Domoic Acid
Introduction
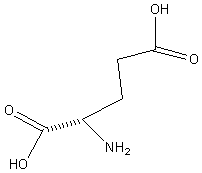
Domoic Acid belongs to the family of molecules collectively known as the kainoid amino acids. In Domoic acid the R-group takes the form of an octadienoic side chain. The acid is also a phycotoxin (a toxin produced by algae). The compound was first synthesized in 1958 from the red marine agla Chondria armanta.
Biological Properties
Members of the Kainoid family display potent biological effects. Domoic acid is no exception; It is well known for is use as an insecticide and as an anthelmintic, a substance that kills or stuns parasitic worms. The latter property was first discovered by the Japanese in the town of Tokunoshima, Kagoshima, where the compound is still used today for that purpose.
Neurological Properties
Domoic acid displays neuroexcitatory properties; it causes neuronal death, literally by exciting cells to death. The actual mechanism for this is similar to that which occurs in sufferers of dementia. Domoic acid and other kainoid derivatives are therefore currently being studied intensively in an effort to develop tools (drugs) to fight other debilitating diseases such as Huntington’s and epilepsy. These neurological properties are believed to derive from the kainoids' structural similarity to the neurotransmitter, glutamic acid.
Domoic acid is the causative agent behind a rare condition known as 'Amnesic shellfish poisoning' or ASP. The condition causes short term memory loss (hence 'amnesic'); dizziness, nausea, vomiting and can eventually result in serious brain damage or death. Domoic acid poisons in this fashion by mimicking the action of glutamic in the hippocampus region of the brain (the area of learning and memory). However when the so called molecular trojan horse (dormoic acid) binds to receptors in the hippocampus an excitotoxic event occurs which causes the continuous sending of impulses, eventually leading to 'burn out' resulting in brain lesions and the memory loss characteristic of the condition.
Synthesis
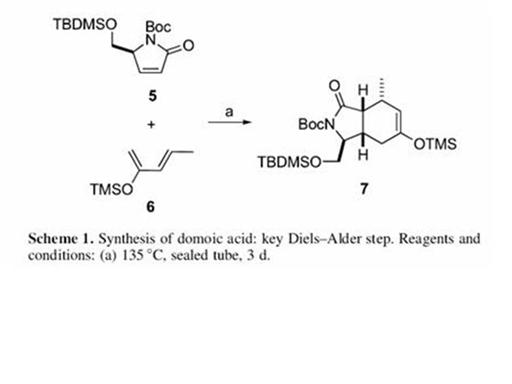
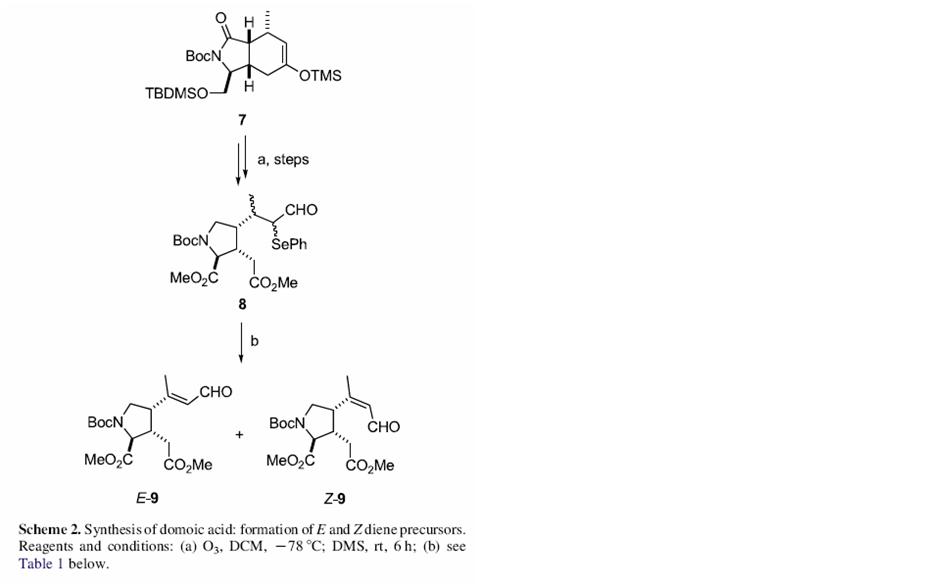
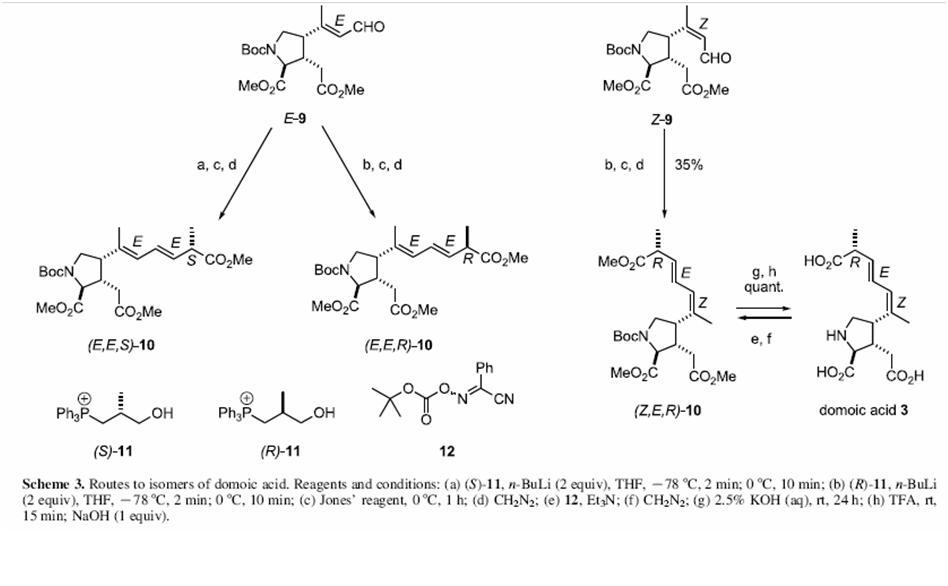
The total synthesis of Domoic as has been reported just once by Ohfune and Tomita in 1982[1]. The various steps in the synthesis are shown below:
References
- ↑ Ohfune, Y.; Tomita, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 3511.
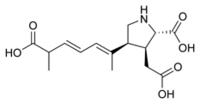
| Domoic Acid | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| General | |||
| Systematic name | 3-Pyrrolidineacetic acid, 2-Carboxy-4-[(1Z,3E,5R)-5-carboxy-1-methyl-1,3-hexadien-1-yl]-(2S,3S,4S) | ||
| Molecular formula | C15H21NO6
| ||
| Molar mass | 311.33 g/mol | ||
| CAS number | 14277-97-5 | ||
| Properties | |||
| Melting point | 490 K (Decomposition) | ||
| Optical Rotatory Power | -109.6 degrees (In water, 589.3nm, 285K) | ||