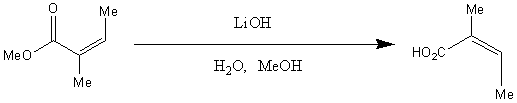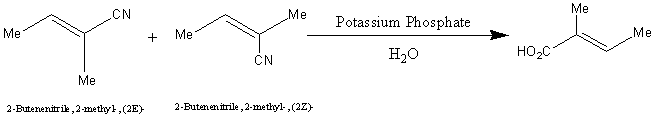It07:Angelic Acid
Angelic Acid
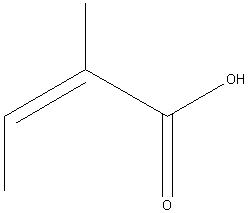
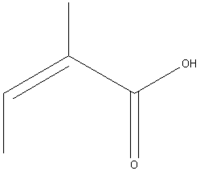
Angelic acid is an organic, carboxylic acid, found in various plants. Despite its name, it is not "angelic" at all since it is used as a defence substance for beetles. It is also known as "(Z)-2-Methyl-2-butenoic acid." 2
| Angelic Acid | |
|---|---|
| |
| General | |
| Systematic name | (Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoic acid |
| Other names | 2-Butenoic acid, 2-methyl-, (Z)-; Angelic acid (6CI,7CI); Crotonic acid, 2-methyl-, (Z)- (8CI); cis-.alpha.,.beta.-Dimethylacrylic acid; cis-2-Methyl-2-butenoic acid |
| Molecular formula | C5H8O2 |
| SMILES | CC=C(C)C(=O)O |
| Molar mass | 100.116g/mol |
| CAS number | 565-63-9 |
| Properties | |
| Density & phase | 0.96 g/cm³ |
| Melting point | 45°C |
| Boiling point | 183 - 185°C |
| Refractive Index | 1.4430 |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | [(data page)#Material Safety Data Sheet|External MSDS] |
| Main hazards | Harmful, Irritating to eyes, Irritating to respiratory system, |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Spectral data | IR, NMR, MS |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | |
Anglic Acid |
Angelic acid is the (Z) isomer. The other isomer, (E), is called "Tiglic Acid," and is also a beetle defence system.

Anglic Acid |
Angelic acid and tiglic acid are a pair of cis-trans isomers. Angelic acid is the (Z) isomer where as tiglic acid is the (E) isomer. Angelic acid has a pungent odour and a biting acid taste. It can also crystallise, giving colourless prisms. Angelic acid used to be used therapeutically as a sedative. 3
Formation of Angelic Acid
Angelic Acid is found to occur naturally and can be made from many different reactions. Its isomer, Tiglic acid, however, is not naturally occurring and has to be synthesized.
Below is the reaction scheme for the formation of angelic acid.
The reactant in this reaction is known as Methyl (Z)-2-methyl-2-butenoate. It has chemical formula
C6H10O2.
Essentially, what is happening here is a hydrolysis reaction. The ester is broken down by water, forming a carboxylic acid (angelic acid) and an alcohol should also form.
The reaction is carried out under reflux and produces a ~90% yield.
The reaction scheme for the formation of tiglic acid is shown below:
This reaction should produce a 100% yield.
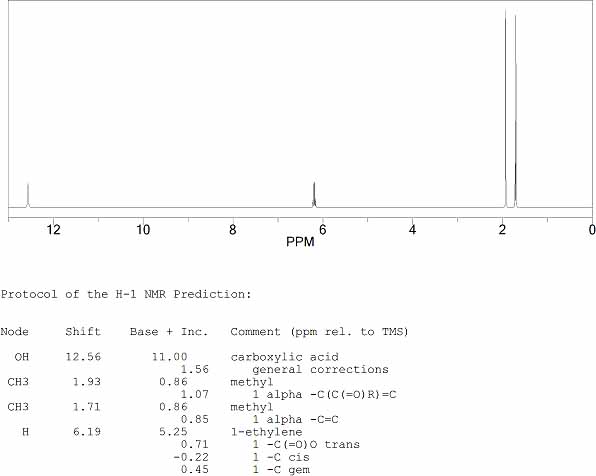
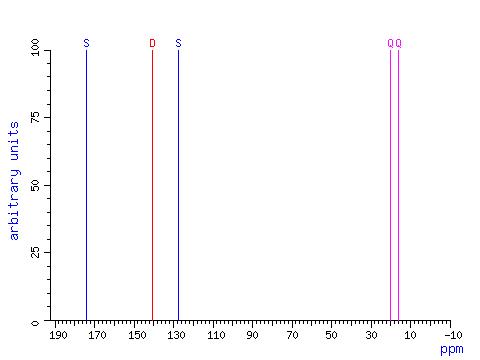
NMR Spectrum
The 13C NMR spectrum of Angelic Acid
The Predicted 1H NMR spectrum of Angelic Acid is shown below.