EM2016
Introduction to Molecular Modelling 2
NH3
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy: -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS Gradient: 0.00000485 a.u.
Point Group: C3V
Bond Length: 1.01798 Å
Bond Angle: 105.741°
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986262D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
NH3 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
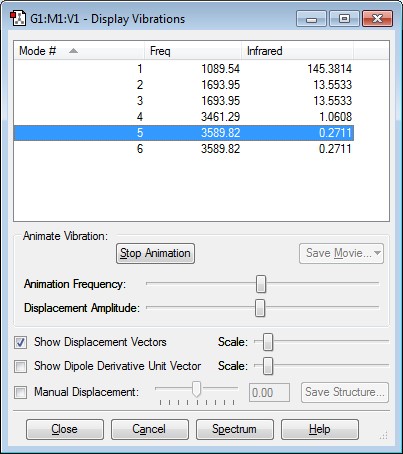
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
6
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
Modes 2 and 3, and 5 and 6 have the same energy.
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Bending Vibrations Modes: Modes 1, 2, 3
Bond Stretch Vibrations Modes: Modes 4, 5, 6
Which mode is highly symmetric?
Mode 4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
Mode 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
4 Bands
Charge Of N and H
The Charge of the N is -1.125 and H is +0.375. The Nitrogen is expected to have a negative charge since it is more electronegative and draws electron density towards itself more strongly than H does. Hence the H would be more positively charged.
N2
What is the molecule?
N2
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-109.52412868 a.u.
What is the RMS gradient?
0.00000060 a.u.
What is the point group of your molecule?
D∞H
Bond Length
1.09200 Å
Bond Angle
180°
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401114D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
N2 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
H2
What is the molecule?
H2
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-1.17853936 a.u.
What is the RMS gradient?
0.00000017 a.u.
What is the point group of your molecule?
D∞H
Bond Length
0.60000 Å
Bond Angle
180°
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.167770D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
H2 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Reaction Calculations
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 Hartrees
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746 Hartrees
E(N2)= -109.52412868 Hartrees
E(H2)= -1.17853936 Hartrees
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 Hartrees
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= [-113.11553746-(-109.52412868 - 3.53561808)]= -0.0557907 Hartrees.
This is equal to -146.48 KJ/Mol. The Ammonia product is more stable.
SiH4
What is the molecule?
SiH4
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-291.88802760 a.u.
What is the RMS gradient?
0.00000002 a.u.
What is the point group of your molecule?
TD
Bond Length
1.48485 Å
Bond Angle
109.471°
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.452094D-14
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(1,5) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(3,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(4,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,5,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(2,1,5,4) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(3,1,5,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
SiH4 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
The Charge distribution of SiH4 is: The Si atom has a charge of 0.629 and the H has a charge of -0.157. H is more electronegative than Si and hence the electron density is orientated more strongly towards the H, making the H more negative.
Molecular Orbitals
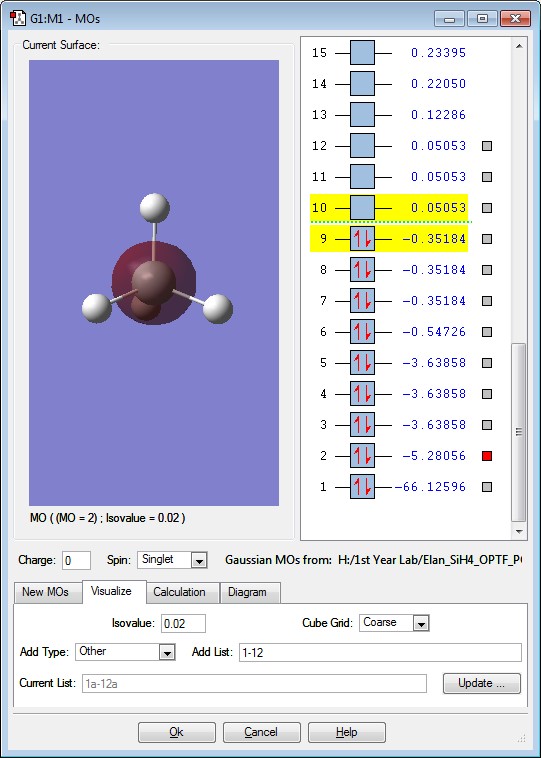
This is the 2s Orbital of Si. It is deep in energy with a value of -5.28056. There are no other Atomic Orbitals contributing towards the 2s Orbital. This orbital is occupied by 2 electrons.
This is the 2px Orbital of Si. It is deep in energy with a value of -3.63858. There are 3 degenerate orbital energies for the 2p orbital. There are no other Atomic Orbitals contributing towards the the 2p orbital. This orbital is occupied by 2 electrons.
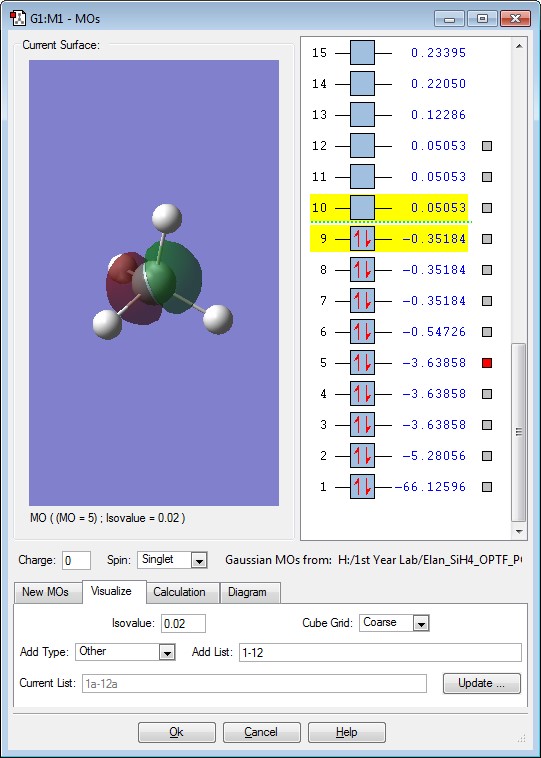
This is the σ interaction between the 3s orbital of the Si and 1s of the H. The energy of this Molecular Orbital is -0.54726. This orbital is occupied by 2 electrons.
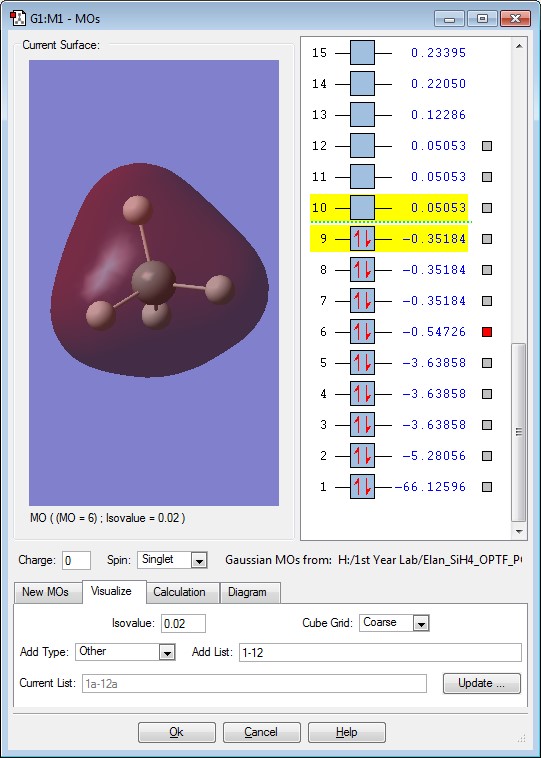
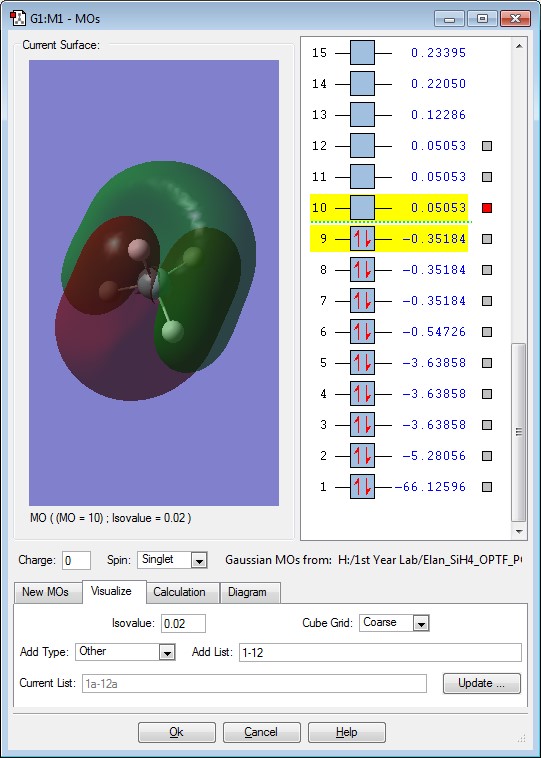
This is the π interaction between the 3p orbital of the Si and the 1s of the H. The energy of this Molecular Orbital is -0.35184. There are 3 degenerate energies for this Molecular Orbital. This orbital is occupied by 2 electrons. This Molecular orbital would be the HOMO of the Molecule.
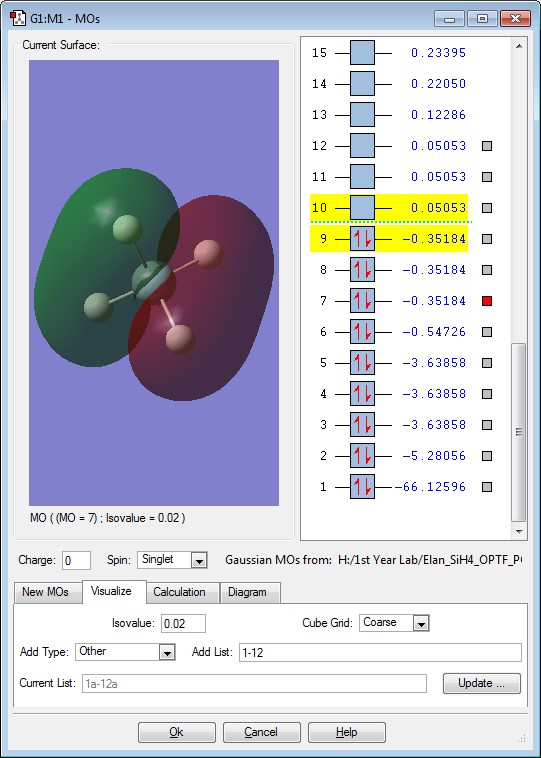
This is the π* Antibonding Molecular orbital between the 3p orbital of the Si and the 1s of the H. The energy of this Antibonding Molecular Orbital is +0.5053. There are 3 degenerate energies for this Antibonding Molecular Orbital. This orbital is unoccupied. This Molecular orbital would be the LUMO of the Molecule, if electrons were to occupy the orbital the molecule would start to destabilize.
Independence- Comparing Methane and Silane
What is the molecule?
CH4
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-40.52401404 a.u.
What is the RMS gradient?
0.00003263 a.u.
What is the point group of your molecule?
TD
Bond Length
1.09197 Å
Bond Angle
109.471°
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000063 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000034 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000179 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000095 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.256037D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R4 R(1,5) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(3,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(4,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,5,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(2,1,5,4) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(3,1,5,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
CH4 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
From the information obtained about Methane the Bond length of Silane is longer than that of Methane, this is supported by the fact that Silane is a larger molecule with a larger central atom. The interaction between the atomic orbitals in Silane are weaker because of the mismatch of the energy of the orbitals, a 3s to 1s and 3p to 1s interaction. Compared to Methane, having a 2s to 1s and 2p to 1s interaction. The Bond angle is the same between Silane and Methane because the hybridisation of the molecules are the same and so the same shape of the molecule is obtained. Also as the bonding and structure is similar, it follows that there are no lone pair of electrons to change the angle of molecule.