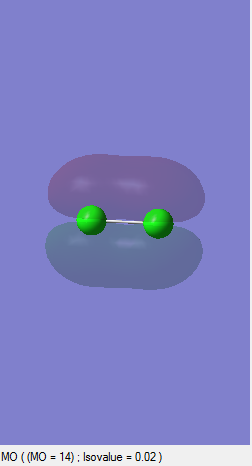
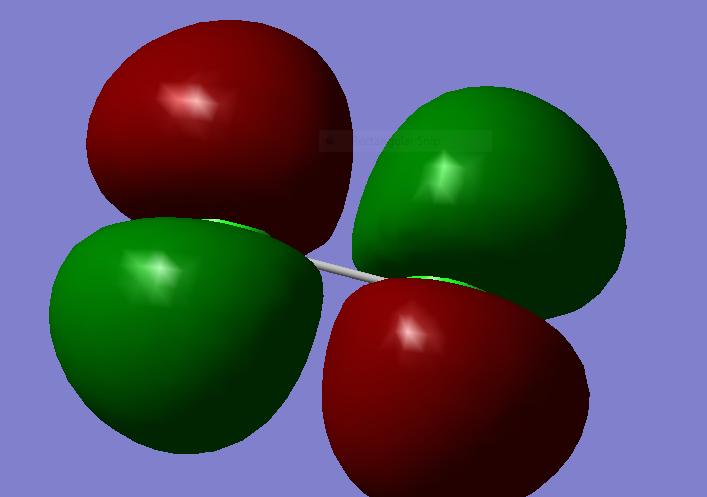
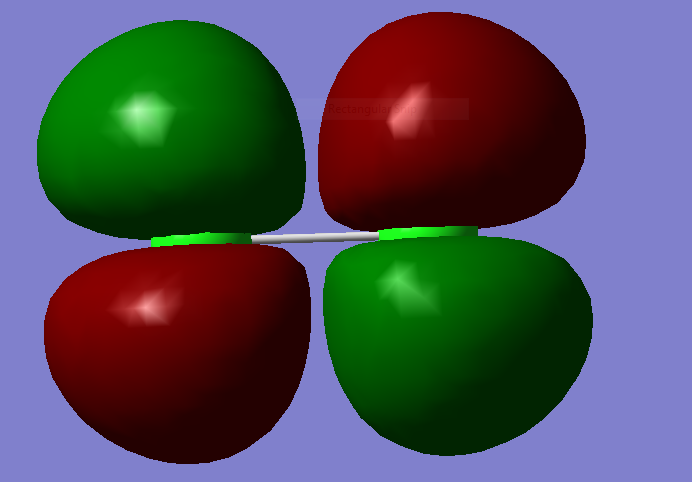
MM2
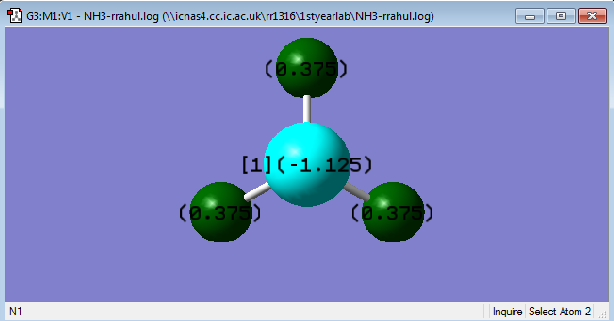
NH3
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
calculation method: RB3LYP
point group: C3V
RMS Gradient Norm:0.00000485 a.u
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986276D-10 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
NH3 molecule |
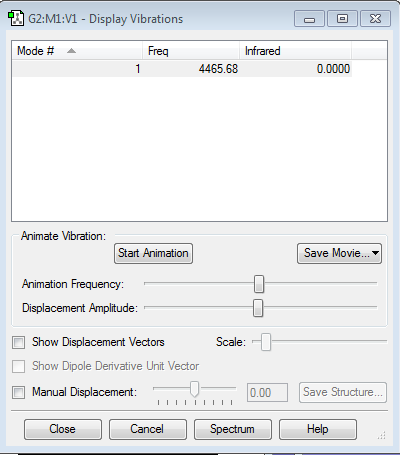
The first is a wagging bending; this is the umbrella mode. The second and third are scissoring bending and degenerate. This is shown by the bending having the same frequency and infrared absorption values. The fourth is a symmetric stretching. The fifth and sixth one are both an asymmetric stretch. there are 4 bands in the IR spectrum.
The nitrogen is more electronegative than the hydrogen. Hence the negative charge on the nitrogen. The negative charges cancel out the 3 positive charges on the hydrogen this shows it is correct.
H2
Calculation Method:RB3LYP
Basis set:6-31G(d,p)
Point Group:D*H
RMS Gradient Norm:0.00000017 a.u.
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.164081D-13 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
HYDROGEN MOLECULE |
Since they are two identical hydrogen molecules there is no net charge.
N2
Calculation Method:RB3LYP
Basis Set:6-31G(d,p)
RMS Gradient Norm:0.00000060 a.u.
Point Group:D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.400959D-13 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
NITROGEN MOLECULE |
Due to the identical nature of the nitrogen atoms each they both have a net charge of zero.
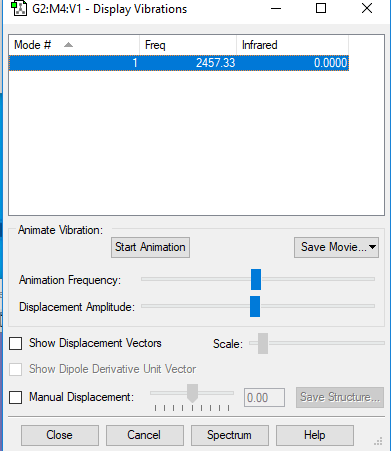
NH3 enthapy of formation
E(NH3)=-56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)=-113.1155374 a.u.
E(N2)=-109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)=-1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-146.47848285 kj/mol
The product is more stable because it is exothermic reaction: energy is released from the reaction. The products are of a lower energy level and so are more stable.
Chlorine
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set:6-31G(d,p)
RMS Gradient Norm:0.00002510
2s orbital that do not contribute to bonding.
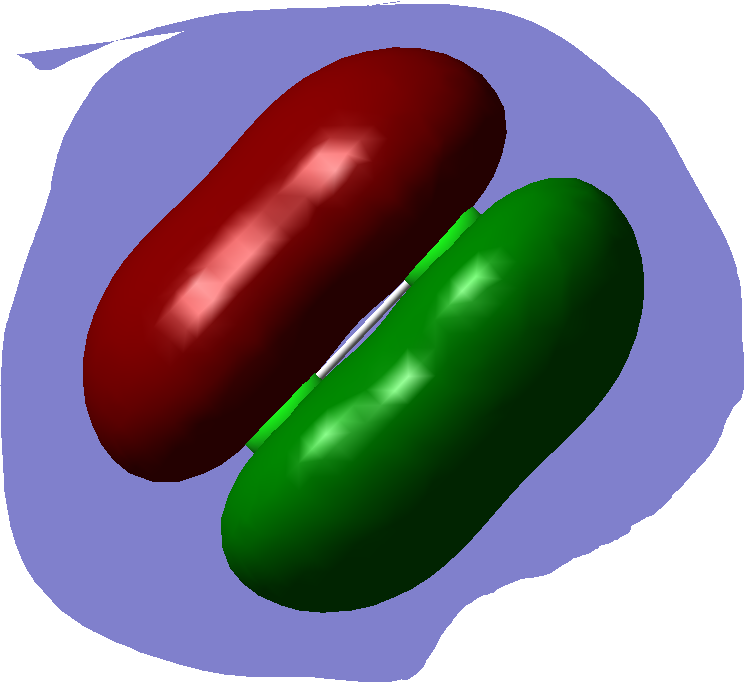
2p pi bonding
this is another 2p pi bond: this is a degenerate bond to the one above.
this is an antibonding orbital. That is a sigma bond.
this is a antibonding orbital that is degenerate immediately above.