Gm1616
NH3 Molecule
The ammonia moleule was optimized using Gaussview under these setttings. The calculation method setting is RB3LYP. The basis set setting is 6-31G(d.p)
The final energy is -56.55776873 a.u.
The RMS gradient is 0.00000485 a.u.
The point group is C3V
The N-H optimized bond length for all 3 N-H bonds was 1.01798 A. The H-N-H angle is 105.74116 degrees, which is close to the expected 107 degree angle for trigonal planar molecules such as ammonia which have 3 bonds and a lone pair.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986278D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
NH3 optimized molecule |
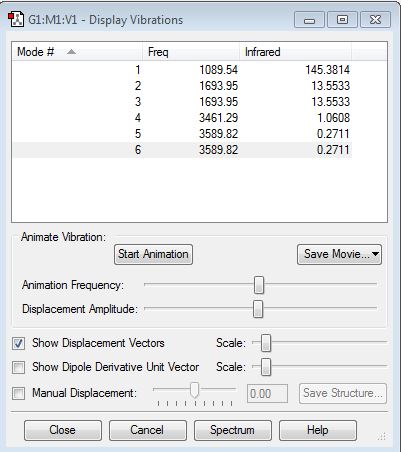
Media:NH3_vibrations_table.JPG
From the 3N-6 rule NH3 is expected to have 3 modes of vibrations. The table shows that the modes at 1096.95cm-1 and 3589.82cm-1 are degenerate. Modes 1 and 4 are stretching and modes 2,3,5 and 6 are bending. The most highly symmetric mode is 4. The 'umbrella' mode is mode 1. There would be 3 vibrational peaks in a spectrum of ammonia but only mode 1 and 2/3 would be seen as the other mode 4, 5 and 6 have too low an intensity.
The Nitrogen has a negative charge of -1.125e and the hydrogens all have a positive charge of 0.375e. This result is expected because the nitrogen is more electronegative than the hydrogens so the nitrogen will be negatively charged. Overall, the charge is 0, which shows that ammonia is a neutral molecule.
Making Ammonia
Hydrogen Molecule
The calculation method is RB3LYP
The basis set is 6-31G(d.p)
The final energy is -1.17853936 a.u.
The RMS gradient is 0.00000017 a.u.
The point group is DinfH
The H-H optimized bond length was 0.74279 A.
The H-H angle is 180 degrees.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
H2 optimized molecule |
The only frequency of vibration for H2 is at 4465.68cm-1 but it would show no peak on an IR spectrum since H2 has no dipole moment.
Nitrogen Molecule
The calculation method is RB3LYP
The basis set is 6-31G(d.p)
The final energy is -109.52412868 a.u.
The RMS gradient is 0.00000060 a.u.
The point group is DinfH
The N-N optimized bond length was 1.10550 A with a triple bond.
The N-N angle is 180 degrees.
<per>Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.401084D-13 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.</per>
N2 optimized molecule |
The vibration for nitrogen is at 2457.33cm-1 but there would be no peak in the spectrum becasue there is no change in dipole.
Haber-Bosch process
E(NH3)=56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)=113.1155375 a.u.
E(N2)=109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)=1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)=3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05579262 a.u.
ΔE= -146.484 kJmol-1 This value indicates that the reactant gases are less stable than the ammonium product, hence the reaction is exothermic and so the condition that produces the greatest yield is a lower temperature. Literature values for the process show that ΔH=-92kJmol-1
ClF3
For analysis the calculation method on Gaussian was RB3LYP and the basis set was 6-31G(d.p). The molecule had to be positioned into a T-shape before analysis or else Gaussian would predict a planar molecule which did not account for the 2 lone pairs of electrons on chlorine.
The final energy is -759.44149573 a.u.
The RMS gradient is 0.00017032 a.u.
The point group is C3
The Cl-F optimized bond length was 1.77281 A. The F-Cl-F angle is 87.0847 degrees which is expected because this is the point of minimum repulsion since the 2 lone pairs of electrons on the chloride repel each other more, so the bond angle between the fluorines is reduced.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000312 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000166 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001473 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000881 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.522335D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found
The charge on the Cl atom is +1.224e and the charge on each of the F atoms is -0.454e or -0.316e. Cl is expected to be positive as it is less electronegative than fluorine.
ClF3 optimized molecule |
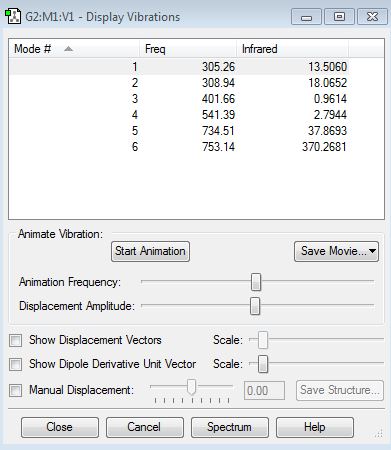
Media:clf3_vibration_table.JPG
An IR spectra of ClF3 would show 4 peaks, the peaks at 305.26cm-1 and 308.94cm-1 or 734.51cm-1 and 753.14cm-1 may overlap so only 2 peaks would be seen. The peak at 541.39cm-1 would not be seen as there is no change in dipole moment in this vibration. The peak at 401.66cm-1 would not be seen as the intensity of the peak is too low to be distinguishable from background noise.