It07:Monosodium glutamate
Monosodium glutamate
Monosodium glutamate,sometimes is called Ajinomoto, Vetsin, or Accent or MSG. It is known as a flavor enhancer and widely used in asian cuisine. MSG was first found by a Japanese company in 1909.
Chemical and Physical property
MSG is a white crystalline power, soulble in water and alcohol at room temperature. When MSG is dissloved in water, sodium cations and glutamate anions would dissociate.When it is heated under high temperature, it decomposes.
MSG exists two chiral enantiomer isomers, but only the L form has flavor enhancing properties.
Structures
Structure of monosodium glutamte:
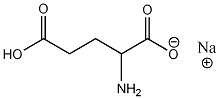
Structure of glutamic acid:
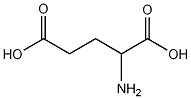
Jmol 3D structural views of the glutamic acid:
| Monosodium glutamate | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Systematic name | sodium (2S)-2-amino-5-hydroxy-5-oxo-pentanoate |
| Molecular formula | C5H8N1O |
| SMILES | C(CC(=O)O)C(C(=O)O-)N.[Na+] |
| Molar mass | 169.11 gmol-1 |
| CAS number | 142-47-2 |
| Properties | |
| Melting point | 225°C |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
Sources of glutamate/MSG
The glutamate which is given off when MSG dissociate occurs naturally. For example,in tomatoes,cheese,mushrooms and canned food.MSG is extracted from starch or corn sugar. MSG is also produced during a natural fermentation process.
MSG in food production
As the proteins in meat decompose during ageing, MSG and inosine monophosphate (IMF) are formed. These chemicals cause the meaty flavour, and amounts of each differ in different types of meat causing a variety of flavours. As MSG is the cheaper of the substances it is used by manufacturers to enhance the flavour of lower quality meat.
References
1.Filer, L. J. Glutamic Acid: Advances in Biochemistry and Physiology. New York: Raven Press, 1979
