Jc6116
NH3 molecule
property of NH3
bond length of N-H is 1.01798 Angstrom
Bond angle of NH3 is 105.741 degrees
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986277D-10 Optimization completed.
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000485 a.u |
| final energy E(RB3LYP) | -56.55776873 a.u |
| Point Group | C3V |
NH3 molecule |
Media:JIANCHEN_NH3_OPTF_POP.LOG
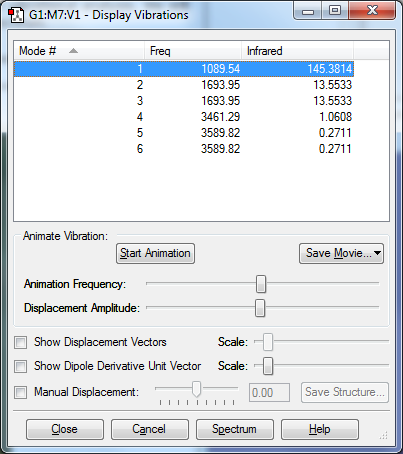
vibration of NH3 molecule
there are 6 type of vibration of NH3.
The mode 2 and mode 3 have same bending frequency at 1693.95 cm-1. The mode 5 and mode 6 have same stretching frequency at 3589.82 cm-1.Thus, there are degenerate.
The mode 1, mode 2 and mode 3 are bending vibration and mode 4, mode 5 and mode 6 are bond stretch vibration.
The mode 1 and mode 4 are the symmetrical vibration. The mode 1 is the umbrella mode.
There are 4 different energy levels in the vibration mode. Therefore, there 4 bands in the vibration spectrum.
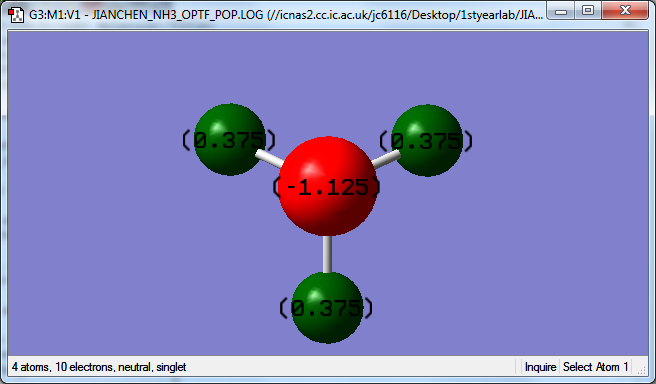
atomic charges of NH3 molecule
The Nitrogen has -1.125 charges and Hydrogen has +0.375 charges
The Nitrogen has higher electronegativity than Hydrogen. Thus, the Nitrogen withdraw electron density from Hydrogen.
H2
property of H2
bond length of H-H is 0.74247 Angstrom
The H2 is a linear molecular, which the bond angle is 180 degrees.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000232 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000232 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000305 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000431 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-7.091616D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00013423 a.u |
| final energy E(RB3LYP) | -1.17853929 a.u |
| Point Group | D*h |
H2 molecule |
Media:JIANCHEN_H2_OPTF_POP.LOG
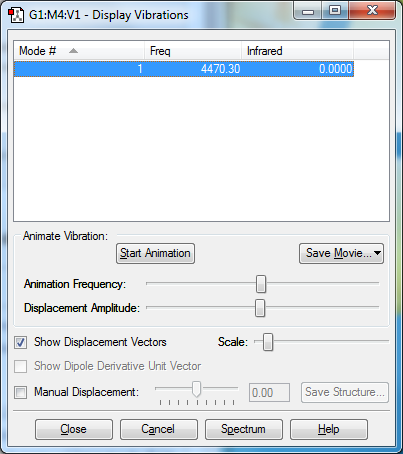
vibration of H2
There is only one symmetrical vibration in the H2 molecule at 4470.30cm-1. There are no band in the infra red.
atmoic charges of H2
There is no charges between two hydrogen atoms due to the same electronegativity of two same atoms.
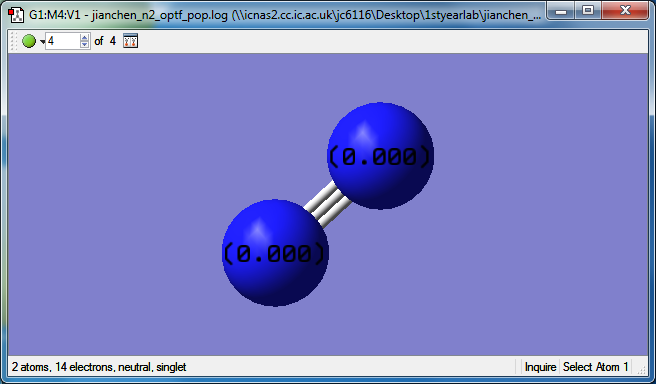
N2 molecule
property of N2 molecule
bond length of N-N is 1.10555 Angstrom
The N2 is a linear molecular, which the bond angle is 180 degrees.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986277D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00008380 a.u |
| final energy E(RB3LYP) | -109.52412867 a.u |
| Point Group | D*h |
N2 molecule |
Media:JIANCHEN_N2_OPTF_POP.LOG
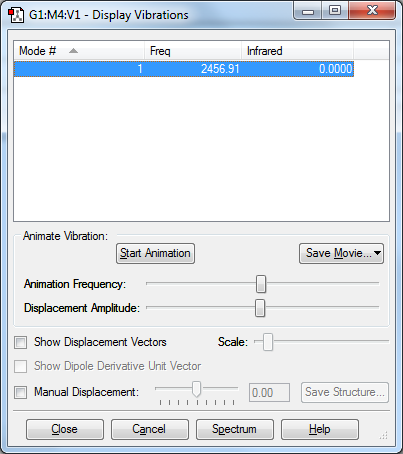
vibration of N2
There is only one symmetrical vibration occur at 2456.91cm-1. There are no band in the infra red.
atomic charges of N2
There is no charge difference between two same atoms dur to the same electronegativity
Reaction energy of Haber Process
Haber Process is N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -148492.4331122 KJ/mol
2*E(NH3)= -296984.8662KJ/mol
E(N2)= -287555.62172791 KJ/mol
E(H2)= -3094.2551416 KJ/mol
3*E(H2)= -9282.765425 KJ/mol
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2</sub)+3*E(H2)]=-296984.8662 + 296838.38715291 = -146.48 KJ/mol
The enthalpy of the reaction is exothermic. Thus, the ammoina product is more stable than the gaseous product.[1]
CH4
property of CH4 molecule
bond length of C-H is 1.09179 Angstrom
The bong angle of C-H-C is 109.471 degrees
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000057 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000030 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000161 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000086 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.829380D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00002940 a.u |
| final energy E(RB3LYP) | -40.52401404 a.u |
| Point Group | Td |
CH4 molecule |
Media:JIANCHEN_CH4_OPTF_POP.LOG
vibration of CH4molecule
There are 9 modes of the vibration in the CH4molecule.
However, mode1, mode2 and mode3 are degenerate due to the same frequency at 1355.84cm-1. Mode1, mode2, mode3, mode4 and mode5 is bending vibration.
Mode6, mode7, mode8 and mode9 is streching vibration.
Moreoer, mode4 and mode5 are degenerate, which have the same vibration frequency at 1578.46cm-1 and mode7, mode8 and mode 9 are degenerate, which have same viation frequnecy at 3163.98cm-1.
Mode4, mode5 and mode6 are the symmetrical vibration that do not form the dipole moments. There are only 2 band will be showed on the infra red.
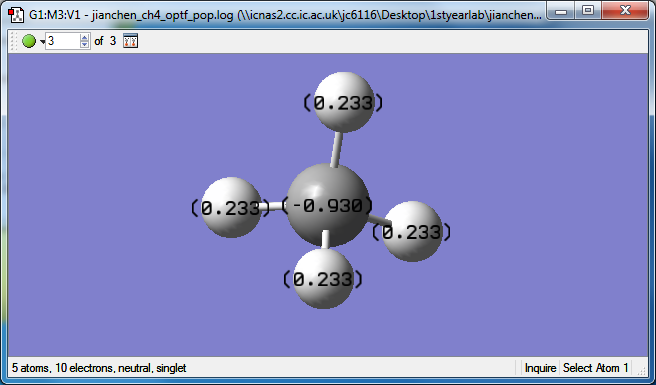
atomic charges of CH4molecule
The charges on the carbon is -0.930 this is because the electronegativity of carbon (2.55) is sightly higher then Hydrogen (2.2). Thus, the charges on Hydrogen is +0.233.
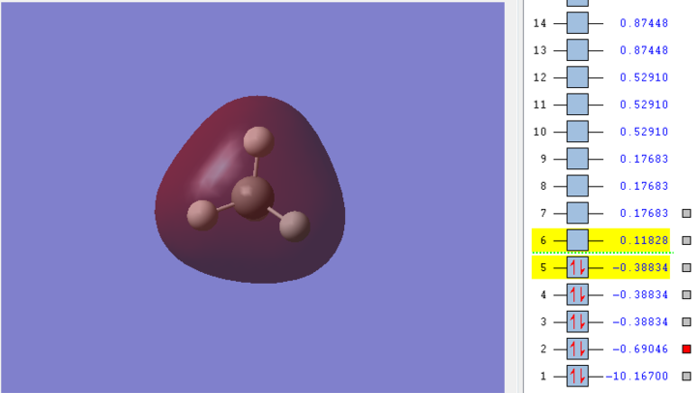
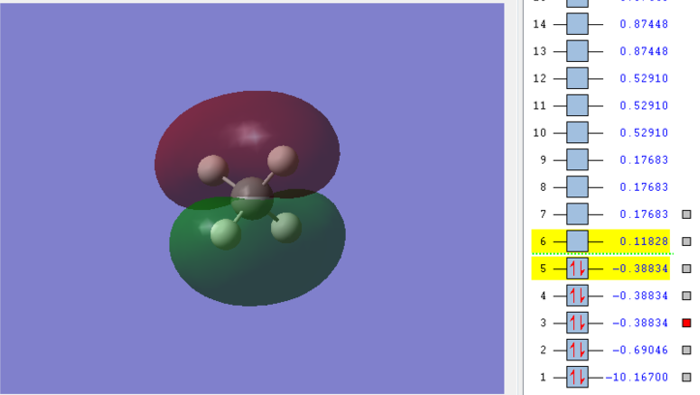
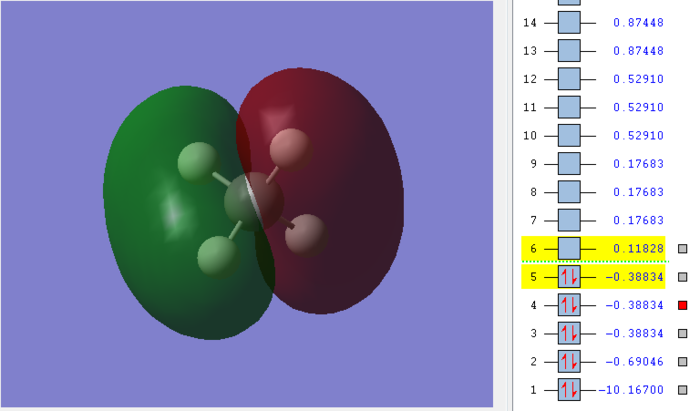
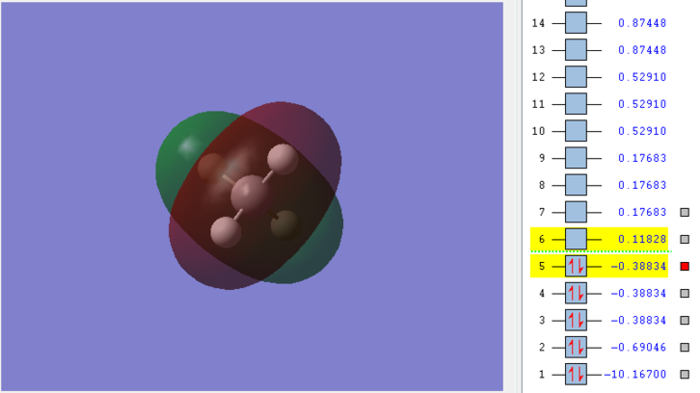
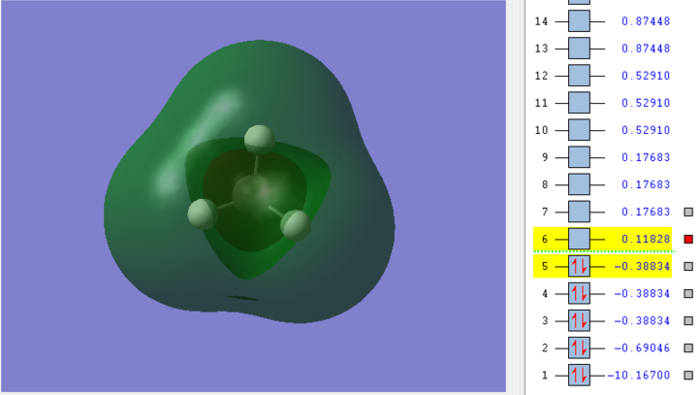
Molecular orbital of CH4molecule
Reference
- ↑ http://www.chemguide.co.uk/physical/equilibria/haber.html (Accessed March 2018)