Inorganic comp MOF17
BH3
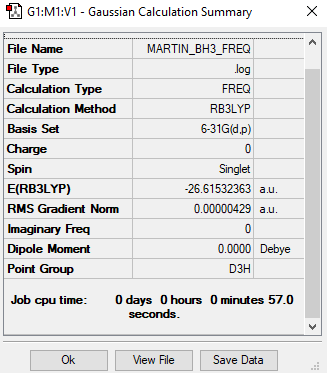
Summary table
Convergence criteria
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000009 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000034 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000017 0.001200 YES
Log file
Frequencies
Low frequencies --- -2.2126 -1.0751 -0.0054 2.2359 10.2633 10.3194 Low frequencies --- 1162.9860 1213.1757 1213.1784
JMol file
BH3 |
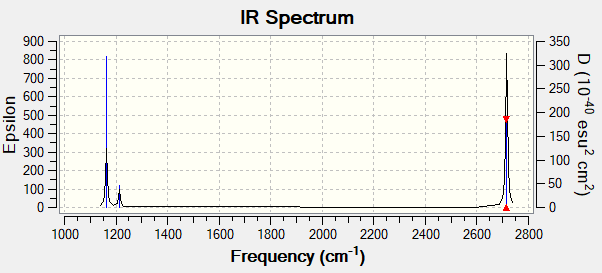
Vibrational analysis
| wavenumber (cm-1 | Intensity (arbitrary units) | symmetry | IR active? | type |
| 1163 | 92.5 | A2" | yes | bend |
| 1213 | 14.1 | E' | very slight | bend in plane |
| 2582 | 0 | A1' | no | symmetric stretch |
| 2715 | 126.3 | E | yes | asymmetric stretch |
Ng611 (talk) 19:51, 13 May 2019 (BST) You need to list all of the modes in this table (I'm guessing you combined the degenerate modes when you put the table together)
There are only three peaks in the spectrum below because two of the vibrations are doubly degenerate and one is not IR active.
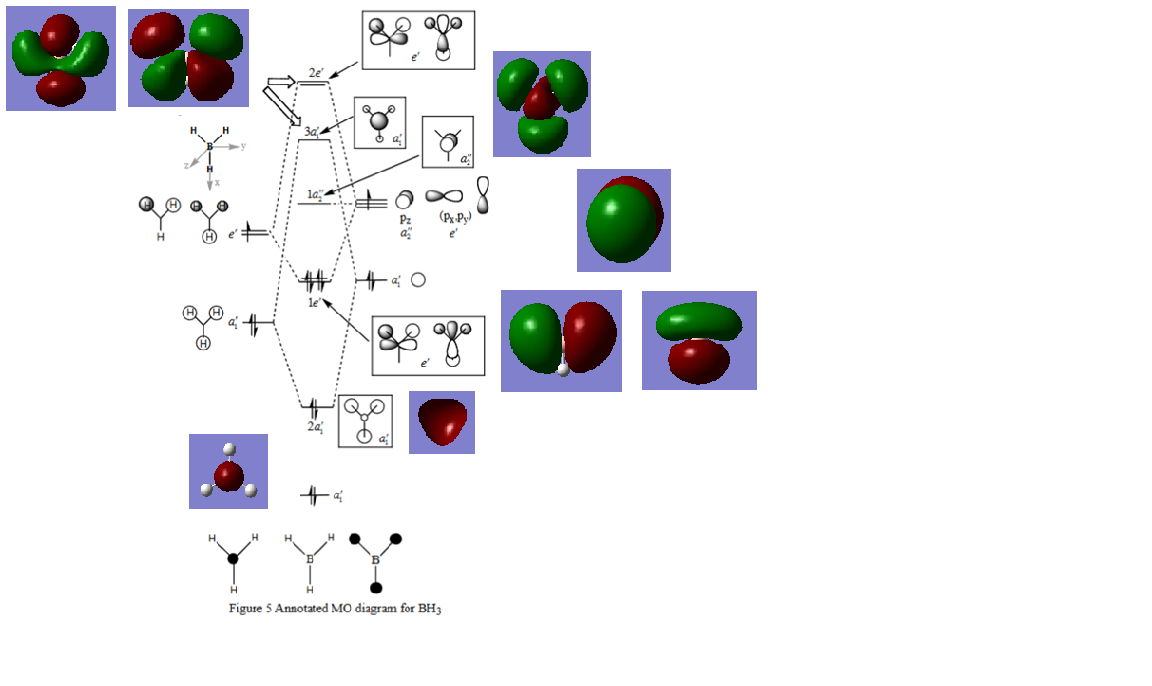
Molecular orbital diagram of BH3
Reference: Hunt Research group; Tutotial problem; available at [1]
The computed MOs do differ slightly from the LCAOs, namely e.g. in the phase distribution, although the general shape and size distribution are both quite good. This does not mean that they are not useful in illustrating the way atomic orbitals combine to result in bonding.
NH3
Summary table
Ng611 (talk) 19:53, 13 May 2019 (BST) This is your BH3 summary table
Convergence criteria
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000005 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000012 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000008 0.001200 YES
Log file
Frequencies
Low frequencies --- -11.5222 -11.4865 -0.0033 0.0245 0.1415 25.6160 Low frequencies --- 1089.6618 1694.1735 1694.1738
JMol file
NH3 |
NH3BH3
Summary table
Convergence criteria
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000122 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000058 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000582 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000320 0.001200 YES
Log file
Frequencies
Low frequencies --- -0.0009 -0.0003 -0.0003 16.8481 17.4133 37.2932 Low frequencies --- 265.8219 632.2116 639.3277
JMol file
NH3BH3 |
Calculating the association energy
E(NH3)=-56.55777 a.u. E(BH3)=-26.61 a.u. E(NH3BH3)=-83.22469 a.u. ΔE=[E(NH3)+E(BH3)] - E(NH3BH3)= - 0.04 a.u. = - 105 kj/mol
Ng611 (talk) 00:36, 15 May 2019 (BST) It looks like you've used varying numbers of d.p. for your calculation and you've got the wrong answer as a result.
If we compare the association (or dissociation energy of the datively bonded NH3 BH3 pair, we can see that it is much weaker than a C-C bond, making ammonia borane thermally unstable. This comparison is sensible due to the fact that ethane is an isostere of ammonia-borane.
Ng611 (talk) 00:36, 15 May 2019 (BST) You should include the bond enthalpy of a C-C bond (and reference it appropriately)
NI3
Summary table
Convergence criteria
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000064 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000038 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000487 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000278 0.001200 YES
Log file
Frequencies
Low frequencies --- -12.7376 -12.7315 -6.2900 -0.0040 0.0188 0.0633 Low frequencies --- 101.0325 101.0333 147.4122
JMol file
NI3 |
Optimised distance
The optimised distance of the NI3 molecule is 2.184 A.
Lewis acids and bases project
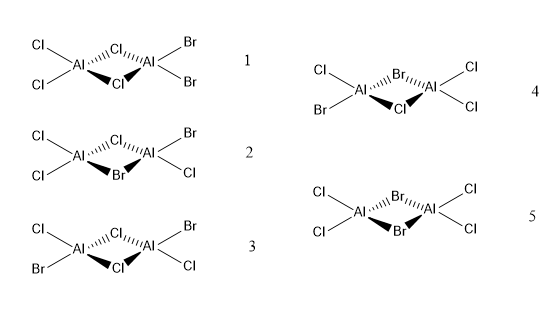
Isomers of AL2CL4Br2
The image above shows the five isomers of Al2Cl4Br2:
1 - The isomer with bromines terminal on the same aluminium
2 - The isomer with one bridging and one terminal Br
3 - The isomer with bromines terminal on different aluminiums and trans
4 - The isomer with one bromine terminal and one bridging
5 - The isomer with bridging bromines
Ng611 (talk) 00:39, 15 May 2019 (BST) What about the point groups?
Two selected isomers
Bridging Br
Summary table
Ng611 (talk) 00:42, 15 May 2019 (BST) You've used the wrong pseudopotential input. Only Br should be subject to a pseudopotential. From the looks of it, you've placed a pseudopotential on Cl as well.
Convergence criteria
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000011 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000005 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001143 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000447 0.001200 YES
Log file
Frequencies
Low frequencies --- -2.1431 -0.7221 -0.0022 -0.0018 -0.0018 2.6967 Low frequencies --- 16.8622 62.4899 84.8790
JMol file
Bridging Br isomer |
Trans isomer
Summary table
Convergence criteria
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000210 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000093 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001293 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000647 0.001200 YES
Log file
Frequencies
Low frequencies --- -4.4638 0.0008 0.0010 0.0013 1.0721 2.7738 Low frequencies --- 18.8020 47.6324 71.2609
JMol file
Trans isomer |
Discussion
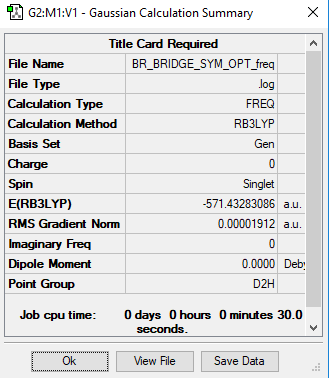
We can read off the energies of the bridging and trans isomers from the summaries tables:
E(bridging)=-571.43283 a.u.
E(trans)=-571.43792 a.u.
ΔE=0.00509=13.36 kj/mol
The reason why the conformer with the bridging bromines (highest energuy of all five conformers) is of higher energy than the trans isomer (which is second only to the isomer with two terminal bromines in being the most stable) is because of the way that the bonding and anti-bonding interactions add up. The aluminium AOs have the best overlap with the chlorine AOs, due to being of a more similar size and therefore diffuseness. Both chlorine and bromine can offer the e-defficient aluminiums electrons by being the bridging atoms, but because the overlap with chlorine is better, it is much more energetically beneficial for the molecule to have as many chlorines as possible as bridging atoms and the bromines on the terminal side.
The dissociation energy of the lowest energy conformer (trans) into two ALCl2Br fragments can be calculated as:
ΔE=2(E(fragment))-E(trans)
ΔE= 2(-285.70300 a.u.)-E(-571.4371 a.u.) = 0.03191 a.u. = 83.779711 kj/mol
Since the dissociation energy is positive, it means that the trans dimer is more stable than the two single monomers.
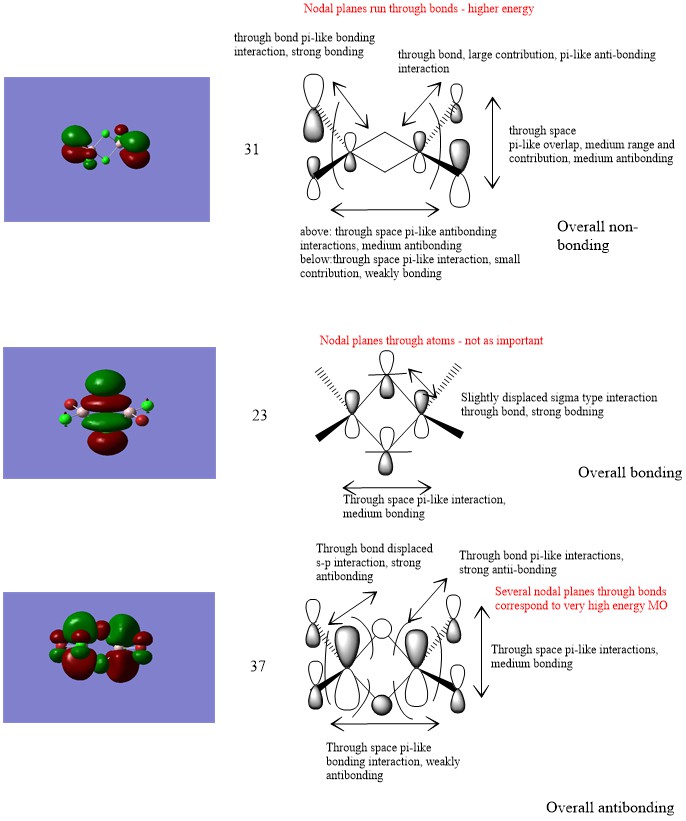
Molecular orbitals presentation
Ng611 (talk) 00:51, 15 May 2019 (BST) A good selection of MO's, well done. I'm dubious as to whether the first one is truly non-bonding, it's more likely that either the bonding or antibonding interactions win out slightly. Otherwise, good!