It07:Sertraline
Sertraline
Sertraline hydrochloride is used as an antidepressant to treat clinical depression in adults. It can also be used to treat obsessive-compulsive, panic, social-anxiety, and even postmenstrual dysphoric disorders. Sertraline is a drug which falls under the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) class and works by restoring the chemical balance of neurotransmitters in the brain.
| It07:Sertraline | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|

| ||||
| General | ||||
| Systematic name | (1S)-cis-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-
N-methyl-1-naphthalenamine | |||
| Other names | Sertraline HCl, Zoloft, Lustral | |||
| Molecular formula | C17H17Cl2N | |||
| SMILES | ClC1=C[C@@]([C@H]2C3=C(C=CC=C3)[C@@H](NC)CC2)=CC=C1Cl | |||
| Molar mass | 306.23g | |||
| Appearance | Yellow oil. Retailed in white/yellow capsules. | |||
| CAS number | 79617-95-1, 79617-96-2, 79617-98-4, 79836-45-6, 79951-46-5, 91797-60-3, 107538-94-3, 107539-00-4, 140631-53-4 | |||
| Properties | ||||
| Density & phase | {{{Density}}} g/cm³ | |||
| Solubility in water | {{{Sol_Water}}} g/100 ml (25°C) | |||
| Melting point | {{{Mp}}} K | |||
| Boiling point | {{{Bp}}} K | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | {{{pKa}}} | |||
| Basicity (pKb) | {{{pKb}}} | |||
| Chiral rotation [α]D | [α]25D= +39.7° | |||
| Viscosity | {{{Viscosity}}} cP at 25°C | |||
| Structure | ||||
| Molecular shape | {{{Mol_Shape}}} | |||
| Coordination geometry |
{{{Coordination}}} | |||
| Crystal structure | {{{Crystal_Structure}}} | |||
| Dipole moment | {{{DM}}} D | |||
| Hazards | ||||
| MSDS | External MSDS | |||
| Main hazards | {{{Hazards}}} | |||
| NFPA 704 | {{{NFPA}}} | |||
| Flash point | {{{Fp}}}°C | |||
| R/S statement | R: {{{R-S}}} S: ? | |||
| RTECS number | {{{RTECS}}} | |||
| Supplementary data page | ||||
| Structure and properties |
n, εr, etc. | |||
| Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour Solid, liquid, gas | |||
| Spectral data | UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
| Related compounds | ||||
| Other anions | {{{Other_anion}}} | |||
| Other cations | {{{Ohter_cation}}} | |||
| Related compounds | {{{Relative_Compounds}}} | |||
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | ||||
| Structure | |
|---|---|
| Molecular shape | {{{MolShape}}} |
| Coordination geometry |
{{{Coordination}}} |
| Crystal structure | {{{CrystalStruct}}} |
| Dipole moment | {{{Dipole}}} D |
How it works
Sertraline is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). This is a common type of drug for treating depression, other SSRI’s include Prozac,Paxil, Celexa and Luvox. Serotonin is produced by nerve cells in the brain as a chemical messenger (neurotransmitter). These nerves release Serotonin which then travels around the brain and attaches other nerves or to the nerve that produced it. This process is called re-uptake. The serotonin is then re-released into the brain and the cycle starts again. This process is used to balance the amount of Serotonin in the brain. Depression, along with other associated mental illnesses such as obsessive compulsive disorder and panic disorder, are believed to be linked to a chemical imbalance in the brain between serotonin and other neurotransmitters. SSRI’s alter the levels of serotonin in the brain by stopping the reuptake process, restoring the chemical balance[1].
Important Cautions
• You should not take Zoloft (sertraline HCl) if you're taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) or pimozide, and there should be a two-week break between stopping or starting Zoloft and starting or stopping on MAOI. Serious, even fatal, complications can occur if these drugs are taken at the same time.
• Patients show be advised not to take Zoloft with alcohol.
• Do not discontinue Zoloft without talking to your doctor. You should also not stop taking Zoloft all at once to avoid SSRI discontinuation syndrome.
• It could take up to eight weeks before your symptoms start to improve.
• Be aware that any antidepressant has the possibility of triggering hypomania or mania, although in clinical trials, this was rare (0.4%) with Zoloft. (sertraline HCl)
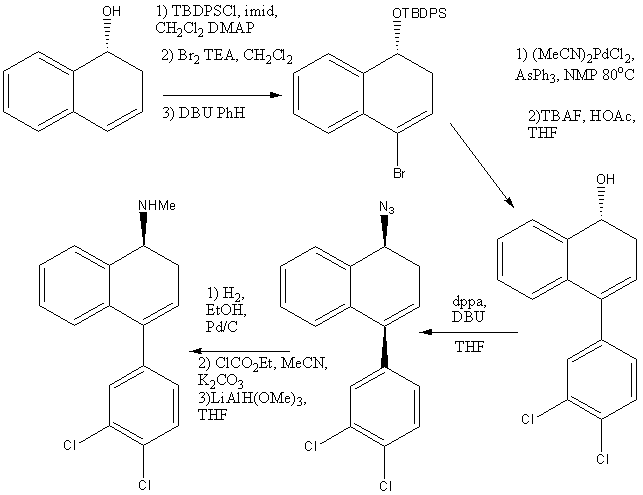
Reaction Scheme