It07:Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone is a yellowish-orange water soluble solid. It is sparingly soluble in methanol and very slightly soluble in ethanol. It is a 3rd generation cephalosporin which has a broad spectrum of activity. This means it is used against both Gram positive and negative bacteria. It has a trade name Rocephin. It is also often used to treat pneumonia, Lyme disease,bacterial meningitis and gonorrhea. Ceftriaxone is given either by injection or infusion.
It07:Ceftriaxone
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC Systematic name | (6R,7R,Z)-7-(2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)- 2-(methoxyimino)acetamido)-3-((6-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-oxo- 2,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazin-3-ylthio)methyl)-8-oxo-5-thia- 1-aza-bicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid | |||
| Molecular formula | C18H18 N8O7S3 | |||
| Pub Chem | 456256 | |||
| CAS number | 63527-52-6 | |||
| ATC_prefix | J01 | |||
| ATC_suffix | DD01 | |||
| PubChem | 456256 | |||
| DrugBank | APRD00395 | |||
| Other Name | Rocephin (Sodium salt of Ceftriaxone) | |||
| Molar mass | 554.58 g/mol | |||
| Dissociation Constant [1] | pK(H+) = 4.32; pK(COOH) = 3 | |||
| Enzyme Kinetics | Km (μM)= 190 [2] | |||
| elimination_half-life | 5.8–8.7 hours | |||
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | ||||
Drug Administration
For gonhorrea and other bacterial STIs, 125mg of the antibiotic is administered intramuscularly into the buttocks. This injection is unusually painful and is therefore taken with an anesthetic e.g. lidocaine.
How does it work
Entering the bloodstream
Ceftriaxone does not have a peptide-based structure, unlike many antibiotics in it's category. This means that it is not transported across the intestinal tract by protein transporters (e.g. PET1) nor does it diffuse into the blood stream because it is hydrophillic and it has a physiological pH. [3]
Antibiotic mechanism
Ceftriaxone is bactericidal. It kills bacteria by interfering with its ability to form cell walls. Without the cell wall, the bacteria break up and die. The mechanism is as follows. Ceftriaxone binds to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) which in turn inhibits the final transpeptidation step of peptidoglycan synthesis in bacterial cell walls, thus inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis.
Excretion
The antibiotic is excreted through the kidneys or in the bile. This means that people with kidney problems can still take Ceftriaxone.
Side Effects
Ceftriaxone may cause severe pain at the injection site. Other side effects are a rash and diahorrea.
Ceftriaxone can bind to Ca2+ ions in the bloodstream or intestine. This causes the antibiotic to precipitate in the body and form solid deposits. These deposits can be fatal for new born babies when they build up in the kidneys or lungs.
Production
One synthesis of Ceftriaxone disodium[4] (the form in which it is administered) is show in part below:
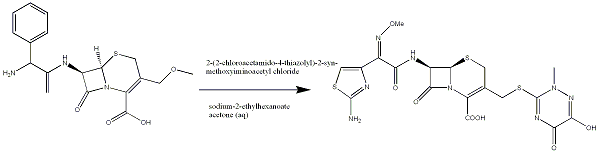
References
- ↑ Alekseev, V. G.; Vorob'ev, N. V.; Yakubovich, Yu. Ya., Zh. Fiz. Khim. 80(9) 2006, 1615-1619
- ↑ Matsumura, Naoki; Mitsuhashi, Susomu, Antimicrob. Agents & Chemother. 39(9) 1995,2132 - 2134
- ↑ SEONG-WAN CHO, JEOUNG SOO LEE, SEUNG-HO CHOI; JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES, VOL. 93, NO. 3, MARCH 2004, 612-620
- ↑ IMPROVED PROCESS FOR THE MANUFACTURE OF CEFTRIAXONE SODIUM; patent number C07D501/00; C07D501/36; C07D501/00; (IPC1-7): C07D501/36
