It07:Sucralose
Appearance
Sucralose
What is Sucralose?
| It07:Sucralose | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| General | ||||
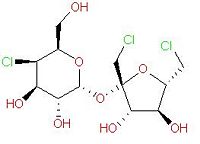
| Systematic name | (2R,3R,4R,5R,6R)-2-[(2R,3S,4S,5S)-2,5-bis(chloromethyl)-3,4-
dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]oxy-5-chloro-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4-diol | |||
| Other names | Trichlorosucrose, Sucralose [BAN], 4,1',6'-Trichloro-4,1',6'-trideoxy-galacto-sucrose, 1,6-Dichloro-1,6-dideoxy-beta-D-fructofuranosyl 4-chloro-4-deoxy-alpha-D-galactopyranoside, Altern | |||
| Molecular formula | C12H19Cl3O8 | |||
| SMILES | Cl[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O[C@@]2(CCl)
[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CCl)O2)O[C@@H]1CO | |||
| Molar mass | 397.63 g/mol | |||
| Appearance | White solid | |||
| CAS number | 56038-13-2 | |||
| Properties | ||||
| Density & phase | {{{Density}}} g/cm³ | |||
| Solubility in water | {{{Sol_Water}}} g/100 ml (25°C) | |||
| Melting point | 403.15 K | |||
| Boiling point | {{{Bp}}} K | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | {{{pKa}}} | |||
| Basicity (pKb) | {{{pKb}}} | |||
| Chiral rotation [α]D | {{{Rotation}}}° | |||
| Viscosity | {{{Viscosity}}} cP at 25°C | |||
| Structure | ||||
| Molecular shape | {{{Mol_Shape}}} | |||
| Coordination geometry |
{{{Coordination}}} | |||
| Crystal structure | {{{Crystal_Structure}}} | |||
| Dipole moment | {{{DM}}} D | |||
| Hazards | ||||
| MSDS | External MSDS | |||
| Main hazards | {{{Hazards}}} | |||
| NFPA 704 | {{{NFPA}}} | |||
| Flash point | {{{Fp}}}°C | |||
| R/S statement | R: {{{R-S}}} S: ? | |||
| RTECS number | {{{RTECS}}} | |||
| Supplementary data page | ||||
| Structure and properties |
n, εr, etc. | |||
| Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour Solid, liquid, gas | |||
| Spectral data | UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
| Related compounds | ||||
| Other anions | {{{Other_anion}}} | |||
| Other cations | {{{Ohter_cation}}} | |||
| Related compounds | {{{Relative_Compounds}}} | |||
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | ||||
| Structure | |
|---|---|
| Molecular shape | {{{MolShape}}} |
| Coordination geometry |
{{{Coordination}}} |
| Crystal structure | {{{CrystalStruct}}} |
| Dipole moment | {{{Dipole}}} D |
14:44, 18 October 2007 (BST)Hkc06
Sucralose is an artificial sweetener, which was discovered by scientists working for Tate and Lyle in 1976. It is also known as Altern.
This is a space-filling model of Sucralose.
Sucralose is a non-caloric artificial sweetener produced from cane sugar through a multi-step manufacturing process by selectively substituting three hydroxyl groups for three chlorine atoms.
Benefits of Sucralose
- As the addition of chlorine changes the structure of the sugar molecules, the body does not recognize sucralose as a carbohydrate and does not break it down for energy, so it contains no calories. It passes vapidly through the body unchanged and does not affect the blood glucose level, carbohydrate metabolism and insulin production. This provides a wider selection of food for people with diabetes to limit their caloric or sugar intake.
- As sucralose is very heat stable (it has a melting point of 403.15K), it is useful in food processing which requires high temperatures, such as canning.
- As sucralose is not a carbohydrate, it does not lead to tooth decay.
