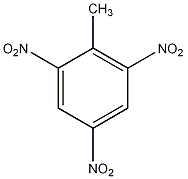
It:TNT
TNT is the acronym for the explosive chemical with the common name trinitrotoluene. Its IUPAC name is 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene and it has the chemical formula C7H5N3O6.
Trinitrotoluene is a high explosive that is immune to ordinary shocks and so it must be set off by a detonator. This makes it relatively safe and so it is commonly used in construction and also as weaponry.
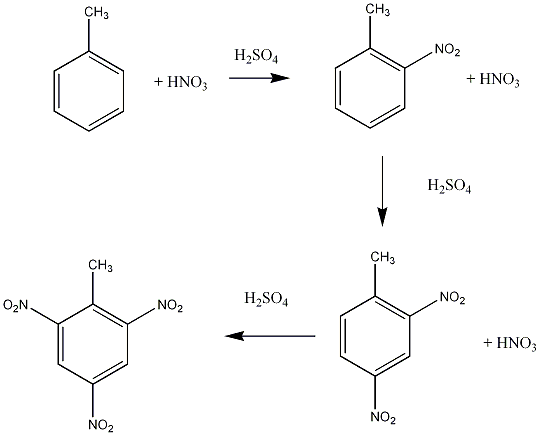
Trinitrotoluene was invented by Joseph Wilbrand in 1863. The nitration of toluene is a simple method of synthesising trinitrotoluene in the laboratory.
Structure and properties
Trinitrotoluene is in the form of long yellow crystals.
It has a melting point of 80.35°C.
It has a density of 1.654g/cm3.
It has a molar mass of 227.131 g/mol.
 The big explosion picture is from http://www.hnd.usace.army.mil/pao/CEAInfo/
The big explosion picture is from http://www.hnd.usace.army.mil/pao/CEAInfo/
Synthesis of TNT
Trinitrotoluene can be synthesised by the stepwise nitration of toluene involving a primary, secondary and tertiary nitration.
Mechanism
The reaction is known as an electrophilic addition reaction. The nitric acid is initially activated by the sulphuric acid, and the two react to give a species known as the nitroneum ion. This species is then added to the toluene.