It07:salicylic acid
Salicylic acid
| It07:salicylic acid | |
|---|---|

| |
| General | |
| Systematic name | 2-hydroxybenzoic acid
o-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
| Other names | ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid |
| Molecular formula | C7H6O3 |
| SMILES | OC(=O)c1ccccc1O |
| Molar mass | 138.123 g/mol |
| Appearance | a white, crystalline solid |
| CAS number | 69-72-7 |
| Properties | |
| Density & phase | 1.44 g/cm (at 20 °C) |
| Solubility in water | 0.2g/100 ml (20°C) |
| Melting point | 159°C |
| Boiling point | 211°C |
| Flash point | 157°C |
| Auto-ignition temperature | 540°C |
Salicylic acid is best known chemically similar but not identical to the active component of aspirin.
Production
It can be synthesised from amino acid phenylalanine, illustrating as followed:
Sodium salicylate is commercially prepared by treating sodium phenoxide with a high pressure of carbon dioxide at high temperature via the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction. Acidification of the product solution gives salicylic acid.
Usage
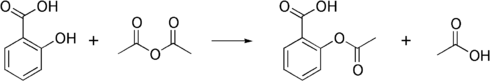
It is used to synthesise aspirin, which is used as an analgesic (to relieve minor aches and pains), antipyretic (to reduce fever), and as an anti-inflammatory. The generic steps are shown below:
 Also, salicylic Acid is best on acne-prone and sensitive skin types. The pore-cleansing properties of salicylic acid make it a more effective comedone fighter. Those with sensitive skin who cannot tolerate alpha hydroxy acids may find that they are able to use salicylic acid with good results. However, alpha hydroxy acid's penetration into the deeper layers of the skin produce better anti-wrinkle and anti-aging benefits.
Also, salicylic Acid is best on acne-prone and sensitive skin types. The pore-cleansing properties of salicylic acid make it a more effective comedone fighter. Those with sensitive skin who cannot tolerate alpha hydroxy acids may find that they are able to use salicylic acid with good results. However, alpha hydroxy acid's penetration into the deeper layers of the skin produce better anti-wrinkle and anti-aging benefits.
Look for concentrations of 1-2% in any salicylic acid product to assure on effective concentration. A 1% concentration would be better or sensitive skin types and a 2% concentration would be useful on stubborn acne.[[1]]
Potential Health Effects
| Types of Effects | Illustration |
|---|---|
| Inhalation | Inhalation of dust may cause irritation due to its acidic character. Coughing, sneezing, and shortness of breath may occur. |
| Ingestion | Ingestion of sizable amounts can cause "salicylism", as evidenced by abdominal pain, vomiting, increased respiration, and mental disturbances. Fatalities resulting from respiratory or cardiovascular failure are known. Mean lethal adult dose of salicylates is between 20 and 30 grams. |
| Skin Contact | Mild irritant, may cause skin rash in sensitive individuals. Absorption of large amounts may produce symptoms paralleling ingestion exposure. |
| Eye Contact | Severe irritant by animal testing. |
| Chronic Exposure | Central nervous system disturbances such as rapid breathing, confusion and even convulsions may develop. Kidneys and pancreas can be affected by prolonged ingestion. |
| Aggravation of Pre-existing Conditions | Persons with pre-existing skin disorders or eye problems or impaired kidney function may be more susceptible to the effects of the substance. |
[[2]]
First Aid Measures
| Effects | Aid Instruction | |
|---|---|---|
| Inhalation | Remove to fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Get medical attention. | |
| Ingestion | Induce vomiting immediately as directed by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Get medical attention. | |
| Skin Contact | Immediately flush skin with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated clothing and shoes. Wash clothing before reuse. Thoroughly clean shoes before reuse. Get medical attention if symptoms occur. | |
| Eye Contact | Immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, lifting lower and upper eyelids occasionally. Get medical attention immediately. |
Spectroscopy Data
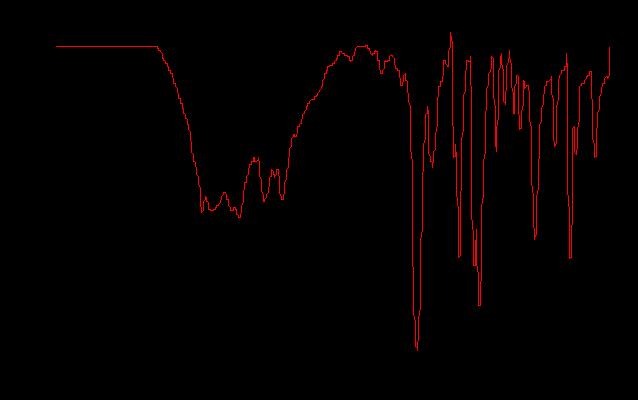
IR SPectroscopy
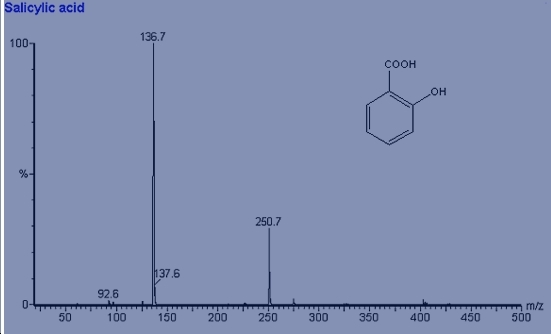
Mass Spectroscopy