It07:Roaccutane
Roaccutane
Roaccutane is one of the trade names of oral isotretinoin, the active ingredient used to treat severe acne. Isotretinoin is a derivative of vitamin A and works by reducing the amount of sebum produced by the skin.
Acne occurs due to excessive production of sebum from the glands in the skin. Sebnum builds up due to blocked glands and therefore the bacteria feed on it and produce fatty acids which inturn creates spots. Since Roaccutane tablets contain istroetinoin, it reduces the size of the sebaceous glands and therefore decreasing the activity of the gland and the production of sebum. This stops the glands getting blocked and so the bacteria is less likely to proliferate.
| Isotretinoin | |||
|---|---|---|---|
[[Image: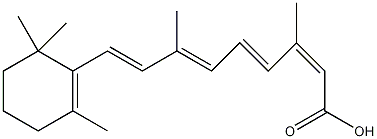 | |||
| IUPAC Systematic name | |||
| (2Z,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-cyclohex-1-enyl)-nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid | |||
| Other name | |||
| acid, [7t,9t,11t,13cretinoic acid, 13-cis-vitamin A acid&btnG=Google+Search&meta= (13Z)-retinoic acid, [7t,9t,11t,13c]retinoic acid, 13-cis-vitamin A acid] | |||
| Indentifiers | |||
| ATC Code | |||
| CAS number | {{{CASNo}}} | ||
| PubChem (CID) | [1] | ||
| SMILES | <'nowiki'>'CC1(C)C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C=C(C)/C(O)=O)=C(C)CCC1'</'nowiki'>' '<'nowiki'>'CC1(C)C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C=C(C)/C(O)=O)=C(C)CCC1'</'nowiki'>' | ||
| Chemical Data | |||
| Molecular formula | C20H28O2 | ||
| Molar mass | 300.44 g/mol | ||
| Pharmacokinetic Data | |||
| Bioavailability | |||
| Protein Binding | {{{Protein_binding}}} | ||
| Metabolism | |||
| Half life | |||
| Excretion | |||
| Therapeutic considerations | |||
| Pregnancy cat. | |||
| Legal status | |||
| Routes | |||
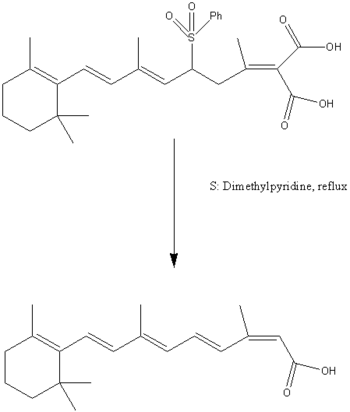
Synthesis
Potential Adverse Effects
Roccutane as a treatment for acne as become a source of controversy after anecdotal evidence of high rates of depression and suicide in patients on the medication. This phenomena was then investigated. In 2006 a study carried out in the University of Texas concluded that mice administered with Roccutane exhibited unusual levels of ‘depression-related’ behaviours in mice.[1]
More minor side affects may include dry lips and skin and in rare cases, muscle aches and nose bleeds. Also, as Roaccutane can harm unborn babies it should not be used to treat acne during pregnancy.
References
1. O'Reilly KC, Shumake J, Gonzalez-Lima F, Lane MA, Bailey SJ. "Chronic administration of 13-cis-retinoic acid increases depression-related behavior in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Sep;31(9):1919-27. Epub 2006 Jan 4.PMID: 16395305"
- ↑ bob