Cetirizine
Cetirizine
Cetirizine 3d.MOL |
General
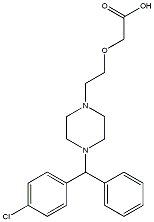
Cetirizine, with the chemical name (±) - [2- [4- [ (4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl] -1- piperazinyl] ethoxy]acetic acid dihydrochloride,a major matabolite of Hydroxyzine,which is an orally active and selective H1-receptor antagonist. The chemical structure is shown below:
This chemical compound is a white, crystalline powder and is water soluble, it is mainly used in medical treatment of allergies, hay fever, angioedema, and urticaria. ZYRTEC tablets(the active component of the chemical compound)are formulated as white, film-coated, rounded-off rectangular shaped tablets for oral administration and are available in 5 and 10 mg strengths.
Synthesis
(S)-cetirizine.2HCl is prepared via the diastereoselective organometallic addition to N-tert-butanesulfnyl adlimines (scheme 1). Organometallic reagent addition to imines is advantageous in that either enantiomeric forms of ceterizine (structure 2) can be produced by changing the imine/ organometallic partner; the imine of 4-chlorobenzaleldehyde (structure 4) with metallobenzene gives the opposite enantiomer to the reaction of benzaldehyde imine (structure 3) with the 4-chlorometallobenzene.
Spectra
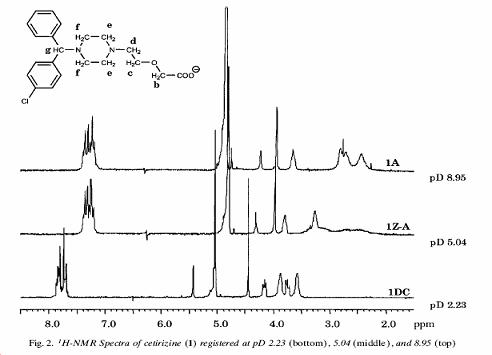
NMR Spectral information showing a variation of chemical shifts against pD; these pD values are obtained when a correction of 0.4 were added to measured pH values[1]
1H-NMR spectra
13C-NMR spectra for the 13C nuclei in D2 nuclei at 24.85 C and 200 MHz.
Pharmaceutical Usage
Usages of ZYRTEC
Preparations
Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis
Symptoms: Zyrtec provides relief to symptoms of sneezing, rhinorrhea, nasal prutitus, ocular pruritus, tearing, and redness of the eyes
Allergens: ragweed, grass and tree pollens are causes of seasonal allergic rhinitis
Perennial Allergic Rhinitis:
Symptoms: sneezing, rhinorrhea, postnasal discharge, nasal pruritus, ocular pruritus, and tearing.
Allergens: dust mites, animal dander and molds
Chronic Urticaria:
Symptoms: uncomplicated skin
Allergens: hives
DOSING: Cetirizine should be taken at doses specifically directed by a physician, it can be taken with food.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Cetirizine should be taken only in doses prescribed. Increasing the dose can be dangerous. When taking cetirizine with theophylline the dose of theophylline may need to be reduced. Cetirizine occasionally can cause sleepiness . Cetirizine can be taken with erythromycin or ketaconazole without the increased risk of heart irregularities common to other non-sedating antihistamines. Cetirizine also can be used to treat children. SIDE EFFECTS: Sleepiness occurs in 14% of patients. Dry mouth, nausea, headache, fatigue, jitteriness and sore throat are infrequently reported with cetirizine. |-
References
| Cetirizine | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Systematic name | (±) - [2- [4- [ (4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl] -1- piperazinyl] ethoxy]acetic acid dihydrochloride |
| Molecular formula | C21H25ClN2O3 |
| SMILES | C1CN(CCN1CCOCC(=O)O)C(C2=CC=CC=C2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl |
| Molar mass | 461.82g/mol |
| Percentage composition | C 64.86%, H 6.48%, Cl 9.12%, N 7.20%, O 12.34% |
| Appearance | White Crystalline powder, water soluble |
| CAS number | 83881-51-0 |
| [1] | Alatrol, Cetirizina MERCK, Cetzine Glaxo, Cetirizin, Humex, Letizen, Razene, Reactine, Zyrtec, Zirtec, Zodac, Zirtek, Zynor, Zyrlek |
| Boiling point | |
| Melting point | 110-115°(for crystals from ethanol) |
| Refractive index | |
| [2] | Well absorbed |
| [3] | 93% avg |
| Lawson Number | 28000, 14305, 3122, 1771 |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Structure and properties |
n, εr, etc. |
| Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour Solid, liquid, gas |