JNPage1
NH3 Molecule
N-H bond length = 1.01798 Å
H-N-H bond angle = 105.741°
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986299D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Calculation method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d.p) Final Energy -56.55776873 a.u. RMS Gradient 0.00000485 a.u. Point group C3V Optimised bond angle 105.741 Optimised bond length 1.01798 Å
File:JNEWINGTON NH3 OPTF POP.log
NH3 molecule |
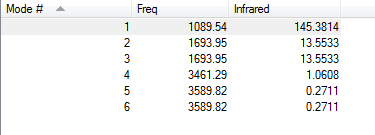
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
(3*4)-6 = 6 modes
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
Modes 2 and 3 are a degenerate pair, as well as modes 5 and 6.
which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
1, 2, and 3 are bending. 4, 5, and 6 are stretching.
which mode is highly symmetric?
Mode 4 is the most highly symmetric.
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
Mode 1 as it looks like opening an umbrella.
how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
2 bands
You would expect a more negative charge distribution around Nitrogen as it is a more electronegative atom.
Charge Distribution: N: -1.125 H: +0.375
H2 molecule
Calculation method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d.p) Final Energy -1.17853936 a.u. RMS Gradient 0.00000017 a.u. Point group D∞h Optimised bond angle 180 Optimised bond length 0.74279 Å
File:JNEWINGTON H2 OPTF POP.LOG
H2 molecule |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Vibration 4465.68
N2 Molecule
Calculation method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d.p) Final Energy -109.52412868 a.u. RMS Gradient 0.00000020 a.u. Point group D∞h Optimised bond angle 180 Optimised bond length 1.10550 Å
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.582737D-14
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Vibration 2457.33
File:JNEWINGTON N2 OPTF POP.LOG
N2 molecule |
Converting N2 and H2 into NH3
E(NH3) = -56.55776873 2*E(NH3) = -113.11553746 E(N2) = -109.52412868 E(H2) = -1.17853936 3*E(H2) = -3.53561808 ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -113.11553746 + 109.52412868 + 3.53561808 = -0.0557907 a.u. - -0.0557907 a.u. = -146.478494kJ/mol
The gaseous product is more stable than reactants. This figure is far off from one found in the literature* of -45.93kJ/mol this can be explained due to the fact that they are calculated under different conditions.
- J. Chem. Soc., Trans., 1903,83, 1168-1184
DOI: 10.1039/CT9038301168
F2 Molecule
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.995024D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.4028 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Calculation method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d.p) Final Energy -199.49825218 a.u. RMS Gradient 0.00007365 a.u. Point group D∞h Optimised bond angle 180 Optimised bond length 1.40281 Å
Literature** cites the bond lenght to be 1.417 Å. This is very close to my value.
Vibration 1065.09
Charge Distribution 0
File:JNEWINGTON F2 OPTF POP.LOG
F2 molecule |
1s and 1s. Energy of -24.79730 a.u. No overlap of atomic orbitals so non-bonding. This is a very deep core molecular orbital
2s and 2s sigma bonding orbital. Energy of -1.33659 a.u.
2s and 2s sigma* antibonding orbital. Energy of -1.09047 a.u.
2p and 2p head on sigma overlap bonding orbital. Energy of -0.58753 a.u.
2p and 2p side on pi overlap bonding orbital. Energy of -0.52332 a.u. This is parallel to the plane of the bond.