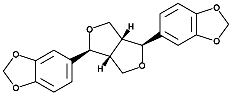
It07:Sesamin
Sesamin
(taken from www.mdidea.com)
Melting point: 122-123°C.
Molecular weight: 354.36.
C20H18O6
Optical rotation: +/- 68°.
Sesamin is an antioxidant which is said to lower blood cholesterol and sugar levels. It was found to increase the insecticidal toxicity of pyrethrins when sesame oil containing sesamin is added to it. Sesamin can be extracted from sesame oil by chromatography on silicic acid. Prior to the invention of that technique, an ultraviolet spectrum of a sample of sesame oil was run but this method had a drawback in that naturally occurring sesame oil contains other organic compounds which show peaks at the values of absorbance.
Mechanisms
The actual mechanisms of the reactions undergone by sesamin inside a human body is unknown, but according to experiments performed on rats, one possibility is that the methylenedioxyphenyl moieties of sesamin are converted to 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl moieties (also known as catechol). It turns out that the dicatechol version of sesamin (rather than sesamin itself) exhibited powerful radical scavenging activities inside the rat livers. It was also found to inhibit intestinal absorption of cholesterol.
In the presence of alcoholic hydrogen chloride, sesamin is converted into isosesamin, which has a value of +/-122° for optical rotation (in fact the two compounds would be in equilibrium). Although it is classified as a relatively inert compound, it does react with strong acids such as hydrogen peroxide and sulphuric acid to effect colour change of sesame oil.
www.chem-online.org.
www.mdidea.com
Morton Beroza, Milton S. Schechter J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1956; 78(6); 1242-1247
Nakai, M.; Harada, M.; Nakahara, K.; Akimoto, K.; Shibata, H.; Miki, W.; Kiso, Y. J. Agric. Food Chem.; (Article); 2003; 51(6); 1666-1670