It:Ferrocene
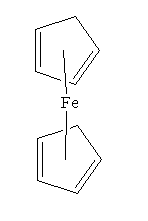
Ferrocene is an organomettalic compound of a type known as sandwich compounds. The name is because the central metal atom is bound between two cyclopentadienyl rings like the filling of a sandwich. The chemical formula of this compound is Fe(C5H5)2.
Structure
Above: 3D structure of ferrocene
Ferrocene is famous for its 'sandwich structure'. This is where the two cyclopentadiene molecules are situated above and below the iron centre, with the bonding occuring via the pi-electrons of the aromatic rings, which are shared with the central iron ion. This delocalised configuration of electrons is particularly stable. X-Ray diffraction in 1952 by Fisher showed that the cylopentadiene rings are staggered.
History
Ernst Fischer and Geoffrey Wilkinson (Inorganic Chemist at Imperial College, London) were awarded the Nobel prize for Chemistry in 1974 for his work in determining the structure of ferrocene. This was for work done 20 years earlier starting in 1952(ref 2), after the compound had first been synthesised in December 1951 by T.J. Kealy and P.L. Pauson (ref 3).
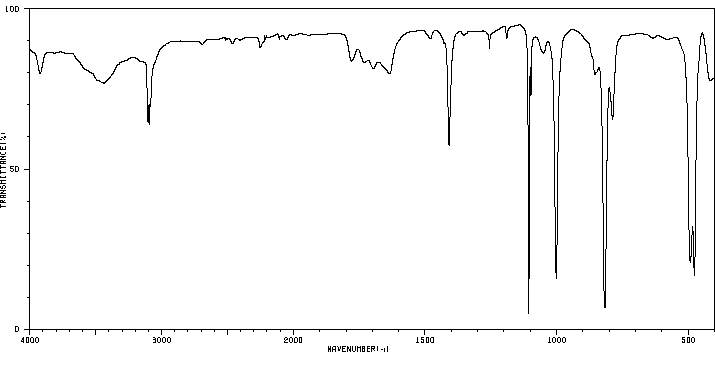
IR Spectrum
Above: IR spectrum of ferrocene (ref 1)
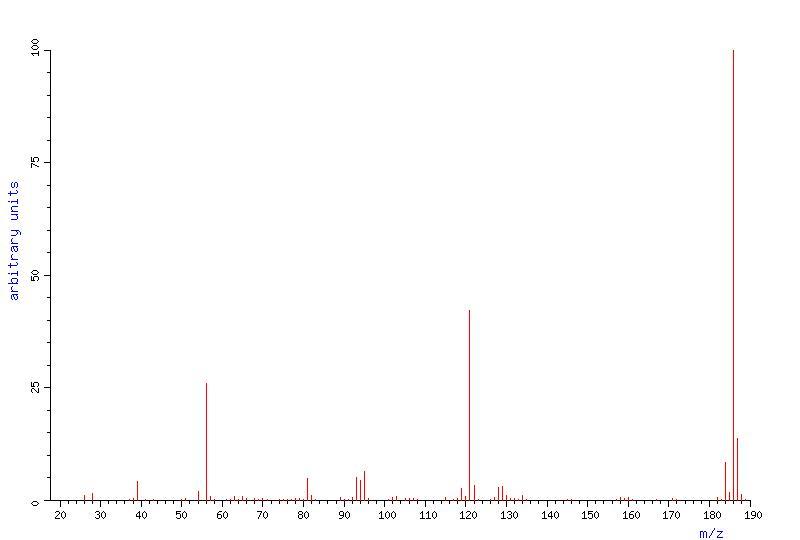
Mass Spectrum
Above: mass spectrum of ferrocene (ref 4)
Chemical Reactions
Ferrocene's characteristic chemical property is that it can do one-electron oxidation reactions at low potentials. Oxidation reactions often use Ferrocenium salts as the oxidant because the redox product of these reactions is ferrocene itself. This is inert enough that it can be readily removed from the desired products.
Apart from this, Ferrocene is also capable of undergoing Friedel-Crafts reactions in the same manner as a regular aromatic compound.
It can also be deprotonated by a strong base such as an organolithium compound. This will result in 1,1'-dilithioferrocene (Chemical Formula:Fe(C5H4Li2)which is a powerful nucleophile.
Physical Properties
Ferrocene is an yellow-orange solid that stable in air. Ferrocene is soluble in organic solvents but is insoluble in water. Ferrocene will sublime in a vacuum
Uses of Ferrocene
Because ferrocene will sublime easily in a vaccuum, it is often used to deposit fullerenes. Apart from this, most of the uses involve ferrocene derivatives rather than ferrocene itself.
Ferrocene can be used in diesel to prevent soot production and in petrol as an anti-knocking agent (it increases the fuels octane rating, meaning that it makes them less likely to detonate early, causing damage to an engine). It is considered safer to use than, for example, Tetra-ethyl lead, but can lead to other problems over time (i.e. sparkplug failure).
Certain salts of ferrocene are being used in experimental anti-cancer drugs including Tamoxifen which is used as a treatment for breast cancer.
It is possible to use ferrocenyl phosphines as ligand scaffolds in reactions catalysed by transition-metals.
References
1. Data provided by the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (Japan)
2. Wilkinson and Woodward( J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 2125)
3. T.J. Kealy and P.L. Pauson (Nature, 15/12/51)
4. Spectral data provided by Wiley Subscription Services, Inc. (US)
5. "Hazardous Substances Data Bank" data are provided by the National Library of Medicine (US)
--Jtm05 12:14, 27 October 2006 (BST)
--Vl105 11:50, 27 October 2006 (BST)