It07:Verbenone
VERBENONE
Verbenone
Natural Product
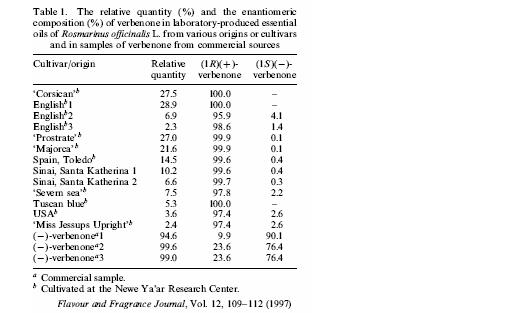
Identification of Verbenone in natural products (essential oils) has been carried out. Its idenfication in Rosmarinus ocinalis L. (Uzi Ravid1, Eli Putievsky1, Irena Katzir1, Efraim Lewinsohn1 and Nativ Dudai1, FLAVOUR AND FRAGRANCE JOURNAL, VOL. 12, 109±112 (1997)) shows that relatively large quantities of verbenone (observed in three rosemary oils) amounted to 27.0±28.9% whilst the average content was only 2.3±21.6%. These relatively low quantities warrants a synthetic route.
Synthesis
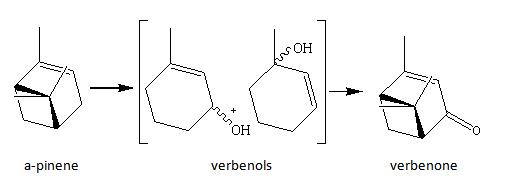
Verbenone results from the autoxidation of a-pinene, simply in air.
Synthetic routes have been estabilshed to catalyse this oxidation. Lajunen and Koskinen (Terrahedmn Lwer.s, Vol. 35. No 25. pp. 44614464, 1994) has used Co(11) to catalyse its oxidation.
1H NMRSpectrum
H NMR spectrum for the cis-verbanone by the incubation with NADPH in H20 (reference:http://www.rsc.org/ejarchive/C3/1993/C39930001426.pdf)
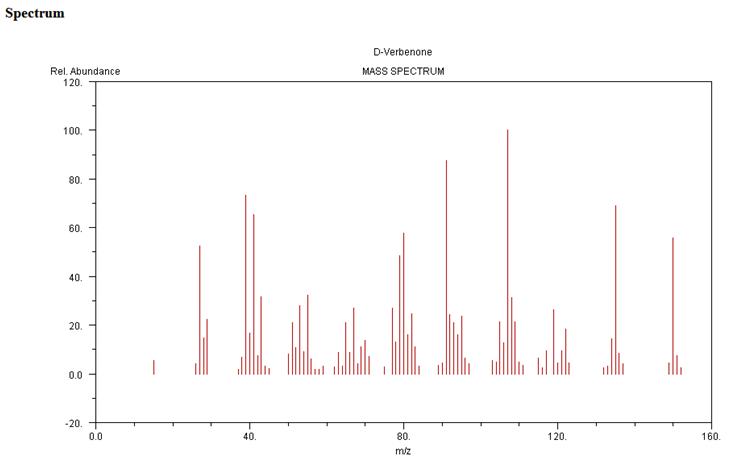
Mass Spectrum
| It07:Verbenone | |
|---|---|
| |
| General | |
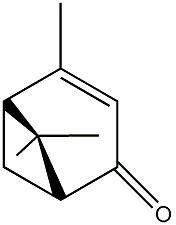
| Systematic name | (1R)-cis-4,6,6-Trimethylbicyclo-
[3.1.1]hept-3-en-2-one |
| Other names | Verbenone
2-Pinen-4-one |
| Molecular formula | C14H10O |
| SMILES | CC(C1C2)(C)C2C(C)=CC1=O |
| Molar mass | 150.21 g/mol |
| CAS number | [18308-32-5] |
| Properties | |
| Melting point | 6.5 °C |
| Boiling point | 227-228 °C |
| Density | 0.978 g/cm3 |
| Physical state | liquid |
| appearance | clear, colorless |
| MSDS | external link to Material Safety and Data Sheet link title |