It07:Bisacodyl
| It07:Bisacodyl | |
|---|---|
| |
| General | |
| Systematic name | (pyridin-2-ylmethylene)di-4,1-phenylene diacetate |
| Other names | 4,4'-Diacetoxydiphenylpyridyl-2-methane; Phenol, 4,4'-(2-pyridinylmethylene)bis-, diacetate; Phenol, 4,4'-(2-pyridinylmethylene)bis-, diacetate (ester); Phenol, 4,4'-(2-pyridylmethylene)di-, diacetate; Bicol; Bis(p-acetoxyphenyl)-2-pyridylmethane; 2-(4,4'-Diacetoxydiphenylmethyl)pyridine; (4,4'-Diacetoxydiphenyl)(2-pyridyl)methane; 4,4'-Diacetoxydiphenylpyrid-2-ylmethane; Di-(p-acetoxyphenyl)-2-pyridylmethane; Di-(4-acetoxyphenyl)-2-pyridylmethane; Dulcolan; Dulcolax; Laxans; LA96A; Pyrilax; 4,4'-(2-Pyridylmethylene)diphenol diacetate; Sk-bisacodyl; Theralax; 4,4'-(2-Pyridylmethylene)diphenol diacetate (ester); 4-[[4-(Acetyloxy)phenyl](2-pyridinyl)methyl]phenyl acetate |
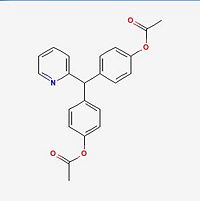
| Molecular formula | C22H19NO4 |
| SMILES | CC(OC(C=C3)=CC=C3C(C2=CC=C(OC(C)=O)C=C2)C1=NC=CC=C1)=O |
| Molar mass | 361.19 g/mol |
| Appearance | {{{Appearance}}} |
| CAS number | 603-50-9 |
| Properties | |
| Density & phase | {{{Density}}} g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | {{{Sol_Water}}} g/100 ml (25°C) |
| Melting point | 407 K |
| Boiling point | {{{Bp}}} K |
| [1] | 2-8°C |
| Acidity (pKa) | {{{pKa}}} |
| Basicity (pKb) | {{{pKb}}} |
| Chiral rotation [α]D | {{{Rotation}}}° |
| Viscosity | {{{Viscosity}}} cP at 25°C |
| Structure | |
| Molecular shape | {{{Mol_Shape}}} |
| Coordination geometry |
{{{Coordination}}} |
| Crystal structure | {{{Crystal_Structure}}} |
| Dipole moment | {{{DM}}} D |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS[2] |
| Main hazards | {{{Hazards}}} |
| NFPA 704 | {{{NFPA}}} |
| Flash point | {{{Fp}}}°C |
| R/S statement | R: {{{R-S}}} S: ? |
| RTECS number | {{{RTECS}}} |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Structure and properties |
n, εr, etc. |
| Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour Solid, liquid, gas |
| Spectral data | UV, IR, NMR, MS |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | {{{Other_anion}}} |
| Other cations | {{{Ohter_cation}}} |
| Related compounds | {{{Relative_Compounds}}} |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | |
| Structure | |
|---|---|
| Molecular shape | {{{MolShape}}} |
| Coordination geometry |
{{{Coordination}}} |
| Crystal structure | {{{CrystalStruct}}} |
| Dipole moment | {{{Dipole}}} D |
Introduction
Bisacodyl is a stimulant laxative, which is used in a short term basis to treat constipation. It acts on nerve endings in the walls of the intestine and the rectum. It causes the muscles in the intestine to contract more often and with increased force. When the intestine contracts it moves the gut contents along faster, thereby relieving constipation. It is also used to empty the bowel before surgery or examination procedures such as X-ray procedures using barium enemas. Bisacodyl is available with or without a medical prescription.
Possible side effects
The side effects of bisacodyl on human include:
- stomach cramps
- upset stomach
- diarrhea
- stomach and intestinal irritation
- faintness
- irritation or burning in the rectum (from suppositories)
Consult the doctor if the above symptoms are severe and persist.
Storage
Store tablets in tightly closed containers in cool place.
3D Structure
Bisacodyl |
Syntheisis of Bisacodyl
A new method of sythesise bisacodyl is introduced by Mereyala, H. B. and Sambaru, K. on 2005. The key step involves migrating the 2-pyridacyl group of phenyl pyridine-2-carboxylate 4 in AlCl[3] at 160 °C to yield the intermediate 4-hydroxyphenyl (2-pyridyl)ketone. The above reaction is then treated with phenol using H3PO4 to give bisacodyl. This method has advantage over the existing literature methods because the starting material, pyridine-2-carboxylic acid is easily available whereas the less stable compound, pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde was normally used previously.
References
1.http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?Name=bisacodyl&Units=SI&cIR=on&cMS=on&cUV=on 2.http://chembank.broad.harvard.edu/chemistry/viewMolecule.htm?cbid=982&desc=* 3.http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/medmaster/a601027.html
