It07:Sodium Valproate
Sodium Valproate
Sodium Valproate is the active ingredient used in Epilim for treatment of epilepsy. It is an antiepileptic/anticonvulsant.
| Sodium Valproate | |
|---|---|
| |
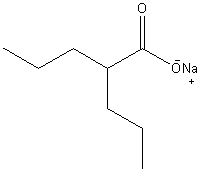
| IUPAC Systematic name | |
| Sodium 2-propylpentanoate | |
| Other name | |
| {{{OtherName}}} | |
| Indentifiers | |
| ATC Code | |
| CAS number | {{{CASNo}}} |
| PubChem (CID) | [3] |
| SMILES | <'nowiki'>'CCCC(CCC)C( [O-)=O.[Na+]'</'nowiki'>' '<'nowiki'>'CCCC(CCC)C([O-])=O.[Na+]'</'nowiki'>'] |
| Chemical Data | |
| Molecular formula | C8H16O2Na |
| Molar mass | 166.19 g/mol |
| Pharmacokinetic Data | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Protein Binding | {{{Protein_binding}}} |
| Metabolism | |
| Half life | 8-20 Hours |
| Excretion | |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. | |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | |
Pentahelicene |
Main Uses
Sodium Valproate is used to treat all forms of epilepsy the main forms being:
Tonic-clonic seizures, tonic being where the patient goes stiff due to all muscles contracting and possibly cry due to the air being forced out of their lungs and clonic where the patient jerks due to the muscles now contracting and relaxing.
General absence where the person is unconscious for a period of time – usually occurs in children
Myoclonic seizures – a sudden contraction of the muscles, the person is unconscious for this time but it is such a short amount they do not appear to be.
Lennox Gastaut Syndrome – a form of severe epilepsy in children.
Other Uses
Sodium Valproate is used also used with great effect as a mood stabiliser in psychiatric illnesses however it is an unlicensed drug and it is unknown how it works in this way apart from the increase of the calming neurotransmitter GABA.
How it works
Sodium Valproate is a white crystalline, odourless powder with a salty tasteIt is hygroscopic and so readily dissolves in the blood stream. Other anticonvulsants have nitrogen in their chemical formula or an aromatic, sodium Valproate is different as it does not.
It works to stabilise electrical activity in the brain. The salt increases the activity of a neurotransmitter (GABA) this is naturally used by the body to “calm” neurones this reduces the activity of the nerves in the brain. It also helps to prevent fits by preventing the sodium to increase in concentration around nerve cells so reducing the rapid firing between cells. The reduction of electrical activity aids in preventing seizures.
Other Names
Convulex (as valproic acid)
Epilim
Epilim Chrono
Epilim EC
Episenta
Epival CR
Orlept
Side Effects
Weight gain
Nausea
Gastric irritation
Drowsiness
Liver impairment
Hair loss
Hormone problems (women only)
Blood disorders
Tremors
Pancreatitis
Rash
Storage
Store in a cool dry place (below 30˚C) out of reach from children.
Hygroscopic – keep in foil packaging until needed.
References
- http://medguides.medicines.org.uk/document.aspx?name=Epilim&use=epilepsy§ion=homepage
- http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/435541.stm
- http://www.tiscali.co.uk/lifestyle/healthfitness/health_advice/netdoctor/archive/100004461.html
- http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/40001628/
- http://www.epilepsy.org.uk/info/drugslist.html
