Grubbs' Catalyst
| Grubbs' Catalyst, 1st Generation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
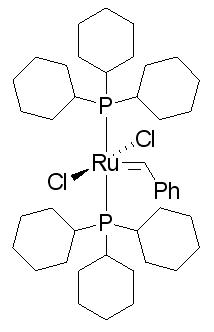 | |||
3D shape - | | |||
| Jmol | |||
| General | |||
| Molecular formula | C43H72C12P2Ru | ||
| Molar mass | 822.96g/mol | ||
| Identifier | |||
| CAS number | 172222-30-9 | ||
| Properties | |||
| Melting point | 153 °C (dec.) | ||
| Appearance | Purple Solid | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | |||
Grubb's Catalyst is a transition metal carbene complex. It was first synthesised by Rober H. Grubbs and it was named after him. There are two generations of the catalyst. Grubbs' Catalyst is very versitile as, unlike other olefin metathesis catalysts, it tolerates other functional groups in the alkene and is compatible with many solvents. [1]
The First Generation Grubb’s Catalyst
The 1st generation Grubbs’ Catalyst is used in olefin cross-metathesis, ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) and ring-closing metathesis. Grubb’s Catalyst is widely used in organic synthesis as it is useful because it is a stable compound in air. [2]
Olefin Metathesis
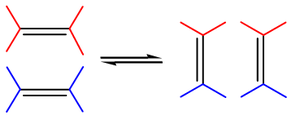
Olefin metathesis is a reaction between two alkene molecules. Olefin metathesis involves redistribution of alkene bonds. The groups bonded to the carbon atoms of the double bond are exchanged between molecules, resulting in two new alkene molecules with swapped groups. The general scope is outlined by the diagram on the left. [3]
The Second Generation Catalyst
The Second Generation Catalyst is also widely used in organic synthesis. In the second generation catalyst the phosphine is replaced with a cyclic bis-amino carbene ligand. It is easily synthesised by combining the first generation catalyst and alkoxy-protected 1,2-dimesityl-4,5-dihydroimidazol-2-ylidene. The resulting ruthenium is coordinated to two carbine groups. The second generation catalyst has a higher activity than the first one does and it is also a air-stable compound. [4]
Application
One of the application of Grubbs’ Catalyst is in aerospace industry. A spaceship has to be made of very strong material, but microcracks form over time. A new material for spaceship hulls contains Grubbs’ Catalyst and capsules of dicyclopentadiene. When a crack forms in the hull, the Grubbs’ Catalyst polymerizes dicyclopentadiene and seals the crack. This is possible as dicyclopentadiene can undergo ring opening metathesis polymerisation.[5]
References
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Grubbs'_catalyst
- http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/ALDRICH/579726
- http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/ALDRICH/569747
- http://www.3dchem.com/molecules.asp?ID=208#
| Grubbs' Catalyst, 2nd Generation | |
|---|---|
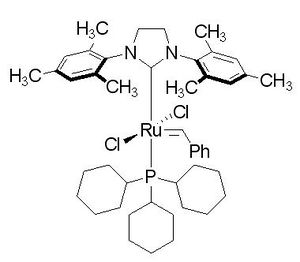 | |
3D shape |- | |
| General | |
| Molecular formula | C46H65C12N2PRu |
| Molar mass | 848.97g/mol |
| Identifier | |
| CAS number | 246047-72-3 |
| Properties | |
| Melting point | 143.5-148.5 °C |
| Appearance | Pinkish-Brown Solid |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | |
