets of E' modes being degenerate with wavenumbers of 1213 cm-1 and 2716 cm-1 so both sets only appear as one peak each. The third peak represents the A2" symmetry out of plane stretch at 1163 cm-1. Finally the A1' symmetric stretch with a wavenumber of 2582 cm-1 is not IR active due to no overall change in dipole moment.
Smf115 (talk) 18:20, 23 May 2018 (BST)Correct assignments of the symmetries and vibrational modes with a clear explaination of why only 3 peaks are seen in the spectrum.
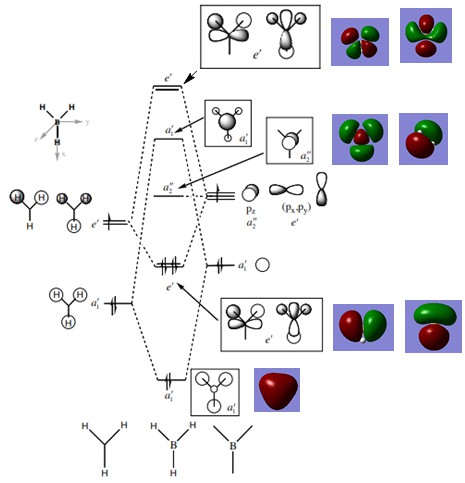
Molecular Orbital Diagram for BH3
Molecular orbital diagram was provided by Dr Tricia Hunt: http://www.huntresearchgroup.org.uk/teaching/teaching_comp_lab_year2a/Tut_MO_diagram_BH3.pdf
The LCAO molecular orbitals from the MO diagram are very similar to that of the computer-generated real MOs. There are not any significant differences between the real and LCAO MOs but rather there are huge similarities. For example, the a1' LCAO bonding and antibonding orbitals both resemble the real MOs as the predicted distributions match the computer-generated MOs. As shown by the MO diagram above, it can be seen that qualitative Mo theory is very accurate and useful as it allows us to predict real molecular orbitals accurately.
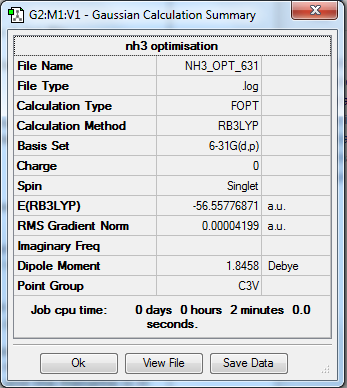
NH3
Calculation Method/Basis Set = RB3LYP/6-31G Level
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000060 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000040 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000369 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000162 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.259202D-08
Frequency Analysis Log File: DMD_NH3_FREQ.LOG
Low frequencies --- -32.4235 -32.4224 -11.4276 -0.0044 0.0115 0.0476 Low frequencies --- 1088.7628 1694.0251 1694.0251
NH3 |
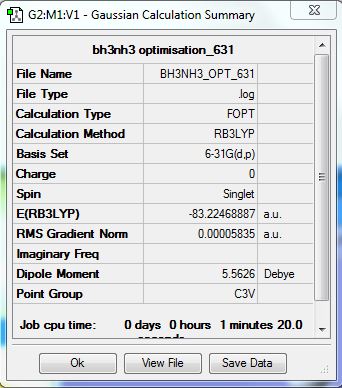
BH3NH3
Calculation Method/Basis Set = RB3LYP/6-31G Level
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000138 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000038 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000766 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000180 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.138823D-07
Frequency Analysis Log File: DMD_BH3NH3_FREQ.LOG
Low frequencies --- -0.1846 -0.0661 -0.0075 10.1601 16.5874 16.6021 Low frequencies --- 263.0277 631.3736 638.8694
NH3 |
| Molecule | Energy (a.u.) |
|---|---|
| NH3 | -26.61532 |
| BH3 | -56.55777 |
| BH3NH3 | -83.22169 |
ΔE=E(NH3BH3)-[E(NH3)+E(BH3)]
ΔE=-83.22169 - (-26.61532 + -56.55777)= -0.0486 a.u.= -127.59931 KJmol-1= Association energy
ΔE=(-26.61532 + -56.55777) - -83.22169= 0.0486 a.u.= 127.59931 KJmol-1= Dissociation energy
The B-N dative bond can be interpreted as weak when compared to common bonds such as a C-C bond or a C-H bond. The dissociation energies of the C-C bond and C-H bonds are 377 KJmol-1= and 439 KJmol-1= respectively.
C-C bond energy: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon%E2%80%93carbon_bond
C-H bond energy: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bond-dissociation_energy
Smf115 (talk) 18:22, 23 May 2018 (BST)Correct calcualtion and good comparison made to referenced bond dissociation energies. However, a slight mistake in the in the energy used for BH3NH3 meant the result was slightly off!
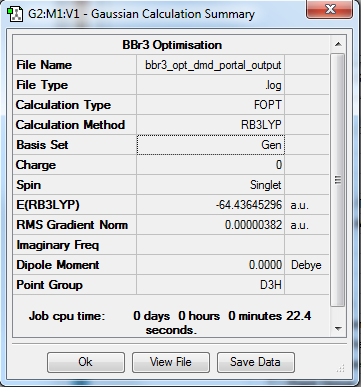
BBr3
Calculation Method/Basis Set = RB3LYP/6-31G Level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000008 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000005 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000036 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000023 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-4.027754D-10
Frequency Analysis Log File: Dmd_bbr3_freq_output.log
The frequency analysis can also be found at:
Low frequencies --- -0.0137 -0.0064 -0.0046 2.4315 2.4315 4.8421 Low frequencies --- 155.9631 155.9651 267.7052
BBr3 |
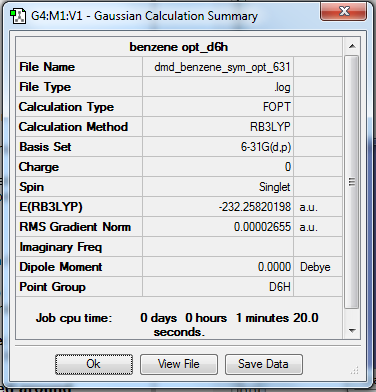
Benzene
Calculation Method/Basis Set = RB3LYP/6-31G Level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000045 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000016 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000097 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000036 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.579830D-08
Frequency Analysis Log File: DMD_BENZENE_FREQ.LOG
Low frequencies --- -0.0088 -0.0043 -0.0042 12.5838 12.5838 16.4940 Low frequencies --- 414.3526 414.3526 621.2606
Benzene |
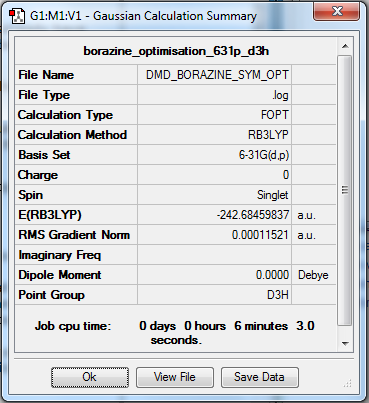
Borazine
RB3LYP/6-31G Level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000121 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000052 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000474 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000175 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.227538D-07
Frequency Analysis Log File: DMD_BORAZINE_FREQ.LOG
Low frequencies --- -9.3558 -9.1151 -8.8680 -0.0103 -0.0087 0.1131 Low frequencies --- 289.2481 289.2567 404.1641
Borazine |
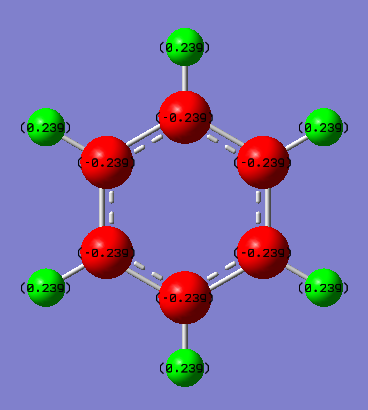
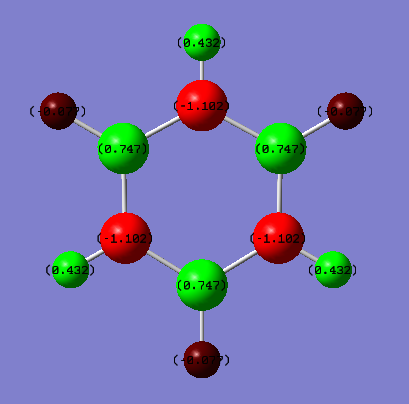
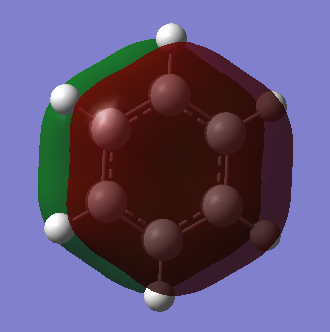
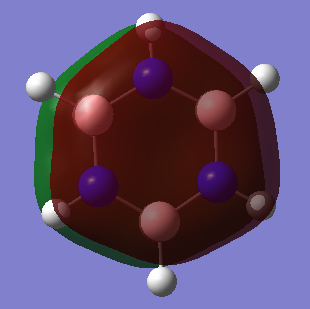
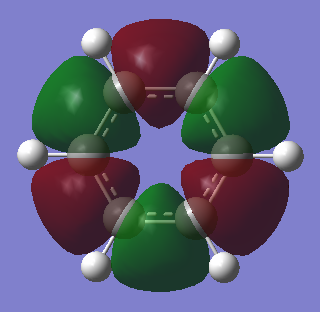
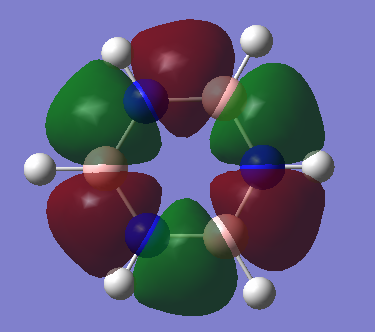
Benzene vs Borazine Charge Analysis
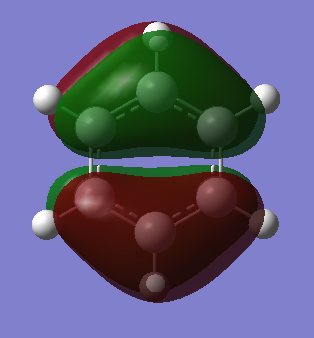
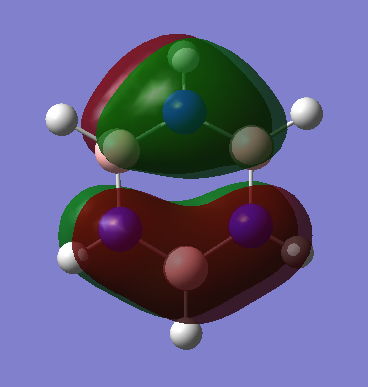
Molecular Orbitals of Benzene and Borazine
Smf115 (talk) 18:12, 23 May 2018 (BST)Nice comparison of the MOs, however it could have been developed further by mentioning the actual symmetry of the orbitals for example. Energies are also not comparable between the molecules, only the relative ordering, and MO 14 and 15 are actually bonding orbitals which can be seen by considering the contributing AOs and position of the nodes.
The Concept of Aromaticity
The basic understanding of aromaticity is given by Huckel's rules:
There must be 4n + 2 pi electrons, where n is 0, 1, 2... The molecule must be planar. The molecule must be cyclic. There must be a continuous ring of p orbitals perpendicular to the plane.
Huckel's rules can be used for predicting whether a simple molecule is aromatic or not. Usual aromatic properties are double bonds which do not undergo electrophilic addition and are generally usually unreactive, the aromaticity providing extra stability. Higher aromatic systems also have stronger ring currents resulting in dramatic shielding and deshielding.
Aromaticity is not restricted to hydrocarbons which can be seen in inorganic compounds such as borazine. Huckel's rule struggles to identify aromaticity in more complex molecules. For example, aromaticity has been applied to systems such as polyhedral boranes, metallobenzenes and spherical systems such as fullerenes. Molecules that would be usually anti-aromatic can twist to a conformation that allows p-orbitals to interact. This shows the concept of overlapping pz AOs are not exactly a good description for aromaticity as even molecules like fullerenes can have aromaticity applied to their system. There are also compounds that adopt hybridization states that do not have a contiguous cyclic array of P orbitals such as the cyclopropenyl anion.
LCAO can be used in molecular orbital diagrams to portray the basic concepts of aromaticity. Generally, it is very accurate - real computer-generated MOs from GaussView generally match the predicted MOs from LCAO; the only major differences being GaussView taking into account electronegativity to generate some polarised lobes as seen in borazine. Aromatic molecules can tend to have very high symmetries and when these symmetries begin to distort slightly, LCAO is not a good method to use to visualise MOs and so GaussView is the better option as it can produce real MOs.
Although pi electron delocalisation has been used as a measure of aromaticity, sigma electron bonding structure has become of importance in investigating aromaticity. Total electron energy computed in the ring critical point could serve as a new and easily estimated quantitative method of pi electron delocalisation. This is reported in: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/chem.200700250
Smf115 (talk) 18:18, 23 May 2018 (BST)Good discussion with examples used well to contradict the key concepts, however, these needed to be referenced from the literature! To improve, consider how the MOs visualised contribute to the delocalistion of the electron density and the idea of sigma-aromaticity rather than just how they compare to the LCAO approach.
Smf115 (talk) 18:18, 23 May 2018 (BST)Overall a decent wiki report with a very good first section.