It:Furosemide
Furosemide
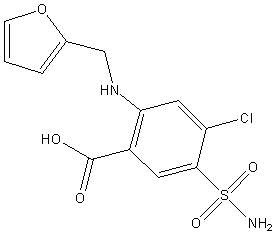
Structures
Chemical Information
| Systematic Name | 5-(aminosulfonyl)-4-chloro-2-[(2-furanylmethyl)amino]benzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H11N2ClO5S |
| Brand names | Aisemide®, Beronald®, Desdemin®, Discoid®, Diural®, Diurapid®, Dryptal®, Durafurid®, Errolon®, Eutensin®, Frusetic®, Frusid®, Fulsix®, Fuluvamide®, Furesis®, Furo-Puren®, Furosedon®, Hydro-rapid®, Impugan®, Katlex®, Lasilix®, Lasix®, Lowpston®, Macasirool®, Mirfat®, Nicorol®, Odemase®, Oedemex®, Profemin®, Rosemide®, Rusyde®, Trofurit®, and Urex®[3] |
What is Furosemide
Furosemide is a loop diuretic due to the fact that it leads to water loss. This is done by the drug increasing the urine production. It stops the body from absorbing to much salt. This means that the salt is then passed out of the body.
Furosemide can be used to treat:
- congestive heart failure
- fluid accumulation and swelling (edema)
- False pregancy (which occurs in female dogs)
- acute and chronic kidney failure
- cirrhosis
- nephrotic syndrome
It is a white tablet which is taken orally
How Does Furosemide Work?
Loop diuretics encourage the kidneys to remove more water from the blood and pass it into the urine therefore more urine is produced. This process reduces the volume of blood circulating in the body, which decreases the workload on the heart. At the same time, diuretics cause fluid to be drawn out of the tissues that are overloaded.
Loop diuretics cause the kidneys to filter out more sodium and potassium, which means that water is drawn out with them. The body automatically keeps the amount of water in the blood and in the tissues equal. This means that when water is removed from the blood, water is drawn out of the tissues to dilute the blood and the symptoms of fluid overload are relieved.
Furosemide causes a large increase in urine output (diuresis). This diuretic effect can cause depletion of water and electrolytes in the body. Careful medical supervision during treatment is therefore necessary.4
Side effects
The common side effects for furosemide are:
- water and electrolyte depletion
- Increased sugar levels in blood[1]
- low blood pressure.
- It also reduces excretion of lithium so can cause lithium toxicity
Less common side effects are:
- jaundice
- ringing in ears (tinnitus)
- rash
- pancreatitis
- nausea
- abdominal pain
- dizziness
- anemia [2]
When should Furosemide not be taken?
Furosemide should not be taken if you have any of the following:
- an allergy to sulfa medicines
- kidney disease
- liver disease
- diabetes mellitus
- gout
It is not known if an unborn baby would be affected by the drug. 5
References
1.http://www.marvistavet.com/html/body_furosemide.html
2.http://www.medicinenet.com/furosemide/article.htm
4.http://www.bupa.co.uk/health_information/html/medicine/loop_diuretics.html#top