It07:Benzocaine
Appearance
Benzocaine
Introduction
Benzocaine is a local anaesthetic with a range of applications, although it is most commonly used as a topical pain reliever in many over-the-counter medications.
| It07:Benzocaine | |
|---|---|
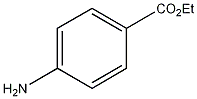
| |
| General | |
| Systematic name | ethyl 4-aminobenzoate |
| Other names | Benzoic acid, p-amino-, ethyl ester; p-(Ethoxycarbonyl)aniline; p-Aminobenzoic acid, ethyl ester; p-Carbethoxyaniline; p-Ethoxycarboxylic aniline; Amben ethyl ester; Anaesthan-syngala; Anaesthesin |
| Molecular formula | C9H11NO2 |
| SMILES | NC1=CC=C(C(OCC)=O)C=C1 |
| Molar mass | 165.19 gmol-1 |
| CAS number | 94-09-7 |
| Properties | |
| Melting point | 88 oC |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | |
Pain Relief
Pain is caused the stimulation of pain receptors at the end of nerves. The stimulation caused sodium to enter the neuron, building up an electrical potential. This signal is then passed along the nerve to the brain where it is interpreted as pain. Benzocaine works by preventing sodium entering the nerve ending. This allows benzocaine to be used as a topical pain reliever.
Uses
Uses of benzocaine
- Appetite suppressants
- Astrigents
- Analgesics
- Burn and sunburn remedies
- Cough tablets, drops and lozenges
- Haemorrhoidal creams, suppositories and enemas
- Oral and gingival products for teething, toothache canker sores and denture irritation
- Oral antibacterial agents
- Treatments for athlete’s foot, corns, calluses and warts
- Sore throat sprays and lozenges
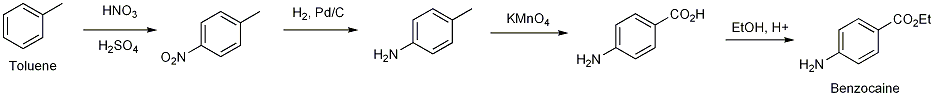
Synthesis
Synthesis pathway for Benzocaine:
Spectra
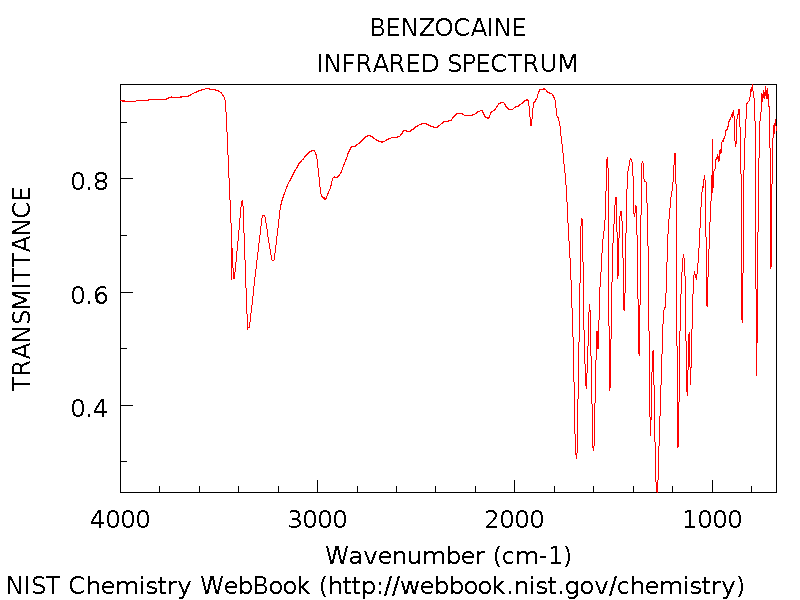
Infrared
Mass Spectrum
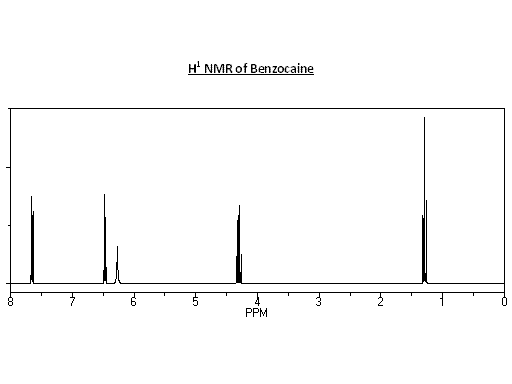
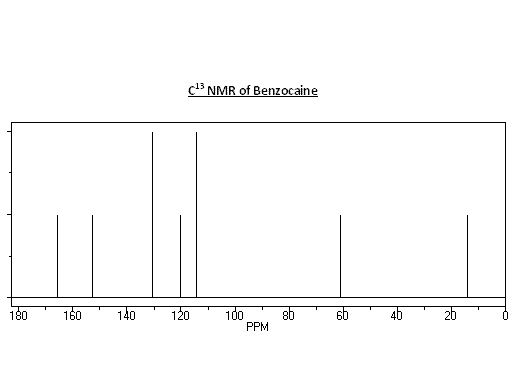
NMR
References
- "Organic Chemistry" Clayden et al
- http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/
- http://www.pcl.ox.ac.uk/MSDS