Jerzypilipczuk
Appearance
NH3
| Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| More Info | |||||
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP | ||||
| Basic Set | 6-31G(d,p) | ||||
| Final Energy | -56.55776873 | ||||
| Point Group | C3v | ||||
| N-H Bond Length | 1.01798 | ||||
| H-N-H Bond Angle | 105.74116 | ||||
| Optimisation File | Link | ||||
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000070 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000033 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.785191D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Questions
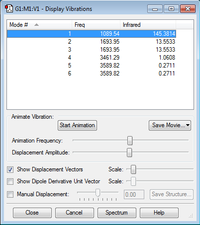
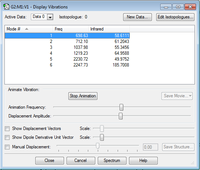
-How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 3 modes -Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? 2 and 3, 5 and 6 -Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? Bend: 1, 2 and 3. Stretch: 4, 5 and 6. -Which mode is highly symmetric? Mode 5. Symmetric stretch of H atoms around N. -One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? Mode 1. symmetric bend of H atoms about N. -How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 2 bands. 2 asymmetric modes which produce dipoles.
N2
| Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| More Info | |||||
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP | ||||
| Basic Set | 6-31G(d,p) | ||||
| Final Energy | -109.52412868 | ||||
| Point Group | Dinf | ||||
| Optimisation File | Link | ||||
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-7.296120D-14
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
H2

| Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| More Info | |||||
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP | ||||
| Basic Set | 6-31G(d,p) | ||||
| Final Energy | -1.17853934 | ||||
| Point Group | Dinf | ||||
| Optimisation File | Link | ||||
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000130 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000130 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000171 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000241 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.130914D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Energy Calculations
E(NH3)= -56.557768 2*E(NH3)=-113.115537 E(N2)=-109.524128 E(H2)=-1.178539 3*E(H2)=-3.535618 ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-297131.344823
H2SiO
| Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| More Info | |||||
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP | ||||
| Basic Set | 6-31G(d,p) | ||||
| Final Energy | -365.90001403 | ||||
| Point Group | Cs | ||||
| H-Si Bond Length | 1.48652 | ||||
| O-Si Bond Length | 1.53172 | ||||
| Optimisation File | Link | ||||
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000023 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000009 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000025 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000018 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.357805D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.