It:Ranitidine
| Structure of Ranitidine | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
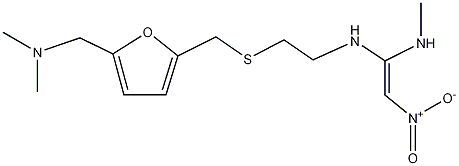
| ||||
| 3D structure | ||||
| CA Index Name | Ranitidine,
(E)-N-(2-((5-((dimethylaminomethyl)furan-2-yl) | |||
| Commercial Name | Zantac (GSK) | |||
| Molecular formula | C13H22N4O3S | |||
| SMILES | CN(C)CC1=CC=C(CSCCN/C(NC)=C/[N+]([O-])=O)O1 | |||
| Molar mass | 314.41 g/mol | |||
| CAS number | 66357-59-3 | |||
| Appearance | tan coloured solid | |||
| Properties | ||||
| Phase | solid | |||
| Solubility in water | 24.7 mg/mL at 25°C | |||
| LogP/Hydrophobicity | 1.93 | |||
| Melting point | 69-70°C | |||
| Hazards | ||||
| MSDS | MSDS for Ranitidine | |||
| Main hazard | ||||
| NFPA 704 | ||||
| Flash point | °C | |||
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | ||||
What is Ranitidine?
Ranitidine is in a class of drugs known as H2 receptor antagonists. It is used to treat conditions such as reflux oesophagitis and ulcers of the stomach and intestine, which are caused by too much acid being produced in the stomach. Ranitidine is available as a tablet, effervescent tablet, oral liquid and injection form.
Uses and Dosage
Ranitidine is commonly used to treat reflux oesophagitis (injury of the esophagus due to backflow of acid from the stomach), gastrointestinal ulcers and conditions in which too much acid is produced in the stomach, for example Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Other uses include aspiration of stomach acid during anesthesia, treatment of upper gastrointestinal bleeding, prevention of stress ulcers and stomach damage from the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). Seek medical consult before the use of Ranitidine for all conditions.
Ranitidine is usually prescribed by a doctor as a tablet, an effervescent tablet, effervescent granules or a syrup to be taken orally. It is to be taken by the patient once a day at bedtime, or two to four times a day, depending on the condition. Effervescent tablets and granules should be dissolved in a full glass (6-8 ounces) of water before drinking. Ranitidine should be taken 30-60 minutes before eating or drinking foods that cause heartburn. Always follow doctor's instructions, do not take it more or less often, or in doses other than that prescribed by the doctor.
Note: Do not take over-the-counter Ranitidine for longer than 2 weeks unless otherwise prescribed by the doctor. If symptoms of heartburn, acid indigestion, etc. persist for more than 2 weeks, stop taking Ranitidine and consult a doctor immediately.[1]
Possible Side Effects
There are some minor side effects which can be caused by Ranitidine use:
- Diarrhoea
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Skin rashes
- Fatigue
- Unusual aches and pains or fever
Serious side effects are not common with this medication, but the following have been noted in some patients:
- Allergic reaction
- Easy or unusual bruising or bleeding
- Bleeding gums
- Irregular heartbeat
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes
