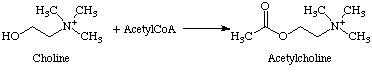It07:Acetylcholine
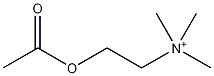
Acetylcholine
| Acetylcholine | |
|---|---|
| |
| General | |
| Systematic name | 2-acetoxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium |
| Other names | ACh |
| Molecular formula | C7H16NO2 |
| SMILES | CC(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)=O |
| Molar mass | 147.22gmol-1 |
| CAS number | 51-84-3 |
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter and was the first of its kind to be discovered, by Henry Hallett Dale in 1914. It is an ester of acetic acid and choline and is the neurotransmitter released upon stimulation of the vagus nerves.
3D Structure
Synthesis
Acetylcholine is synthesised by the reaction of choline with acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) and is catalysed by choline acetyltransferase, a biological enzyme.
Image taken from http://www.neurosci.pharm.utoledo.edu/MBC3320/acetylcholine.htm.
Once the acetylcholine has performed its function, it is degraded by acetylcholinesterase, another important biological enzyme.
Function
Acetylcholine has uses in both the central nervous system (CNS), and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). In the peripheral nervous system (ie nervous pathways not involving the brain and spinal chord) acetylcholine is one of the main neurotransmitters involved in the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is involved in regulation and homeostasis. In the autonomic nervous system acetylcholine stimulates muscles by activating receptors on the cell membranes of target cells, which then release sodium ions into the intended cell, which in turn triggers an action potential, resulting in muscle contraction.
Uses
Acetylcholine has been used directly as a treatment for certain conditions. Its action in the body can be altered, by either blocking its effects altogether, or by merely hindering its effects. It can also be introduced to the body to certain target areas. For example it can be used during eye surgery to induce rapid pupil constriction. Also, inhibitors which stop acetylcholinesterase degrading acetylcholine are used to counter the effects of muscle relaxants, and are also found in certain medications used to treat Alzheimer’s.
References
- http://www.neurosci.pharm.utoledo.edu/MBC3320/acetylcholine.htm
- C. Y, Hong, L. J. Lai, Y. T, Huang; Life Sciences; Vol. 57; Issue 13; 1995
- http://www.iscid.org/encyclopedia/Acetylcholine
Awc106 13:52, 28 November 2007 (UTC)