It:Beta Carotene
General Information
Beta-carotene belongs to a family of natural chemicals known as carotenes which is widely found in plants, fruits and vegetables which are orange red in colour.
Beta-carotene is used by the body to make retinol, which is required for healthy vision. As excessive amounts of dietary vitamin A is toxic, beta carotene is a safer supplement because the body will only convert the need amounts of carotene into vitamin A, thus not poisoning the body. Beta-carotene is an antioxidant and protects the body by reacting with free radicals to prevent oxidation.
Beta-carotene is also used to treat sun sensitivity and Scleroderma. However, people are known to suffer from side effects when taking excessive amounts of beta-carotene. These effects include skin discolouration, bruising and joint pains.
Structure of Beta Carotene
3D Sructure
2D Sructure
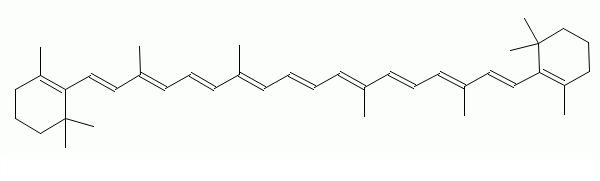
BCarotene.JPG
Properties of Beta Carotene
| Properites | ||
| IUPAC Systematic Name | 3,7,12,16-tetramethyl-1,18-bis(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)-octadec
a-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaene | |
| Chemical Name | Beta Carotene | |
| Synonyms | Provitamin A, Provatene, Natural Yellow | |
| Molecular formula | C40H56 | |
| Molecular Mass | 536.87 gmol-1 | |
| Melting Point | 180 - 182oC | |
| Solubility | Fat soluble, practically insoluble in water | |
| Type of Substance | Carotenoid | |
| CAS Registry Number | 7235-40-7 | |
| SMILES string | CC2(C)CCCC(\C)=C2\C=C\C(\C)=C\C=C\C(\C)=C\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(/C)CCCC1(C)C | |
| Colour | Dark Red to Brown | |
UV-Vis Spectra of Beta Carotene
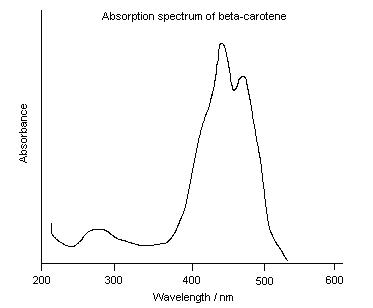
The spectra shows a maxima at approximately 440nm, which corresponds to the absorption of blue light and so the chemical appears orange.
Synthesising Beta Carotene
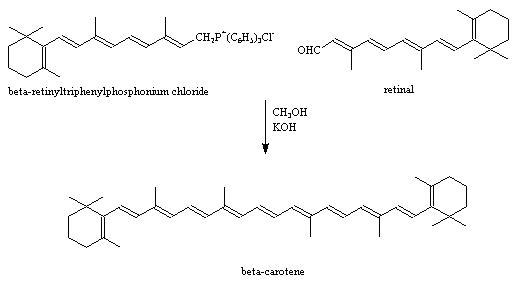
Synthetic Route
This mechanism was developed by the Badische Anilin- & Soda-Fabrik ( BASF) and is based on the Wittig reaction. The general process involves reacting a ylide with an aldehyde or ketone, and the resultant is an alkene. The posphonium molecule is overall neutral and reacts with the aldehyde; in this case retinal, a chromophore found in photoreceptor cells of the retina. The reaction involves the formation of a 4 membered ring intermediate. The prcess is driven by the very stable and strong formation of a phosphine oxide bond (P=O). once this is eliminated, the alkene has formed i.e. beta carotene.
Beta Carotene can also be synthesised by using a Grignard reagent.
Roche Synthesis of Beta-Carotene
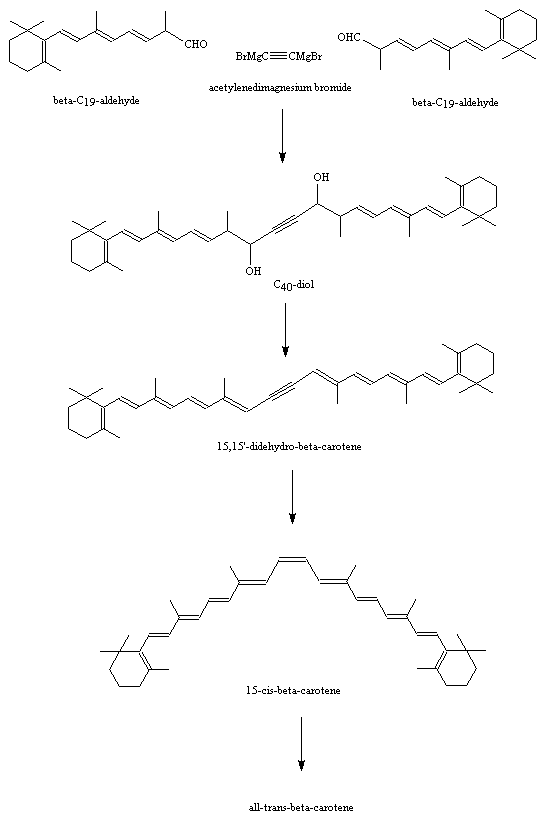
Image taken from http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/carotene/
This synthesis of beta-carotene was developed later by F. Hoffman-La Roche & Co. Ltd. It is a symmetrical reaction using two C19 chains combined with a C2 Grignard reactant to give a C40 carotene chain.
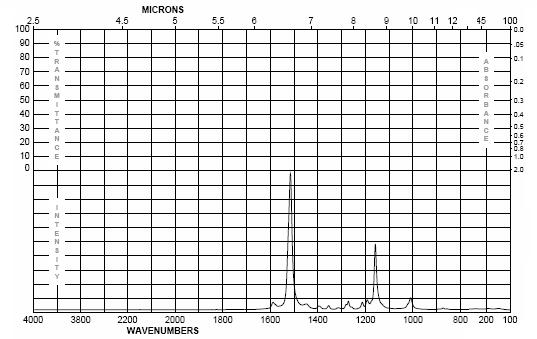
IR Spectra of Beta Carotene
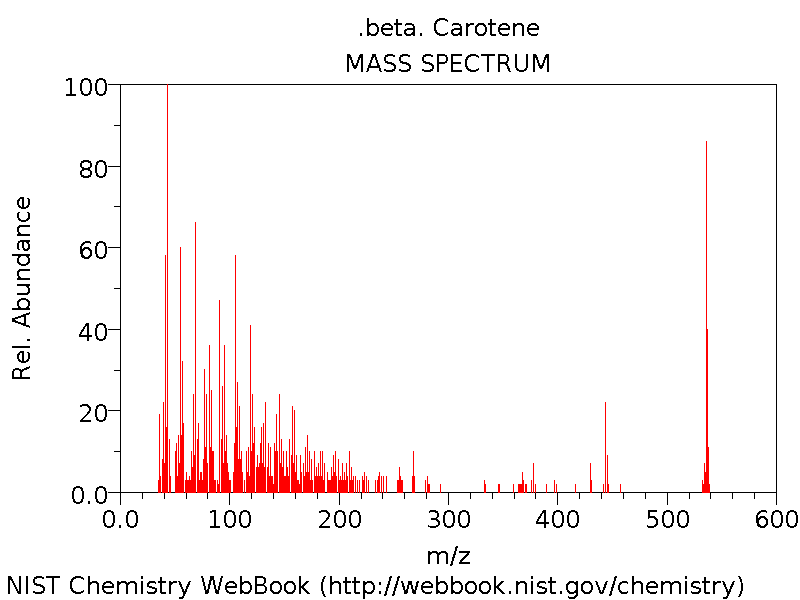
Mass Spectrum
References
1. Zechmeister; Pinckard (J. Am. Chem. Soc), 1947
2. Caris-Veyrat, Catherine; Amiot, Marie-Josephe; Ramasseul, Rene; Marchon, Jean-Claude (New J. Chem), 2001.
4. http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/carotene/beta-carotene_synthesis.html
