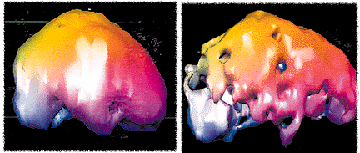It:Crystal Meth
Methamphetamine
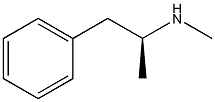
Methamphetamine (C10H15N) or chrystal meth as is most commmonly known, is an intensive psychostimulant and belongs in the family of drugs known as amphetamines.There are two forms of methamphetamine, the D-form and the L-form. The D-form is the drug known as "speed" whereas the L form of the drug is a decongestant used in the U.S Vicks inhaler. Its pharmaceutical form Desoxyn is used to treat narcolepsy, ADD/ADHD and exogenous obesity. The drug works directly on the brain and spinal cord by interfering with normal neurotransmission with the main neurotransmitter to be affected being dopamine .
| Methamphetamine
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| General | |||
| IUPAC name | (S)-N-methyl-1-phenyl-propan-2-amine | ||
| Other names | Desoxyn; Methedrine;speed; meth; chalk; Christina or Tina; ice; crank; L.A; snot | ||
| CAS number | 537-46-2 | ||
| Pub Chem | 1206 | ||
| Chemical formula | C10H15N | ||
| Molecular mass | 149.2 g/mol | ||
| Properties | |||
| Melting point | 170-175°C(m) | ||
| Density | 0.907 ± 0.06 g/cm3 ] | ||
| H2O Solubility | Soluble | ||
| Apperance | White crystalline powder | ||
| Half Life | 4-8 hours | ||
| 3D structure |
| ||
History
Methamphetamine was originally discovered in Japan in 1919 following the synthesis of amphetamine in Germany in 1887 . As its crystalline powdery form was readily soluble in water, it was ideal for injection. Widespread use of the substance began during World War II where amphetamines were widely used to keep the fighting men going (during the Vietnam war, American soldiers used more amphetamines than the rest of the world did during WWII!). Even Adolph Hitler is rumoured to have received injections of the substance. In Japan, intravenous methamphetamine abuse reached epidemic proportions immediately after World War II when supplies stored for military use became available to the public. The substance became readily available in the United States in the form of manufactured tablets of methamphetamine (Methedrine) in the 1950s.User groups included college students, truck drivers, and athletes, meking the abuse of methamphetamine a common phenomenon.Methamphetamine the derivative of amphetaminewas widely prescribed in the 1950s and 1960s as a medication for depression and obesity, reaching a peak of 31 million prescriptions in the United States in 1967
In the 1970s however its use decreased greatly as the 1970 Controlled Substances Act severely restricted the legal production of injectable methamphetamine.
Until the late 1980s, illicit use and manufacture of methamphetamine was mainly restricted to California, but the user population has broadened in nature and in regional distribution, with increased use occurring in midwestern states. An estimated 4.7 million Americans (2.1% of the U.S. population) have tried methamphetamine at some time in their lives.It is still legally produced in the U.S., sold under the trade name Desoxyn.
Production
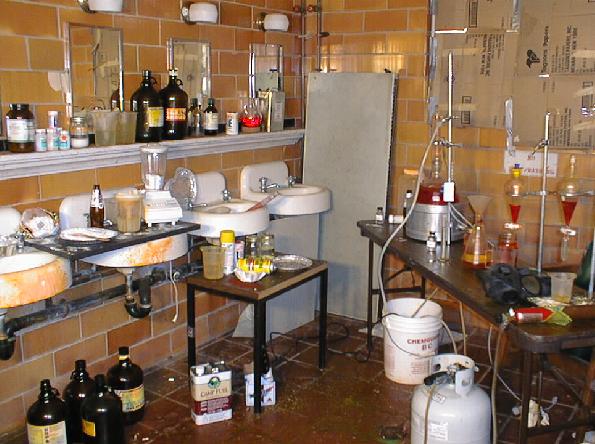
Cold and asthma medications containing ephedrine or pseudoephedrine, red phosphorous, hydrochloric acid, drain cleaner, battery acid, lye, lantern fuel, and antifreeze are among the ingredients most commonly used for the synthesis of crystal meth.
Secret production accounts for almost all of the methamphetamine trafficked and abused in the United States. However production of the compound by unqualified persons is extremely dangerous as hazardous products such as phosphine gas can be produced. The illicit manufacture of methamphetamine can be accomplished in a variety of ways, but is produced most commonly using the ephedrine / pseudoephedrine reduction method (see below). Large-scale production of methamphetamine using this method is dependent on ready access to bulk quantities of ephedrine and pseudoephedrine.
Ephedrine Reduction
C6H5-(CHOH)-CH(NHCH3)-CH3 + HI =====> C6H5-(CHI)-CH(NHCH3)-CH3 + H2O
C6H5-(CHI)-CH(NHCH3)-CH3 + HI =====> C6H5-CH2-CH(NHCH3)-CH3 + I2
A chrystal Meth lab or 'Pop and Mom' lab as is commonly known

Action
Ice induces a profound sense of euphoria in the user by blocking the reuptake, and stimulating the release, of dopamine and noradrenaline in the central nervous system. Unlike base cocaine, smoking meth will extend its effects for up to 24 hrs per ingestion. This form of methamphetamine is known as snot . Crystal meth increases arousal in the central nervous system by pumping up levels of two neurotransmitters, norepinephrine and dopamine.
Methamphetamine use:
-increases heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, and rate of breathing
-produces extra energy and stamina, an increased libido, a sense of invulnerability (exhilaration and euphoria)
-produces a decrease in appetite
Spectra
The IR Spectrum of methamphetamine was recorded in the gas phase. As concentration information is not available for this spectrum molar absorptivity values cannot be derived.
Data compiled by: NIST Mass Spec Data Center, S.E. Stein, director
Addiction and Effects
Route of administration can influence the rate of addiction and disability caused by using the drug. Smoking and injecting meth result in the largest amounts of drug being delivered most rapidly to the brain and central nervous system. Meth is also referred to as Poor Man's Cocaine" as it generally costs the same or less than crack cocaine (ranging from $25 to $100 per gram) but because the user's body metabolizes it more slowly, the stimulation lasts much longer.
Chronic, high-dose methamphetamine abusers may exhibit:
-increased nervousness
-paranoia, schizophrenia-like symptoms; hallucinations
-irritability, confusion
-insomnia
-Violent and erratic behaviors (last phase of meth use) disorganized lifestyle
-lowered resistance to illnesses
-possible brain damage
Withdrawal from high doses of meth invariably produces depression, which varies in severity and duration but may last for months or even years.
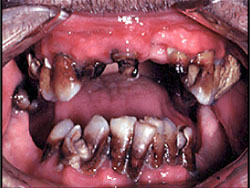
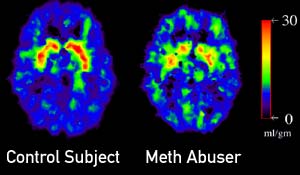
Effects of methamphetamine on teeth and brain scans before and after use
References
Brain scan images from Dr. Volkow's study. Image copyright Nora Volkow/American Journal of Psychiatry.
1. http://www.health.state.mn.us/divs/eh/meth/index.html
2. http://www.mappsd.org/How%20Meth%20Affects.htm
3. http://www.stopmethaddiction.com/pic-meth-users.htm (BRAIN IMAGES)
4. http://www.stopaddiction.com/meth_history.html
5. NIST Chemistry Webbook http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/