It07:THC
Tetrahydrocannabinol
| Tetrahydrocannabinol | |
|---|---|
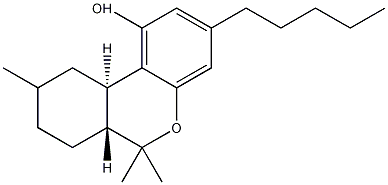
| |
| General | |
| Systematic name | Tetrahydro-6,6,9-trimethyl-3-pentyl-6H-dibenzo{b,d}pyran-1-ol |
| Other names | 6,6,9-trimehtyl-3-pentyl-6a,7,8,10,a-tetrahydro-6H-benzo[c]chromen-1-ol, Tetrahydrocannabinol, THC |
| Molecular formula | C21H30O2 |
| SMILES | CCCCCC1=CC(O)=C([C@@](CC(C)CC3)([H])[C@]3([H])C(C)(C)O2)C2=C1 |
| Molar mass | 314.46gmol-1 |
| CAS number | 1972-08-3 |
| Properties | |
| Boiling point | 200°C |
| Chiral rotation [α]D | -150.5° |
Tetrahydrocannabinol is the active constituent of marijuana. Marijuana is also know as cannabis, and is part of the plant Cannabis sativa. There is evidence that the drug has been consumed for thousands of years. The Δ1–3,4 trans isomer (Δ9–THC) is the main active constituent of the drug.
3D Structure
Toxicity
The toxicity of Δ9–THC is LD50 1270 mg/kg in male Fisher rats, and 730 mg/kg in female Fisher rats taken orally. It is mildly toxic by ingestion, having a depressing effect on the central nervous system.
Uses
As discussed perviously Δ9–THC is the main active component of the Cannabis sativa plant. The plant is a know narcotic and is illegal in many countries, including the USA and the UK. It is usually smoked or eaten by the user, and upon inhalation of the drug narcotic effects are experienced by the user. The effects include eurphoria, loss of coordiantion, paranoia and an increased heart rate.
However there have been more recent developments using tetrahydrocannabinol in medicine. It has been used experimentally to treat a range of ailments, from cancer to multiple sclerosis, and also to treat conditions such as epilepsy and AIDS.
References
- C. J. Hillard, S. Patel; Journal of Parmacology and Experimental Therapeutics; VOl. 318; 2006.
- Merck Index; 13th EDITION; p1643
- http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/SIGMA/T2386
- http://www.erowid.org/plants/cannabis/thc_data_sheet.shtml
- http://health.howstuffworks.com/marijuana3.htm
Awc106 16:28, 27 November 2007 (UTC)
