Cute yd3717
NH3
General information
Molecule name: NH3
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy: E(RB3LYP) = -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS gradient norm: 0.00000485 a.u.
Point group: C3V
N-H bond distance: 1.01798
Experimental N-H bond distance: 1.0124 [1]
H-N-H bond angle: 105.741
Experimental H-N-H bond angle: 106.670 [1]
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
File:YD3717 PHUNT NH3 OPTF POP.LOG
NH3 molecule |
Frequency analysis
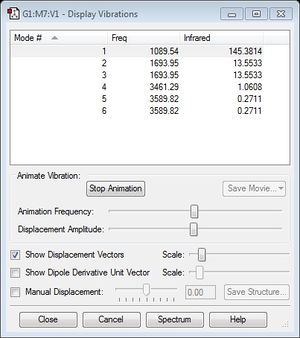
From 3N-6 rule, 6 modes are expected
Mode #2 & #3, also #5 & #6 are degenerate
Mode #1 & #2 & #3 are bending vibrations
Mode #4 & #5 & #6 are bond stretching vibrations
Mode #4 is highly symmetric
Mode #1 is known as the 'umbrella' mode
2 bands are expected to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia, one is #1 and #2 & #3 (they are degenerate). These two are shown because they have a large change in dipole moment.
Atomic charges
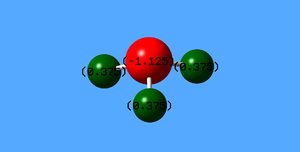
Charge on each N atom : -1.125 e
Charge on each H atom : +0.375 e
H atom was expected to be +1 e, and N atom was expected to be -3 e, so that NH3 would be neutral.
However, due to shielding effect of inner electrons, effective nuclear charge is smaller.
Reaction energies
N2
Molecule name: N2
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy: E(RB3LYP) = -109.52412868 a.u.
RMS gradient norm: 0.00000060 a.u.
Point group: D*H
N-N bond distance: 1.10550
Literature value of N-N bond distance: 1.10 [2]
N-N bond angle: 180
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
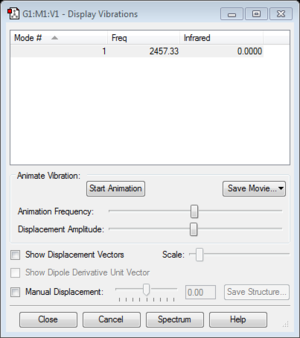
Frequency #1 : 2457.33
N2 molecule |
H2
Molecule name: H2
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy: E(RB3LYP) = -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS gradient norm: 0.00000017 a.u.
Point group: D*H
H-H bond distance: 0.74279
Literature value of H-H bond distance: 0.74 [2]
H-H bond angle: 180
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
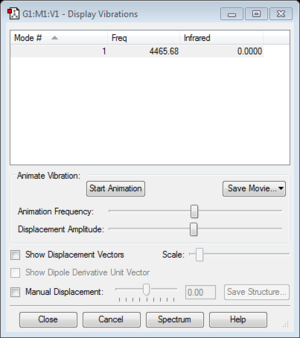
Frequency #1 : 4465.68
H2 molecule |
Reaction
Haber-Bosch process : N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579074 a.u. = -146.478599028 kJ/mol
The ammonia product is more stable than the gaseous reactants
HCl
General information
Molecule name: HCl
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy: E(RB3LYP) = -460.80077875 a.u.
RMS gradient norm: 0.00005211 a.u.
Point group: C*V
H-Cl bond distance: 1.28599
Literature value of H-Cl bond distance: 1.27 [2]
H-Cl bond angle: 180
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000090 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000090 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000139 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000197 0.001200 YES
HCl molecule |
Frequency analysis
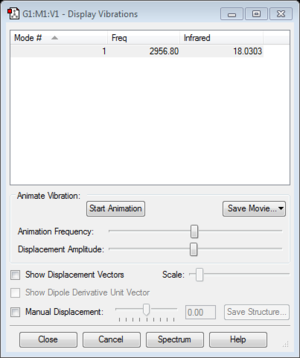
Only one frequency : 2956.80
According to 3N-5 rule, one peak is expected for HCl molecule in the IR spectrum
Atomic charges
Charge on H atom : +0.284 e
Charge on Cl atom : -0.284 e
H atom was expected to be +1 e, and Cl atom was expected to be -1 e, so that HCl would be neutral.
However, due to shielding effect of inner electrons, effective nuclear charge is smaller.
Molecular orbitals
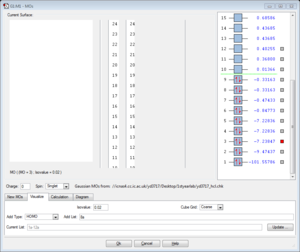
5th MO

This is a molecular orbital of Cl derived from the 2p atomic orbital and it is non-bonding. There should be three degenerate 2p orbital : 3px, 3py and 3pz, each have the same dumbbell shape but orient in different direction. However, the GaussView MO diagram shows there are two degenerate 2p orbitals (#4 & #5) and one 2p orbital slightly lower in energy (#3). This is because #3 2p orbital align with the bond and stabilized by the bond.
6th MO
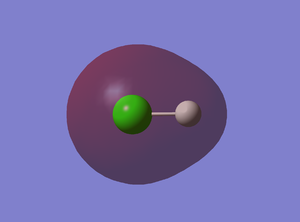
This is a bonding molecular orbital derived from 1s AO of H and 3s AO of Cl. The two AOs overlap in phase to form this sigma garade orbital. It is occupied by two electrons and there is no node.
7th MO
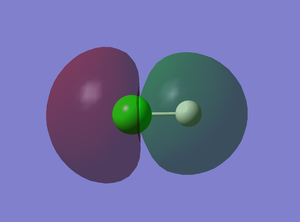
This is a bonding molecular orbital derived from 1s AO of H and 3pz AO of Cl. The two AOs overlap in phase to form this sigma orbital. It is occupied by two electrons and there is one node on the Cl atom.
9th MO
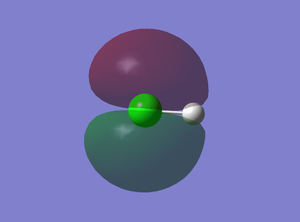
This is a molecular orbital of Cl derived from the 3p AO and it is non-bonding. There are two degenerate 3p orbital : 3px and 3py which corresponds to #8 & #9. 3pz is not degenerate because it is used in bonding (7th MO). The 9th orbital is the HOMO and it is occupied by two electrons.
10th MO
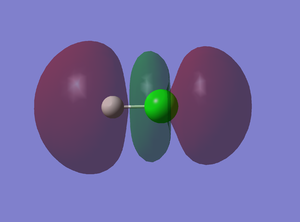
This is an anti-bonding sigma* orbital derived from 1s AO of H and 3pz AO of Cl. The two AOs overlap out of phase and there are two nodes. This is the LOMO molecular orbital.
