It07:Lipitor
Lipitor
3D image of Lipitor| It07:Lipitor | |
|---|---|
| |
| Identification | |
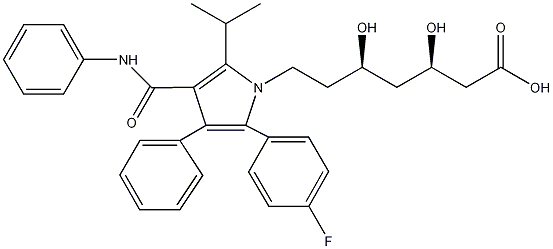
| Systematic name | [R-(R*, R*)]-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-beta, delta-dihydroxy-5- (1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4- [(phenylamino)carbonyl]-1H- pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid |
| Molecular formula | C33H35FN2O5 |
| Molar mass | 558.64 |
| CAS number | 134523-00-5 |
| SMILES | O=C(C2=C(C(C)C)N(CC[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O)C
(C4=CC=C(F)C=C4)=C2C3=CC=CC=C3)NC1=CC=CC=C1 |
| Properties | |
| Density & phase | {{{Density}}} g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | 1.23 g/L (25°C) |
| Melting point | {{{Mp}}} K |
| Boiling point | {{{Bp}}} K |
| Acidity (pKa) | {{{pKa}}} |
| Basicity (pKb) | {{{pKb}}} |
| Chiral rotation [α]D | [alpha] = -7.4°
Conc. 1g/100ml Solvent dimethylsulphoxide Wavelength 589 nm |
| Viscosity | {{{Viscosity}}} cP at 25°C |
| Structure | |
|---|---|
| Molecular shape | {{{MolShape}}} |
| Coordination geometry |
{{{Coordination}}} |
| Crystal structure | {{{CrystalStruct}}} |
| Dipole moment | {{{Dipole}}} D |
Atorvastatin (INN) (IPA: [əˈtɔvəˌstætn]), marketed under the trade name Lipitor and several others, is a member of the drug class known as statins, used for lowering cholesterol. Lipitor ( Atrovostatin ) is from a class of pharmaceutical agents that helps lowering cholestrol level in people. The mechanism by which it works is it inhibits the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. Inhibition of this enzyme in the liver stimulates LDL receptors, resulting in an increased clearance of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) from the bloodstream and a decrease in blood cholesterol levels. The first results can be seen after one week of use and the effect is maximal after four to six weeks.Atorvastatin inhibits the rate-determining enzyme located in hepatic tissue that produces mevalonate, a small molecule used in the synthesis of cholesterol and other mevalonate derivatives. This lowers the amount of cholesterol produced which in turn lowers the total amount of LDL cholesterol.Lowering cholesterol levels can help prevent heart disease and hardening of the arteries, conditions that can lead to heart attack, stroke, and vascular disease.
Lipitor is used to treat high cholesterol. In addition, it is used to lower the risk of stroke, heart attack, or other heart complications in people with coronary heart disease or type 2 diabetes.
With 2006 sales of US$12.9 billion under the brand name Lipitor, it is the largest selling drug in the world.[1]
A similar drug, simvastatin, is available as a cheaper generic alternative.
As with other statins, atorvastatin is a competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase. Unlike most others, however, it is a completely synthetic compound. HMG-CoA reductase catalyzes the reduction of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) to mevalonate, which is the rate-limiting step in hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis. Inhibition of the enzyme decreases de novo cholesterol synthesis, increasing expression of low-density lipoprotein receptors (LDL receptors) on hepatocytes. This increases LDL uptake by the hepatocytes, decreasing the amount of LDL-cholesterol in the blood. Like other statins, atorvastatin also reduces blood levels of triglycerides and slightly increases levels of HDL-cholesterol.
In clinical trials, adding ezetimibe (Zetia) to Lipitor lowered cholesterol more effectively than Vytorin (ezetimibe + simvastatin).
Cholestroral metabolism
Most circulating cholesterol is manufactured internally through the HMG-CoA reductase pathway. Cholesterol is not water-soluble, and is therefore carried in the blood in the form of lipoproteins, the type being determined by the apoprotein, a protein coating that acts as an emulsifier. The relative balance between these lipoproteins is determined by various factors, including genetics, diet, and insulin resistance. Low density lipoprotein (LDL) and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) carry cholesterol toward tissues, and elevated levels of these lipoproteins are associated with atheroma formation and cardiovascular disease. High density lipoprotein, in contrast, carries cholesterol back to the liver and is associated with protection against cardiovascular disease.
Lipitor( Statins) act by competitively inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, the first committed enzyme of the HMG-CoA reductase pathway. By reducing intracellular cholesterol levels, they cause liver cells to make more LDL receptors, leading to increased clearance of low-density lipoprotein from the bloodstream. However, they have less effect in raising HDL-cholesterol (”good cholesterol”).
"http://boostyourlife.wordpress.com/2007/11/05/facts-about-lipitoranti-cholesterol-drugs/"
Official Website for Lipitor
[Lipitor]
Mechanism for formation of Lipitor
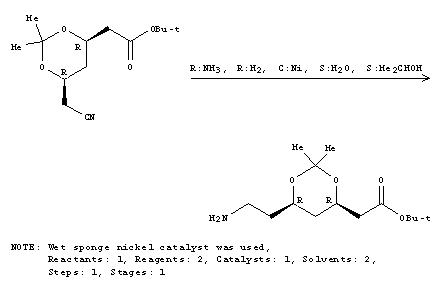
Step 1
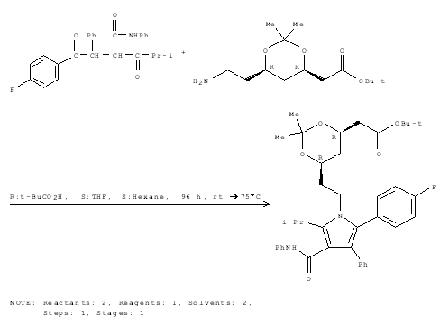
Step 2
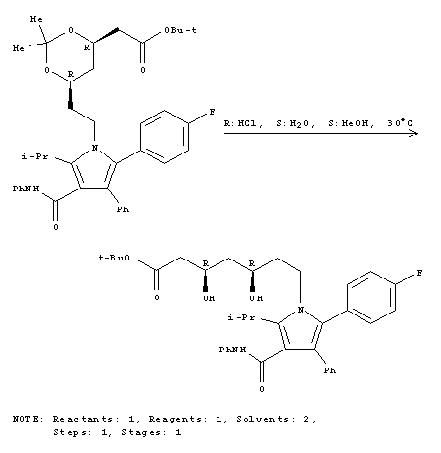
Step 3
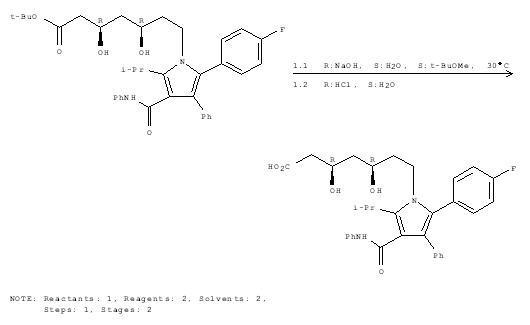
Step 4
Copyrights
CAPLUS: Copyright 2007 American Chemical Society. All Rights Reserved. (The UK patent material in this product/service is UK Crown copyright and is made available with permission. Crown Copyright. The French (FR) patent material in this product/service is made available from Institut National de la Propriete Industrielle (INPI).)
MEDLINE: Produced by the U.S. National Library of Medicine
REGISTRY: Copyright 2007 American Chemical Society. All Rights Reserved. (Some records contain information from GenBank(R). See also: Benson D.A., Karsch-Mizrachi I., Lipman D.J., Ostell J., Rapp B.A., Wheeler D.L. Genbank. Nucl. Acids Res. 28(1):15-18 (2000). Property values tagged with IC are from the ZIC/VINITI data file provided by InfoChem.) CAS Registry is a service mark of the American Chemical Society.
CASREACT: Copyright 2007 American Chemical Society. All Rights Reserved. (In addition to reactions indexed by CAS, CASREACT contains reactions derived from the following sources: ZIC/VINITI database (1974-1999) provided by InfoChem, INPI data prior to 1986, and Biotransformations database compiled under the direction of Professor Dr. Klaus Kieslich.)
CASREACT Copyright (C) 2007 ACS. In addition to reactions indexed by CAS, CASREACT contains reactions derived from the following sources: ZIC/VINITI database (1974-1999) provided by InfoChem, INPI data prior to 1986, and Biotransformations database compiled under the direction of Professor Dr. Klaus Kieslich.
CHEMLIST, CHEMCATS: Copyright 2007 American Chemical Society. All Rights Reserved.
Data sourced from SciFinder and Crossfire
Further Reading
- Alternative mechanism for synthesis and 1H NMR data; J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm.,Year 2000, Vol 43, Issue 3, Page 261-270, Authours Chen, Bang-Chi; Sundeen, Joseph E.; Guo, Peng; Bednarz, Mark S.; Hangeland, Jon J.; Ahmed, Syed Z.; Jemal, Mohammed.
- This can be found at Wiley InterScience