It07:Terbutaline Sulphate
| Terbutaline Sulphate | |
|---|---|
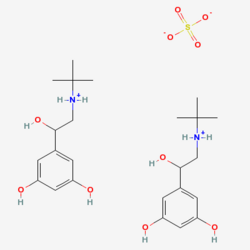
| |
| IUPAC Systematic name | |
| tert-butyl-[2-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]azanium sulfate | |
| Other name | |
| Bricanyl | |
| Indentifiers | |
| ATC Code | R03AC03R03CC03 |
| CAS number | {{{CASNo}}} |
| PubChem (CID) | 36120 |
| SMILES | [NH2+CC(C1=CC(=CC(=C1)O)O)O.CC(C)(C)
[NH2+]CC(C1=CC(=CC(=C1)O)O)O.[O-]S(=O)(=O)[O- CC(C)(C)[NH2+]CC(C1=CC(=CC(=C1)O)O)O.CC(C)(C) [NH2+]CC(C1=CC(=CC(=C1)O)O)O.[O-]S(=O)(=O)[O-] |
| Chemical Data | |
| Molecular formula | (C12H20NO3)2 SO4 |
| Molar mass | 548.6468 g/mol |
| Pharmacokinetic Data | |
| Bioavailability | {{{Bioavailability}}} |
| Protein Binding | {{{Protein_binding}}} |
| Metabolism | GI tract (oral), liver; CYP450: unknown |
| Half life | urine 90% (60% unchanged), bile/faeces; Half-life: 3-4h |
| Excretion | {{{Excretion}}} |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. | B |
| Legal status | POM |
| Routes | SQ, Oral, Inhaled |
Terbutaline Sulphate
Structure
mo_terbutaline_sulphate.pdb |
Crystal Structure
TESU.cif |
Terbutaline sulphate belongs to a class of drugs known as short acting beta 2 agonistslike salbutamol. It is a bronchodilator These drugs work by acting on the lungs' beta 2 receptors. Stimulation of these recpetors cause the relaxation of muscles in the airway, thus allowing the opening of the airway. Terbutaline sulphate is used in the treatment of conditions that cause the narrowing of airways such as asthma, bronchitis and emphysema. Terbutaline sulphate is mainly administered as an inhaler, where the drug can directly get to the lungs. It can also be taken in tablet form if the inhaler is being used frequently to ease shortness of breath. The tablets can be taken regularly to help keep the airways constantly open and reduce inhaler usage. However the inhaler has the advantage of reducing the chance of side effects occuring in other body parts, as the quantity of the drug absorbed by the blood via inhalation is smaller than the quantity taken orally.[1]
Conditions where the drug is used
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Bronchospasm (narrowing of the airways) in other lung conditions (e.g. bronchitis and emphysema)
Asthma [1]
Side Effects
Chest discomfort
Breathing difficulty
Dizziness
Drowsiness
Fast, irregular heartbeat
Headache
Increased heart rate
Nausea
Sweating
Tremors
Weakness [2]
Synthesis
To synthesise terbutaline sulphate, first terbutaline needs to be formed from the parent cyanohydrin. This done via a Ritter reaction to convert the nitrile group into an N-alkyl amide. [3]
When the N-alkyl amide has been made; treat with sulphuric acid to make terbutaline sulphate.
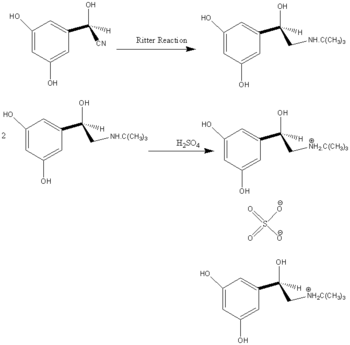
Image taken from Synthesis of the Adrenergic Bronchodilators (R)-Terbutaline and (R)-Salbutamol from (R)-Cyanohydrins1 Effenberger, F.; Jager, J. J. Org. Chem.; (Article); 1997; 62(12); 3867-3873. DOI: 10.1021/jo970032d
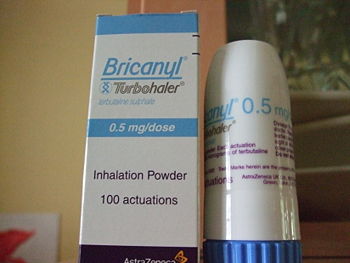
Real Life Product
Below is a Bricanyl inhaler, which contains terbutaline sulphate.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 http://www.tiscali.co.uk/lifestyle/healthfitness/health_advice/netdoctor/archive/100002557.html
- ↑ http://www.drugs.com/pdr/terbutaline-sulfate.html
- ↑ Synthesis of the Adrenergic Bronchodilators (R)-Terbutaline and (R)-Salbutamol from (R)-Cyanohydrins1 Effenberger, F.; Jager, J. J. Org. Chem.; (Article); 1997; 62(12); 3867-3873. DOI: 10.1021/jo970032d
