It07:h3nbh3
Ammonia-borane
| Template:Ammonia Borane | |
|---|---|
| |
| General | |
| Systematic name | Ammonia Borane |
| Other names | - |
| Molecular formula | H3NBH3 |
| SMILES | [H][N@@]([H])([H])[B@]([H])([H])[H] |
| Molar mass | 30.87 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colourless, waxy solid |
| CAS number | 13774-81-7 |
| Properties | |
| Density & phase | Density = 0.780 g/cm³, solid / ? g/ml, liquid / ? g/l, gas --> |
| Solubility in water | Good |
| Melting point | 377 K |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| Dipole moment | 5.2 D |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS |
| Main hazards | Flammmable |
| R/S statement | R: 5 S: 14-15-26-36/37/39 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | NaBH4, B3N3H6, BH3, C2H6 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | |
General
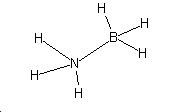
Ammonia-borane has the following structure:
Right click on molecule to explore.
The point group is C3V
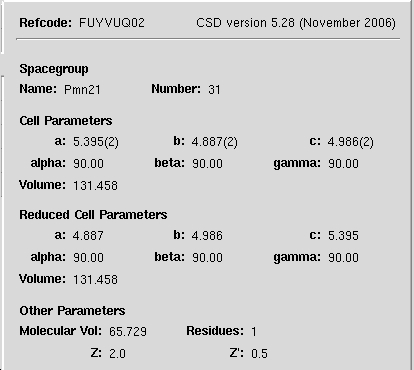
Crystal Structure
6
3D representation of the crystal unit cell. Right click on image to explore unit cell.
All cell parameter values in Å. Method used to determine unit cell details is neutron diffraction
Synthesis
High purity (98%) and high yields (>95%) of ammonia borane can be achieved with reactions involving the direct addition of ammonium salts and sodium borohydride. 1
Ammonia borane can be synthesised by direct reaction of BH3(THF) and ammonia: BH3(THF) + NH3 --> BH3NH3 The main product in this reaction is ammonia-borane.
Other synthetic routes
- Diborane + bisamminedihydroboriumtetrahydroborate --> ammonia-borane 2
Solvent: diglyme, Note: Slow reaction
- Ammodiumamidosulfonat + natrium boron hydride --> ammonia borane + H2 + NaNH2SO3 3
Solvent: liquid ammonia + ether, Purification/Isolation: solution was allowed to warm to room temperature; filtered; ether evaporated.
- Ammonium Chloride + Lithium Borohydride ---> ammonia borane + H2 4
Byproduct: LiCl
- Borane methylsulfide + ammonia --> ammonia borane + bisamminedihydroboriumtetrahydroborate 5
Solvent: No solvent required , General conditions: -20oC , Purification/Isolation: Recrystallisation from ether
Uses and applications
Ammonia borane is becoming an increasingly interesting molecule for hydrogen storage. It has found uses in applications such as motor vehicles and power generators in portable devices. Ammonia borane can hold large quantities of hydrogen but is not easily reversible. Part of the reason for this irreversibility is due to entropic reasons. When ammonia boarane is heated it decomposes into hydrogen gas and a few other compounds depending on conditions; as a result hydrogen can be readily evolved but the process cannot be easily reversed to recycle any unused hydrogen for later usage. Approximately one millilitre of ammonia borane can produce up to 1.8 litres of hydrogen gas. 10
Another advantage of using ammonia borane as hydrogen storage as opposed to hydrogen gas is because it has a melting point at -34 degrees Celsius, which is a lot higher than that of hydrogen. Also, ammonia borane becomes liquid at room temperature at 9 atmospheres pressure, this makes it much more convenient to use as a transportation fuel.11
Ammonia borane has also found many uses in organic synthesis, replacing diborane due to it being stable in air.
Properties of Ammonia-borane
Bond Lengths
- B-N: 1.58 Å
- B-H: 1.15 Å
- N-H: 0.96 Å
Physical Properties
- Appearance: Colourless, waxy solid
- Melting point: 104oC
- Boiling point: Decomposes
- Solubility in water: Good
- Decomposition: 80oC 7
- Ionization potential (Photoelectron spectroscopy [vertical]): 10.33eV-10.9eV 8
Ammonia-borane dissolves well in water due to the strong ionic component in the N-B bond given that there is a significant difference in the pauling electronegativity ( 3.04[N]-2.04[B]=1) between nitrogen and boron. This means that water molecules can easily solvate ammonia-borane as there is a strong attractive component between the permanent dipoles on the water molecules and the B-N bond in ammonia-borane.
- Density: 0.780 g/cm3
- Crystal structure: 14mm (tetragonal, >200K)
- Dipole moment: 5.2D 9
The dipole moment of ammonia borane arises due to the large difference in pauling electronegativity (as discussed with the solubility in water). Water has a dipole moment of 1.85D; therefore ammonia borane's dipole moment is approximately 3 times as much. To compare, this explains why water is a liquid in room temperature and pressure while ammonia borane is a solid due to the strong dipole-dipole interactions.
Stability
Ammonia borane is stable at room temperature and can last for hours when placed in aqueous solution. However, it decomposes rapidly when the compound is added to liquid ammonia or ether after addition of water. The molecule is also stable in anhydrous ether or liquid ammonia.
Hazards
- Flammable / keep away from heat
- Explosive (Heating causes ammonia borane to decompose into hydrogen gas!)
- Toxic if swallowed. 12
- Harmful by inhalation. 12
- Irritating to eyes.12
References
- 1)http://pubs.acs.org/cgi-bin/abstract.cgi/inocaj/2007/46/i19/abs/ic700772a.html
- 2)Mayer E, Inorg. chem, vol 12, 1973, Pg 1954-1952 DOI reference
- 3)Thorne L R , Chem Phys Lett, vol 78, 1981, pg157-160 DOI reference
- 4)Parry R W, J.am.chem.soc, vol 77, 1955, pg 2072-2074
- 5)Adams R M, Inorg. Chem, vol 10, 1971, pg 2072-2074
- 6) W T Klooster, J.Am.Chem.Soc., vol 121, 1999, pg 6337 DOI reference
- 7) Tubyanskaya V.S, Zh.fiz.khim, vol 40, 1966, pg 122-124
- 8) Lloyd D.R, J.chem.soc.D, 1970, pg 1545-1546
- 9) Crabtree Robert H, J.am.chem.soc, vol 121, 1999, 6333-6343
- 10) http://biopact.com/2007/08/storing-hydrogen-in-solid-ammonia.html
- 11) http://www.americanscientist.org/template/AssetDetail/assetid/45942
- 12)http://www.americanscientist.org/template/AssetDetail/assetid/45942