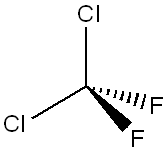
It:dichlorodifluromethane
Introduction
Dichlorodifluoromethane is a colorless, nonflammable gas with almost no odor (ether-like odor at extremely high concentrations).It is used as a refrigerant gas, an aerosol propellant, in plastics, and as a leak detecting agent until its manufacture was discontinued in 1995, due to concerns about damage to the ozone layer. The ozone depletion potential of R-12 is 0.82, which is relatively high.
History
The Major use of dichlorodifluoromethane is as a refrigerant gas. Refrigerants like sulfur dioxide and methyl chloride (used in early days when refrigerators were invented) were causing people to die. Ammonia had an equally serious toxic effect if it leaked. Refrigeration engineers searched for acceptable substitutes until the 1920s, when a number of synthetic refrigerants called halocarbons or CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) were developed by Frigidaire. The best known of these substances was patented under the brand name of Freon. Chemically, Freon was created by the substitution of two chlorine and two fluorine atoms for the four hydrogen atoms in methane (CH4); the result, dichlorodifluoromethane (CCl2F2), is odourless and is toxic only in extremely large doses.
Synthesis of Dichlorodifluoromethane
Laboratory:
CCl4 + HF → CFCl3 + CCl2F2 + HCl (Catalyst: SbF3Cl2)
Industry:
HF(g) + CCl4 → CCl3F + CCl2F2 + CClF3 (Carbon catalyst)
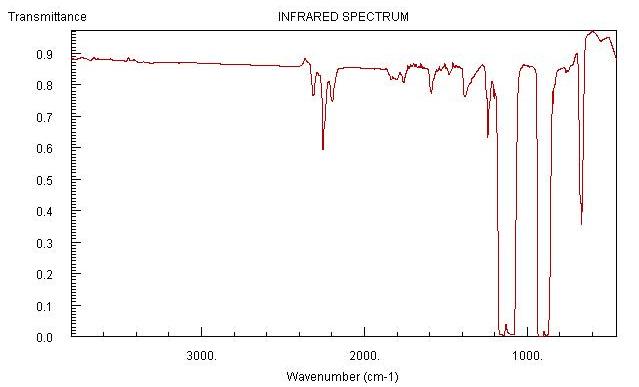
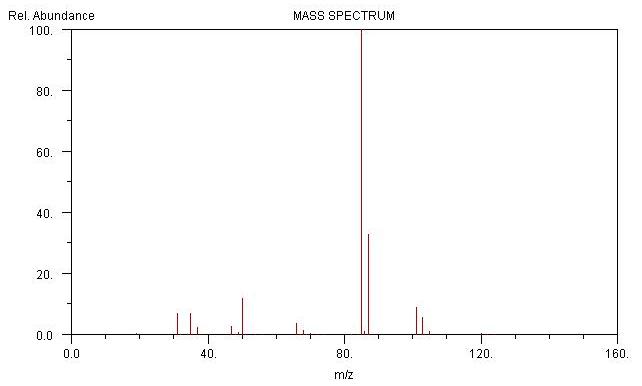
Spectrums of Dichlorodifluoromethane
Hazard
- Dichlorodifluoromethane can affect you when breathed in.
- Contact with the liquid can cause cracking anf drying of the skin, and may cause frostbite.
- Dichlorodifluoromethane can cause eye irritation and severe eye pain.
- Breathing the gas can irritate the mouth, nose and throat.
- Exposure to high concentrations of the gas can cause the heart to beat irregularly or to stop. This can cause death.
- Exposure can cause dizziness, light-headedness, and trouble with concentration.
Reference
1. http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=75-71-8&Type=IR-SPEC&Index=QUANT-IR,0#IR-SPEC
2. http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C75718&Mask=200#Mass-Spec