Inorganic:01338507
BH3 molecule
Computational level and basis set: RB3LYP/6-31G level
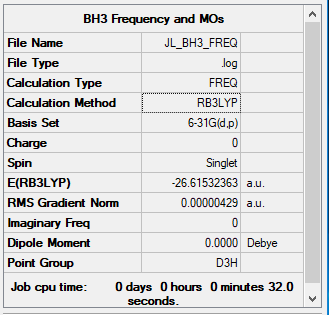
Summary table image:
Item table:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000009 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000034 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000017 0.001200 YES
Frequency analysis log file BH3_frequency.log
Low frequencies:
Low frequencies --- -2.2126 -1.0751 -0.0054 2.2359 10.2633 10.3194 Low frequencies --- 1162.9860 1213.1757 1213.1784
Jmol image of BH3:
BH3 molecule |
Information about BH3 vibrations:
| Mode | Wavenumbers (cm-1) | Intensity | Symmetry | Dipoles (D) | IR active? | Types of vibration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1163 | 317 | A2 | 92.55 | YES | out-of-plane bend |
| 2 | 1213 | 46 | E' | 14.05 | YES | bend |
| 3 | 1213 | 46 | E' | 14.06 | YES | bend |
| 4 | 2582 | 0 | A1' | 0.00 | NO | symmetric stretch |
| 5 | 2715 | 185 | E' | 126.33 | YES | asymmetric stretch |
| 6 | 2715 | 185 | E' | 126.32 | YES | symmetric stretch |
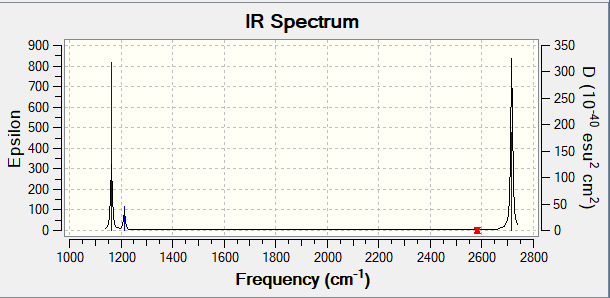
Snapshot of IR spectrum:
Explanations of IR spectrum:
There are six vibration modes of BH3 molecule. However, only four peaks are seen in the IR spectrum. As modes 2 and 3 have same wavenumbers and intensities, peaks of these two modes overlap, therefore overall only 1 peak can be seen for these two modes. So as modes 5 and 6. As for mode 4, there is no change in dipole, therefore IR radiation cannot be absorbed. Mode 4 is IR inactive, no peak can be seen on spectrum.
Ng611 (talk) 19:21, 29 May 2019 (BST) Good!
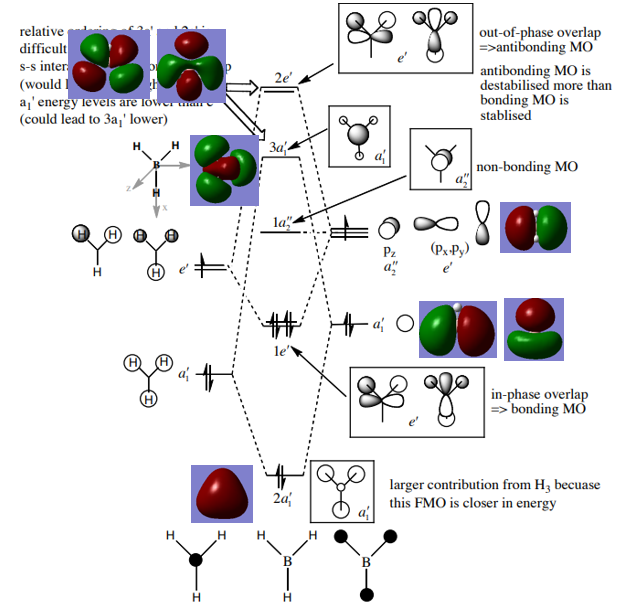
MOs for BH3:
- ↑ Hunt research group tutorial materials
Questions about BH3 MOs:
1. Are there any significant differences between the real and LCAO MOs?
The LCAO MOs only shows the individual AOs fragments and are only theoretical predictions. Real MOs shows the real electronic structure of the molecule. Real MOs shows the exact amount of each AO contribution.
Ng611 (talk) 19:23, 29 May 2019 (BST) How will this affect the predictive power of qualitative MO theory?
2. What does this say about the accuracy and usefulness of qualitative MO theory?
Compared the LCAOs MOs and real MOs, it can be seen that theory predictions correspond to real situation. Therefore, MO theory is useful for making predictions.
Ng611 (talk) 19:23, 29 May 2019 (BST) True, but there are minor differences which you should be able to spot.
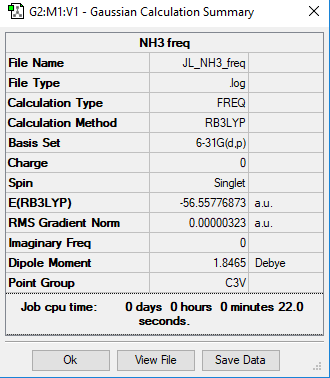
NH3 molecule
Method and Basis set: B3LYP/6-31G(d,p)
Summary table:
Frequency File: Media:JL NH3 FREQ.LOG
Item table:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000012 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000008 0.001200 YES
Frequency Table:
Low frequencies --- -0.0128 -0.0024 0.0002 7.0724 8.1020 8.1023 Low frequencies --- 1089.3849 1693.9369 1693.9369
Image:
optimised NH3 molecule |
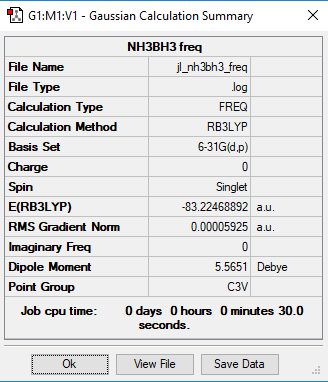
NH3BH3 molecule
Method and Basis set: B3LYP/6-31G(d,p)
Item table:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000121 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000057 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000501 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000293 0.001200 YES
Summary table:
Frequency File: Media:JL NH3BH3 FREQ.LOG
Frequency Table:
Low frequencies --- -0.0252 -0.0033 -0.0009 17.0313 17.0339 36.9288 Low frequencies --- 265.7545 632.2151 639.3376
Image:
optimised NH3BH3 molecule |
Association energies: Ammonia-Borane
energy in AU individual molecules:
E(NH3)= -56.55777 a.u.
E(BH3)= -26.61532 a.u.
E(NH3BH3)= -83.22469 a.u.
Energy difference:
ΔE=E(NH3BH3)-[E(NH3)+E(BH3)]= -0.0516 a.u.= -135 kJ/mol
Ng611 (talk) 19:24, 29 May 2019 (BST) Good calculation!
Questions:
Based on your energy calculation is the B-N dative bond weak, medium or strong? What comparison have you made to come to this conclusion?
The bond strength of C-C bond is 346 kJ/mol. Compared to the energy of C-C bond, the bond strength of N-B bond is much smaller that that of C-C. It can be concluded that B-N dative bond is very weak.
Ng611 (talk) 19:24, 29 May 2019 (BST) Good comparison, but provide a reference for your bond enthalpy values!
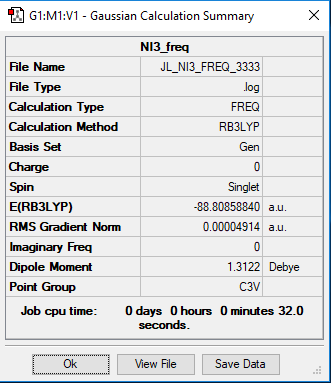
Heavy molecule NI3
Method and Basis set: B3LYB/Gen
Summary table:
Item table:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000139 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000090 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001129 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000796 0.001200 YES
Frequency file: Media:JL NI3 FREQ 3333.LOG
Frequency Table:
Low frequencies --- -12.7178 -12.7118 -6.4125 -0.0039 0.0189 0.0621 Low frequencies --- 101.0754 101.0761 147.4556
Image:
optimised NI3 molecule |
Optimised N-I distance: 2.18370 Å
Ng611 (talk) 19:27, 29 May 2019 (BST) Good! Keep the precision of your result in mind, bond lengths are generally reported to 3 d.p.
Mini project: Ionic Liquids: Designer Solvents
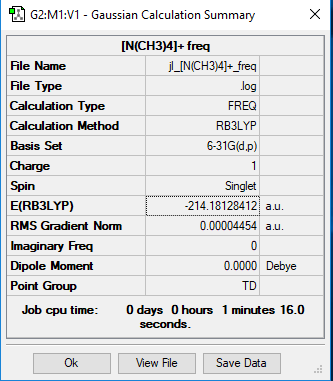
[N(CH3)4]+
Method and Basis set: B3LYP/6-31G(d,p)
Item table:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000068 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000027 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000151 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000067 0.001200 YES
Summary table:
Frequency File: Media:JL -N(CH3)4-+ FREQ.LOG
Frequency Table:
Low frequencies --- -0.0006 -0.0005 0.0009 22.7128 22.7128 22.7128 Low frequencies --- 190.7452 294.0628 294.0628
Image:
optimised [N(CH3)4]+ molecule |
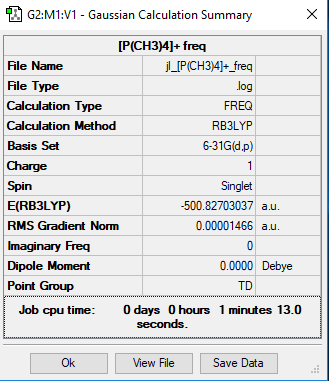
[P(CH3)4]+
Method and Basis set: B3LYP/6-31G(d,p)
Item table:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000030 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000012 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000107 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000044 0.001200 YES
Summary table:
Frequency File: Media:JL -P(CH3)4-+ FREQ.LOG
Frequency Table:
Low frequencies --- -0.0023 0.0023 0.0028 25.3058 25.3058 25.3058 Low frequencies --- 161.2512 195.7467 195.7467
Image:
optimised [P(CH3)4]+ molecule |
Compare charge distribution of [N(CH3)4]+ and [P(CH3)4]+
Charge distribution from NBOs charge analysis:
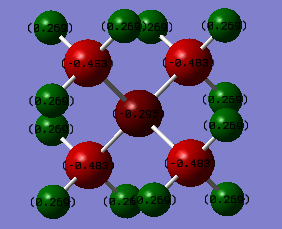

Charge distribution comparison:
[N(CH3)4]+ N:-0.295 C: -0.483 H: 0.269 [P(CH3)4]+ P:1.667 C: -1.252 H: 0.298
Interpret the charge distribution results:
Both [N(CH3)4]+ and [P(CH3)4]+ carry +1 charge. In [N(CH3)4]+, all the positive charge sit on H atoms, while in [P(CH3)4]+ positive charge spread on both H and P atoms. This result can be explained by the electronegativity difference of N and P. As N is much more electronegative than P (N: 3.0, P:2.1), N carries negative charge in [N(CH3)4]+ while P carries some positive charge in [P(CH3)4]+.
In [P(CH3)4]+, C is the most electronegative atom while P and H have nearly the same electronegativity.(P: 2.1, H: 2.1, C: 2.5) Positive charge therefore are on P and H.
In [N(CH3)4]+, N is the most electronegative atom (N: 3.0, C: 2.5, H: 2.1), therefore positive charge are all on H atoms. According to traditional formal charge assignment, the positive charge is assigned on N. This represents the electron deficiency of N compared to its normal valence electron numbers. This traditional formal charge assignment ignores the relative electronegativity of all atoms and assumes all electrons are shared evenly between atoms.
Ng611 (talk) 19:31, 29 May 2019 (BST) Good charge analysis. THink also about the effect of symmetry. What do you mean when you say that 'all electrons are shared evenly between atoms' more specificity is needed.
Molecular orbitals LCAO MO diagram

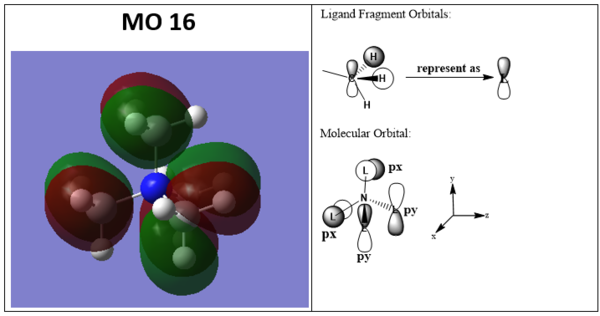
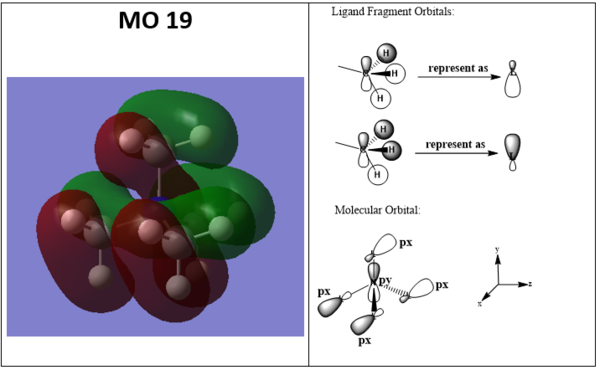
Ng611 (talk) 19:34, 29 May 2019 (BST) Overall an excellent LCAO analysis. It's hard to confirm that the orientation of your p-type FOs in MO19 correspond correctly, although I gave you the benefit of the doubt. Also, try to label and describe the key orbital interactions.