Comp 01190874 ABR
Inorganic Lab 2019
BH3
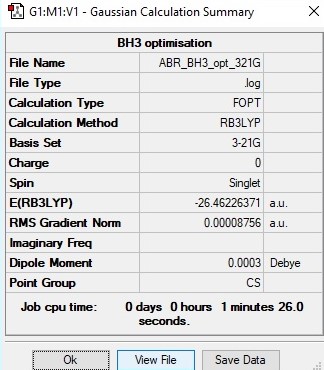
Initial Calculation
B3LYP/3-21G level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000217 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000105 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000919 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000441 0.001200 YES
NB: This is a nice inclusion but not necessary/relevant in terms of presentation. To improve it would have been good to see a comment about why the calculation was done at the lower level of theory first etc. just to make it relevant. Smf115 (talk) 11:50, 26 May 2019 (BST)
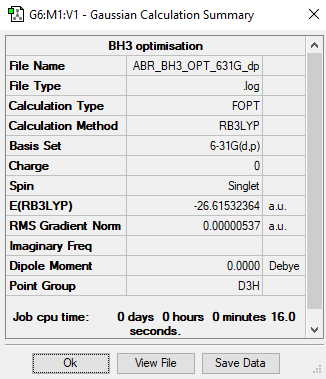
Higher Accuracy Calculation
B3LYP/6-31G level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000012 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000008 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000064 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000039 0.001200 YES
Total energy for 3-21G calculationː-26.46226371 a.u.
Total energy for 6-31G calculation with D3h symmetryː -26.61532364 a.u.
Low frequencies --- -7.5936 -1.5614 -0.0055 0.6514 6.9319 7.1055 Low frequencies --- 1162.9677 1213.1634 1213.1661
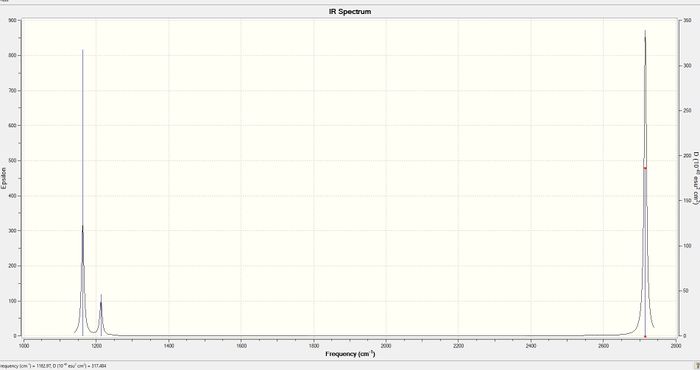
Vibrational Spectrum
| wavenumber (cm-1 | Intensity (arbitrary units) | symmetry | IR active? | type |
| 1163 | 93 | A2 | yes | out-of-plane bend |
| 1213 | 14 | E' | very slight | bend |
| 1213 | 14 | E' | very slight | bend |
| 2582 | 0 | A1' | no | symmetric stretch |
| 2716 | 126 | E' | yes | asymmetric stretch |
| 2716 | 126 | E' | yes | asymmetric stretch |
There are six vibrations for BH3 and only three peaks in the IR spectrum because some vibrations do not produce an overall change in dipole moment and are therefore not IR active - the symmetric stretch is not IR active and is not seen in the spectrum. Some vibrations are degenerate (ie. have the same energies) and therefore appear as one peak in the spectrum - the two asymmetric stretches appear as one as do the two bends. Therefore only three peaks are seen in the IR spectrum.
BH3 |
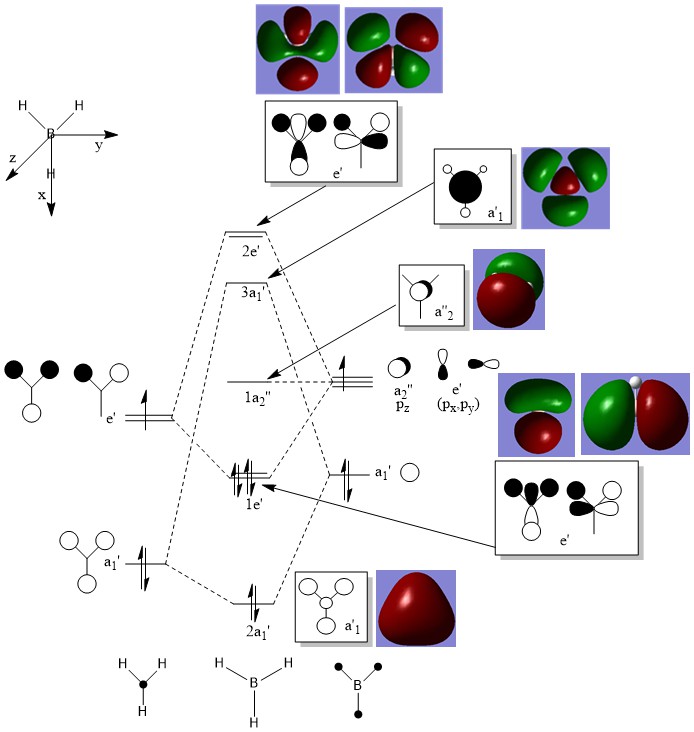
Molecular Orbital Analysis
Although qualitative MO theory does not give a perfect representation of the real MOs, it creates a good prediction of the real MOs. For this reason, qualitative MO theory is relatively usefull in predicting real MOs, as it gives a decently accurate depiction.
Clear inclusion of the calculated MOs on to the diagram with the corresponding LCAOs. While the LCAOs are a good prediction here, it would be an improvement to consider some of the differences which do occur between the calculated and LCAO MOs (e.g. compare the contributions for the 3a' MO). Smf115 (talk) 23:45, 25 May 2019 (BST)
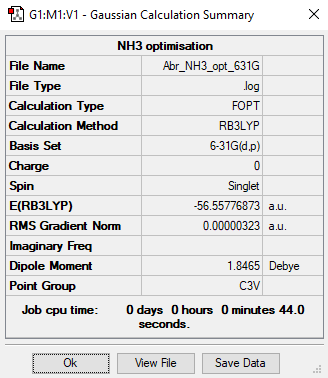
NH3
B3LYP/6-31G level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000012 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000008 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- -8.5646 -8.5588 -0.0047 0.0454 0.1784 26.4183 Low frequencies --- 1089.7603 1694.1865 1694.1865
Total energy isː-56.55776873 a.u.
NH3 |
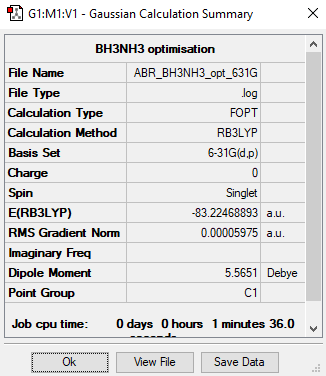
Association Energies - BH3NH3
BH3NH3
B3LYP/6-31G level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000122 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000058 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000513 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000296 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- -0.0010 -0.0010 0.0007 18.4381 27.1658 40.5145 Low frequencies --- 266.4358 632.3947 639.7877
Total energy isː -83.22468893 a.u.
BH3NH3 |
Association Energy Calculations
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
E(BH3)= -26.61532364 a.u.
E(NH3BH3)=-83.22468893 a.u.
ΔE=E(NH3BH3)-[E(NH3)+E(BH3)]
ΔE=-83.22468893-(-56.55776873 + -26.61532364)
ΔE=-0.05159656 a.u. ie. -135.466778599 KJmol-1
This is a sensible value for a bond energy (ie. several hundred KJmol-1.
A BN covalent bond has a dissociation energy of -389±21 KJmol-1. Since the bond strength calculated here is -135.466778599 KJmol-1, this dative covalent bond is significantly weaker than the normal covalent BN bond.
Clear presentation of the respective molecular energies and correct calculation. The accuracy of your final reported energy value needs considering (nearest 1 kJmol-1) and references should always be given for literature values! Smf115 (talk) 23:48, 25 May 2019 (BST)
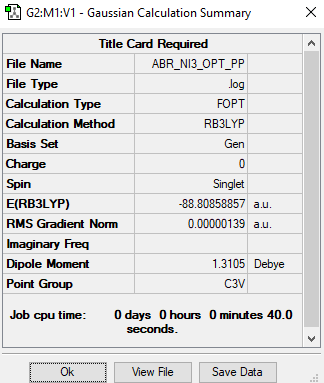
NI3
Maximum Force 0.000002 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000002 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000022 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000014 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- -12.5522 -12.5460 -6.0047 -0.0039 0.0191 0.0664 Low frequencies --- 100.9969 100.9977 147.3377
NI3 |
Final optimised N-I bond distance: 2.18396 Angstrom.
Ionic Liquids Mini Project
Please note that for this section I am aware that my low frequency values are outside the desired range of ± 20-30 cm-1. I was unable to reduce these values while working with demonstrators to resolve the problem, and was told mention this in my wiki.
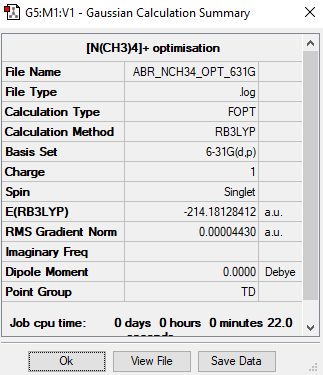
[N(CH3)4]+
Maximum Force 0.000062 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000025 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000152 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000064 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- 0.0002 0.0010 0.0012 35.2347 35.2348 35.2348 Low frequencies --- 218.5716 317.3185 317.3185
N(CH3)4 |
[P(CH3)4]+
Low frequencies --- -0.0027 -0.0025 -0.0015 50.8172 50.8172 50.8172 Low frequencies --- 186.8946 211.7454 211.7454
Maximum Force 0.000030 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000012 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000107 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000044 0.001200 YES
P(CH3)4 |
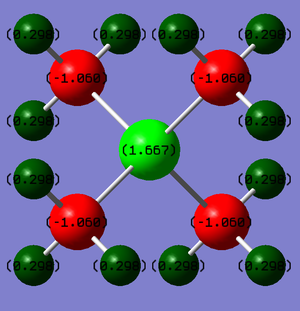
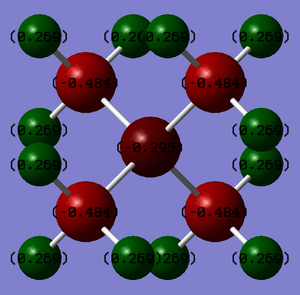
Charge Analysis
Formal charges are a way of estimating the electron distribution of a molecule. In the traditional picture, a formal positive charge on N represents the fact that the N atom has made 4 bonds rather than its preferred 3.
You've presented the NBO charges with an equal charge range across both molecules which is good. However, your answer lacks any analysis of the distributions and you haven't really explained how the traditional formal charge arises (i.e. considering Lewis structures and formal electron counting). Smf115 (talk) 12:19, 30 May 2019 (BST)
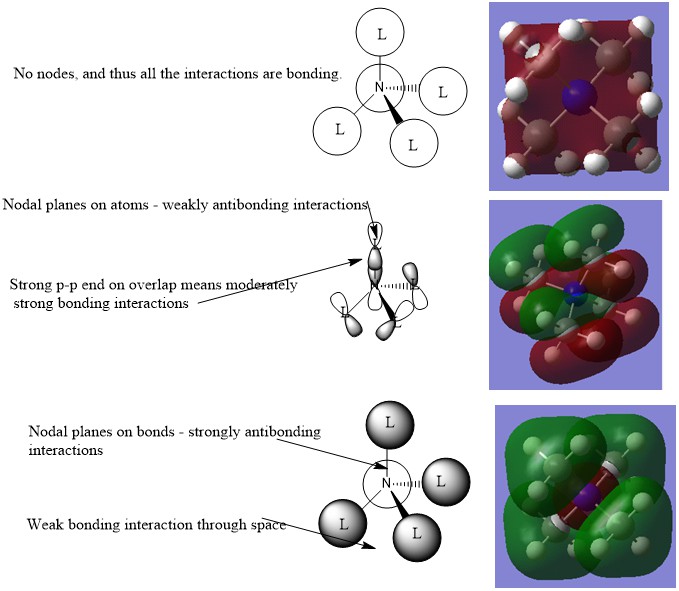
Molecular Orbital Analysis
The top MO shown above is a very bonding one, the middle one is intermediate, and the bottom one is mostly antibonding.
The top MO has all constituents in the same phase, and thus there are no nodes. Thus this represents a very bonding orbital. This is MO 6
The middle MO has some antibonding interactions through space but not along bonds, and some bonding interactions through bonds. It is thus intermediate. This is MO 19
The bottom MO has antibonding interactions along bonds, ie. it has nodal planes intersecting the N-C bonds, and thus represents a fairly antibonding MO. This is MO 10.
You've had a good attempt at evaluating the overall character of the MOs and selected a good range. However, while some of the LCAOs are correct you haven't shown the formation of the corresponding ligand FOs which was a main part of the section. Smf115 (talk) 12:20, 30 May 2019 (BST)
Overall, an ok report but the project section lacks a lot of the necessary analysis. Smf115 (talk) 12:20, 30 May 2019 (BST)