It:Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate
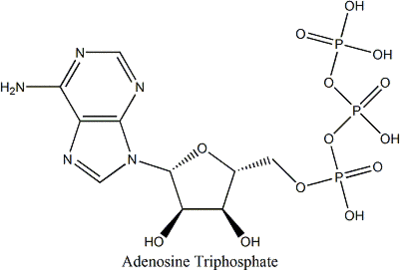
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) (C10H16O13N5P3) is found in muscles as an energy source.
Structure
ATP consists of adenosine(made up of an adenine ring and a ribose sugar)and three phosphate groups.
Working Principles of ATP
Adenosine Triphospate is made up of 3 phosphate groups. When the third phosphate group of ATP is removed by hydrolysis, energy is released. This amount is relatively large, and easily accessible in biological terms. As such, the bond between the last and second phosphate group is known as a "high energy" bond.
Advantages of using ATP
The body uses ATP as a convenient source of energy as the energy released during the hydrolysis of ATP into ADP is sufficient to "power" most cellular reactions. Direct hydrolysis of a glucose molecule produces too much energy and would be a waste. Glucose molecules are also too large compared to the small and portable ATP packets.
ATP in respiration
In the Kreb's Cycle, full oxidation of a single glucose molecule can produce up to 30 units of ATP for use. This involves the use of complex electron transfer chains within membranes of respiratory organelles such as mitochondria. This processes involve the use of coenzymes such as NAD, NADPH, as well as Acetyl Coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA) in oxidative phosphorylation where ADP is converted back into ATP.