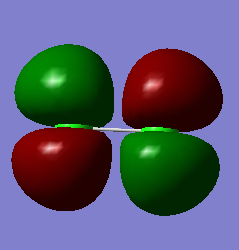
Do261717991799
NH3 Molecule
Summary Data
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy(au) | -56.55776873 a.u |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000485 |
| Point Group | C3v |
| N-H Bond Length | 1.3 Å |
| H-N-H bond angle | 109.471° |
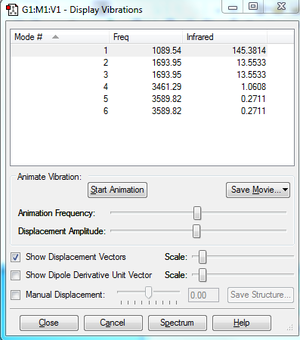
Optimisation Results
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 Molecule |
Here is a link to my NH3 file: here
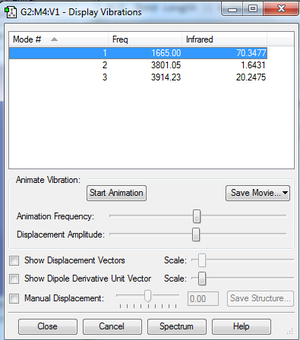
Vibrations
Clicking on the image will take you to the uploaded file page for the image.
- The number of nodes for a non-linear molecule =3N-6, so for NH3, we expect to see 6 nodes
- Modes 2 and 3 are degenerate as well as modes 5 and 6
- Modes 4,5 and 6 are bond stretching and modes 1, 2 and 3 are bond bending vibrations
- Mode 4 is highly symmetric
- Mode 1 is the umbrella mode
- 4 bands would be seen in the experimental spectrum of gaseous NH3
Atomic Charges
- The charge on the Nitrogen atom is -1.125 and on each Hydrogen atom +0.375
- Nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen so it is expected that nitrogen has a negative charge
N2 Molecule
Summary Data
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy(au) | -109.52412868 a.u |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000060 a.u |
| Point Group | D*H |
| N≡N Bond Length | 1.10550 Å |
Optimisation results
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
As seen by the table above, all items did converge.
Vibrations
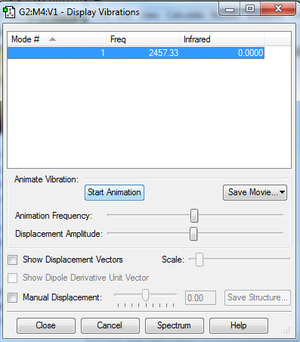
- Clicking on the image will take you to the uploaded file page for the image.
- As seen, the molecule is infrared inactive due to there being no permanent dipole in the molecule.
H2 Molecule
Summary Data
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy(au) | -1.17853936 a.u |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000017 a.u |
| Point Group | D*H |
| H-H Bond Length | 0.74279 Å |
Optimisation results
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
As seen by the table above, all items did converge.
Vibrations
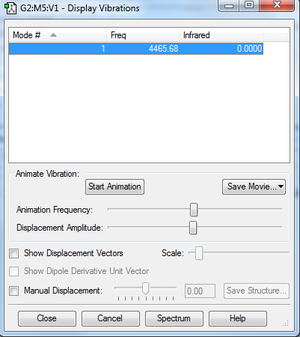
- Clicking on the image will take you to the uploaded file page for the image.
- As seen, the molecule is infrared inactive due to there being no permanent dipole in the molecule.
Energy of reaction for the Haber-Bosch process
- Overall the reaction is: N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
| E(NH3) | -56.55776873 a.u |
| 2*E(NH3) | -113.11553750 a.u |
| E(N2) | -109.52412868 a.u |
| E(H2) | -1.17853936 a.u |
| 3*E(H2) | -3.53561808 a.u |
- ΔE = [2*E(NH3)] - [E(N2) + 3*E(H2)] = [-113.11553750 a.u] - [-109.52412868 a.u + -3.53561808 a.u] = -0.05579070 a.u
- Converting from a.u to KJ/mol, ΔE = -0.05579070 a.u × 2625.5 = -146.48 KJ/mol (2 d.p)
- As ΔH=-ve, the reaction is exothermic, and as such, on an energy diagram, the products (ammonia) will be lower in energy and therefore more stable.
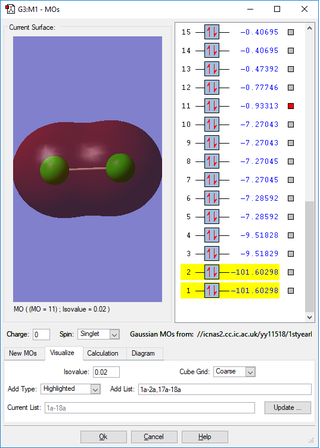
Cl2
Summary Data
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy(au) | -920.34987886 a.u |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00002510 |
| Point Group | D*H |
| Cl-Cl Bond Length(Angstroms) | 2.04174 |
Optimisation Results
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES
- As seen by the table above, all items did converge.
Vibrations
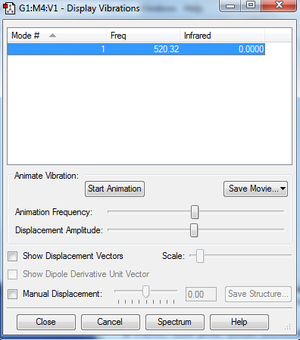
- Clicking on the image will take you to the uploaded file page for the image.
- As seen, the molecule is infrared inactive due to there being no permanent dipole in the molecule.
Atomic Charges
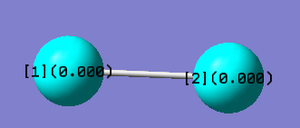
- Clicking on the image will take you to the uploaded file page for the image.
- The Cl2 molecule has no permanent dipole because both atoms both have the same electronegativity. This means no atom has an overall charge.