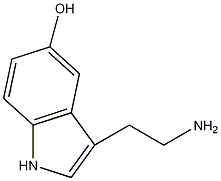
It:Serotonin
What is Serotonin
- Serotonin is a hormone manufactured by the brain that is associated with opiate-specific receptors - so helps maintain a happy feeling.
- It is a neurotransmitter which means that it is a chemical messenger in the brain, which allows the brain to communicate with nerve cells.
- An effective way of increasing serotonin levels is vigorous exercise, as in the case of mild depression. This exercise increases the levels for many days after the exercise takes place.
- Your diet will also effect the levels of serotonin. Low levels of omega 3 and vitamin C in the diet will cause a reduction in the amount of serotonin in the body.
What Does Serotonin Do
Serotonin affects many basic psychological functions such as anxiety mechanisms and the regulation of mood, thoughts, aggression, appetite, sex drive and the sleep/wake cycle. Multiple observations suggest that serotonin, which is one of the more abundant neurotransmitters, plays an important role in the regulation of mood and a key role in the treatment of depression.
Due to this, lack of serotonin is often associated with depression. Restoring the normal or enhanced level of this neurotransmitter acts as mood enhancer. Prozac is a mood enhancing drug, which acts in the central nervous system by inhibiting the re-uptake mechanism of serotonin into the synapse. The synapse is a junction where a signal is transmitted from one nerve cell to another. Since serotonin is not degraded in the synaptic cleft, Prozac promotes a prolonged presence of serotonin keeping the post-synaptic membrane active.
In the central nervous system, serotonin is involved in fear and "flight" responses, an activity which is opposed by the aggression or "fight" stimulating hormone adrenaline (epinephrine) and neurotransmitter dopamine.
Light modulates the production of certain hormones and brain chemicals including serotonin. The amount of serotonin in your brain reflects the amount of light in your environment. More light = more serotonin = more energy, a better mood, and fewer carbohydrate cravings.
Serotonin in our bodies
Serotonin originates in neurons deep in the midline of the brainstem. Because these neurons profile diffusely throughout the brain, serotonin can affect various brain functions, such as depression. It also interacts with many other neurotransmitters, either directly through neurons that use both serotonin and another neurotransmitter, or by serotonin neurons influencing neurons that primarily use these other transmitters.
Serotonin can be found in three main areas of the body: the intestinal wall, blood vessels, and the central nervous system.
Sources of Serotonin
- It is manufactured in the human brain using the essential amino acid tryptophan which is found in pineapples, plums, turkey and milk.
- Bananas also contain tryptophan, which the body converts into serotonin, known to make you relax, improve your mood and generally make you feel happier.
- Tryptophan is also found in chocolate, again causing the release of serotonin; which is often why it is eaten as a comfort food.
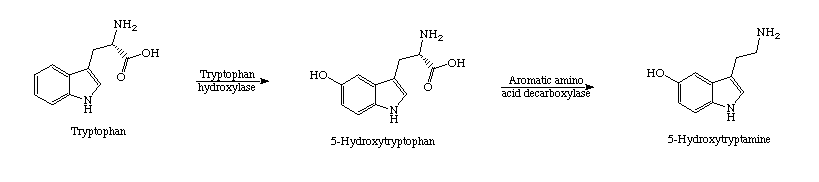
Synthesis of Serotonin
Serotonin is synthesized from the amino acid precursor tryptophan, packaged into vesicles, and released into the synapse following an action potential. Once in the synapse, serotonin can interact with both the pre- and postsynaptic receptors.
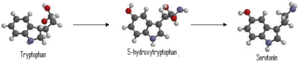
Detail of Synthesis:
Images of Serotonin
| Electron Density of Serotonin | Electrostatic Potential of Serotonin |
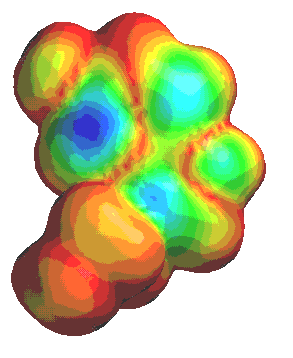
|
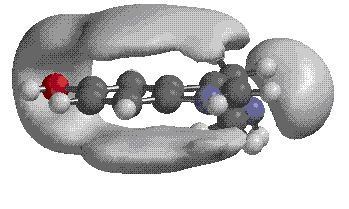
|
| Electron density is the measure of the probability of an
electron being present at a specific location. |
Electrostatic potential is used to describe the potential energy associated
with a charge distribution. It provides a visual method to understand the relative polarity of a molecule. |
Serotonin: Interesting Thoughts
- Studies show that there is a chemical hierarchy in humans associated with social "rank" that is linked with serotonin levels. Those in high office, higher positions on sports teams and those of higher rank in academic clubs have been found to have higher levels of serotonin than their lower ranking peers. [3]
- Serotonergic activity gradually decreases as one becomes drowsy and enters slow-wave sleep. An overall slowing of serotonergic activity is observed during slow-wave sleep known as non-REM sleep. During REM sleep (Rapid Eye Movement-the original dream sleep), serotonergic activity falls completely silent. Serotonergic activity returns to its basic level several seconds prior to the end of REM sleep. [4]
- The stimulant in the drug Ecstasy forces the brain to release serotonin, in abnormally large amounts. The neurons (brain cells) that store serotonin are deformed or destroyed. Scientists have found that these injured neurons can regrow, but they may grow back abnormally or in the wrong locations. When Ecstasy wears off, the overflow of serotonin reverses to a lack of serotonin. Without enough serotonin it is difficult to sleep, learn, remember, or feel happy. [5]
- When UV light interacts with your skin, it triggers the formation of vitamin D. Vitamin D stimulates the production of feel-good brain chemicals such as serotonin and dopamine.
- The light that enters your eyes has an immediate effect on your mood, so bright light- especially blue light (around the wavelength 460 nm) shuts down the production of melatonin, the night-time sleep hormone, and stimulates the production of serotonin, its energising, daytime counterpart.
References
- Healthscout- What does Serotonin do?
- University of Bristol: Chemistry- Synthesis of Serotonin
- MBC Serotonin- Detail of Synthesis
- CMSTE- Images of Serotonin
- Serotonin- What does Serotonin do?
- Body Blues- What does Serotonin do?
- [Belstein (2006/03]- Properties