It07:Sorafenib(Nexavar®)
Sorafenib (Nexavar®)
| Sorafenib | |
|---|---|
| |
| IUPAC Systematic name | |
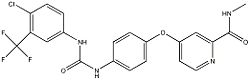
| 4-[4-[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoylamino] phenoxy]-N-methyl-pyridine-2-carboxamide | |
| Other name | |
| Nexavar | |
| Indentifiers | |
| ATC Code | L01-XE05 |
| CAS number | {{{CASNo}}} |
| PubChem (CID) | 216239 |
| SMILES | [1] |
| Chemical Data | |
| Molecular formula | C21H16ClF4O3 |
| Molar mass | 464.825 g/mol |
| Pharmacokinetic Data | |
| Bioavailability | 29-49% |
| Protein Binding | 99.5% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic oxidation and glucuronidation (CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Half life | 25–48 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal (77%) and renal (19%) |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. | D |
| Legal status | EU, United states |
| Routes | oral |
Clinical use
Sorafenib also called Nexavar® is used to treat renal cell carcinoma a type of kidney cancer. It has been submitted for marketing in the United States and Europe. The promising anticancer drug is jointly researched and has been developed by Bayer HealthCare and Onyx Pharmaceuticals and is used to treat other types of cancer such as metastasizing skin cancer and advanced liver cancer as part of research trials .
How it works
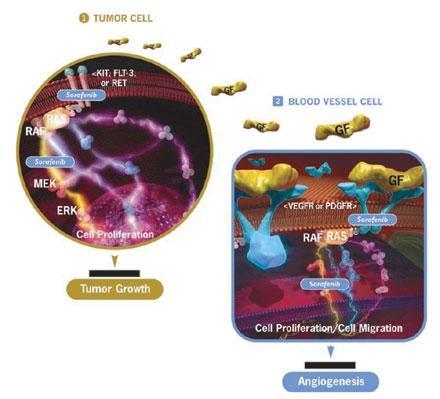
Sorafenib is a drug which is a multi-targeted kinase inhibitor which can take two possible modes of action on renal cell carcinoma. The first mechanism would consist of blocking the multiplication of cancer cells. The second mechanism would consist in preventing the formation of new blood vessels within the tumour, since these are critical for the survival of the cancer cells . It works either by disrupting the growth of cancer cells in the kidney by deliberating the growth of new blood vessels inside the tumour; this is known as inhibiting angiogenesis. As a kinase inhibitor sorafenib can interfere with kinase proteins; which are imperative in regulating the growth and functionality of cells. It works by blocking signals within cells which instruct it to divide and formulate new cells hence stunting the growth of further cancer cells.
Dual action of Sorafenib
The first effect of Sorafenib begins with the central junctions inside cells are the points at which signal pathways for cell growth and division come together. Sorafenib blocks one of these points called the Ras signal pathway. This is called the Ras pathway as it is the Ras protein which controls the first step in the process. The cell receives a command to grow from outside the cell when a growth factor connects to the cell surface. The signal is carried inside the cell and the Ras protein receives it and is activated and switches on the Raf protein kinase. A surge of enzymes activate each other where the message reaches the cell nucleus triggering cell division. The Ras pathway is hyperactive and incessantly sends out signals for cell division. Sorafenib does not bind to Ras itself but instead blocks the next protein in the chain the Raf kinase hence deliberating the growth and the making of new cells.
The second effect of sorafenib is how it prevents new blood vessels from forming in the tumour site. Angiogenesis is the process of forming new blood vessels. Many malignant tumours use angiogenesis as a growth mechanism. Tumours must grow their own blood vessels after they have grown to a size of a few millimetres or more, their supply of nutrients and oxygen is insufficient for the tumour to continue to grow and spread. This is particularly dangerous to the inner cells of a tumour[1] . Sorafenib inhibits the RAF pathway and in parallel impedes angiogenesis by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor-2 (VEGF-2) and platelet-derived growth factor-beta (PDGF-β) the compound also targets other kinases including FLT-3 and c-KIT[2]
Possible side effects
Effects on the skin; Hand and or foot reactions are common with hand and feet becoming sore or swollen accompanied by redness. Rashes, dryness and itching are common. High blood pressure, if it happens is likely to occur in the first few weeks of taking sorafenib. Medicines can be prescribed to control this. Tiredness and fatigue is also experienced. Diarrhoea, mild nausea and constipation may be observed. Sore mouth and ulcers of which prescribed mouthwashes can prevent infections. Temporary hair loss may be experienced which is likely to re-grow after the treatment is complete. Muscle pains, joint or bone pain may also be experienced.
References
- ↑ Bayer AG. Leverkusen, " Bayer - research -PDF download: Anticancer substance ", www.bayer.com/en/anticancer-substance.pdfx
- ↑ S.Leopold, " Mechanisms of drug inhibition of signalling molecules ", www.nature.com/nature/journal/v441/n7092/full/nature04874.html, 2006-05-04
- ↑ Malorye A. Branca, " Multi-kinase inhibitors at ASCO",www.nature.com/nbt/journal/v23/n6/full/nbt0605-639.html,2005-06-05
