Bc2116x
In the articles below, I have used the software "Guassview" to obtain and explore essential information on NH3, H2, N2, and another small molecule of my own interest as an assignment for First Year Computational Chemistry.
NH3
NH3 is an important molecule in the modern age, with intangible links to our agriculture, industries and economy. It is more commonly known as ammonia. Although it is bonded to three hydrogens, nitrogen is SP3 hybridized due to its lone pair. This causes NH3 to form a pyramidal conformation (pseudo-structure).
test molecule |
Summary of Information on NH3 from Gaussview
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Energy | -56.55776873 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000485 |
| Dipole Moment | 1.8466 debye |
| Point Group | C3V |
Additional Information on Structure
Bond length: 1.01798A
H-N-H Angle: 105.74118A
Point Group: C3v
Item table from LOG.file on NH3
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986273D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Completed NH3 Optimization File
Note: file attached is in .rtf format instead of .log
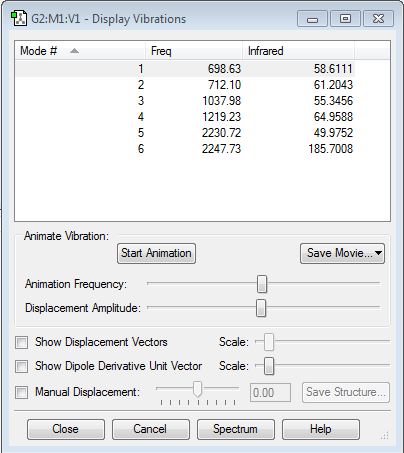
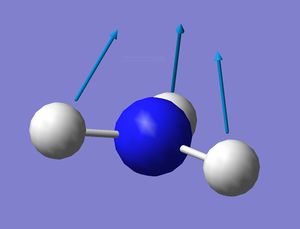
NH3 Vibration Mode
1. 6 vibrational modes are expected from NH3 using the 3N-6 llaw: 3x4-6=6.
2. 2 pairs of degenrate vibrational modes.
3. vibrational modes 1, 2, 3, are bending modes which have lower energies, and 4, 5, 6 are stretching modes.
4. vibrational mode 1 and 4 are highly symmetrical.
5. vibrational mode 1 is otherwise known as umbrella stretching mode.
6. 4 bands is expected in nh3's experimental IR result.
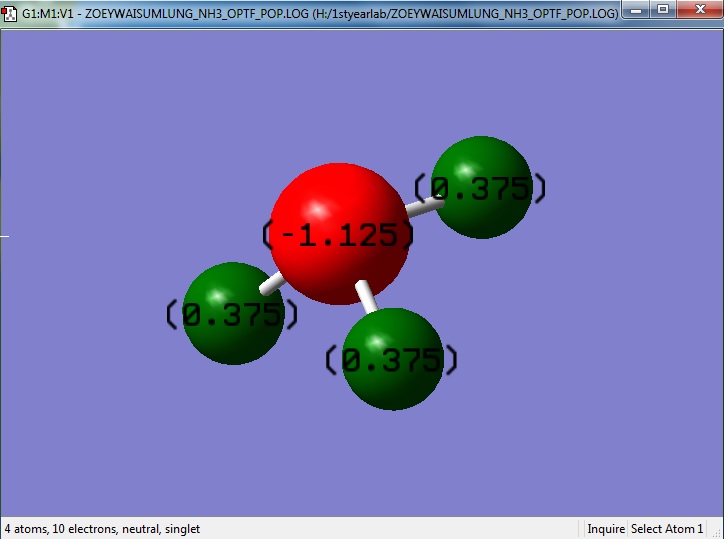
NH3 Charge
H2
Hydrogen is the lightest atom in universe, usually forming H2 gas. Hydrogen gas readily reacts with oxygen, causing explosive reactions.
test molecule |
Summary of Information on H2 from Gaussview
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Energy | -1.14905693 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.11151049 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 debye |
| Point Group | D*H |
Additional Information on Structure
Bond length: 0.76172A
Point Group: D*H
Item table from LOG.file on H2
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000001 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-4.516917D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7617 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
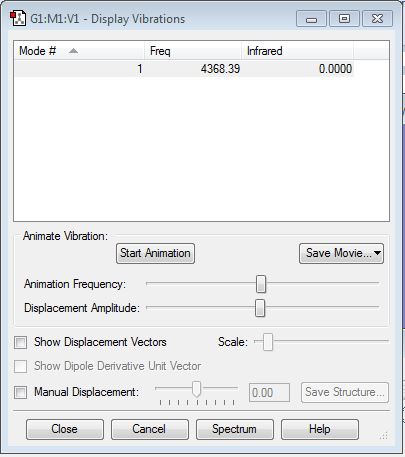
H2 Vibration Mode
H2 is infra red inactive because it has no dipole moment.
N2
Nitrogen forms the inert N2 gas, which can be useful for reactions that requires to be isolated from oxygen.
test molecule |
Summary of Information on N2 from Gaussview
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Energy | -109.52412868 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000060 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 debye |
| Point Group | D*H |
Additional Information on Structure
Bond length: 1.10550A
Point Group: D*H
Item table from LOG.file on N2
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401036D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
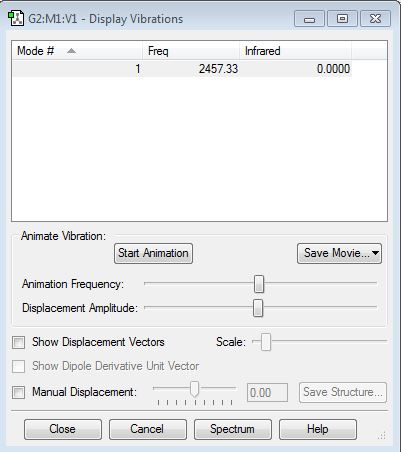
N2 Vibration Mode
Nitrogen is infra red inactive because it has no dipole moment.
Haber Bosch Process and Enthalpy Calculation Using Gaussview Data
Haber Bosch Process
Haber Bosch Process is the widely used process to produce ammonia from hydrogen gas and nitrogen. In normal conditions the two gases are kinetically inert to react, however in the presence of a catalyst (e.g. iron), reaction can occur at significant rate.
Calculations
energy calculation: E(NH3)=-56.55776873a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746a.u.
E(N2)=-109.52412868a.u.
E(H2)=-1.14905693a.u.
3*E(H2)=3.44717079a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.14423799a.u.=-378.696871593kJ/mol
reactants are less thermodynamically stable than product because there is a decrease in enthalpy from reactants to product. This also shows that the process is exothermic.
Small Molecule of Interest: H2SiO
HSiO |
Summary of Information on H2SiO from Gaussview
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Energy | -365.89319642 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.03065697 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 3.8556 debye |
| Point Group | CS |
Additional Information on Structure
Si-H Bond length: 1.53172A
Si=O Bond Length: 1.48652A
H-Si=O Angle: 124.15648
Point Group: CS
Item table from LOG.file on H2SiO
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000023 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000009 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000023 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000017 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.109748D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.4865 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.4865 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.5317 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 111.686 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 124.1565 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 124.1576 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
H2SiO Vibration Mode
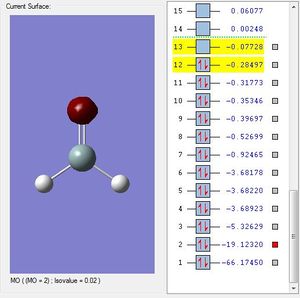
H2SiO Molecular Orbitals
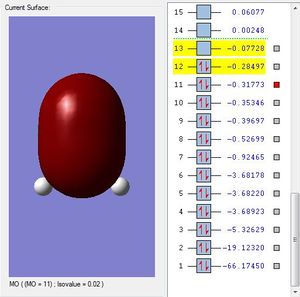
Molecular Orbital #11 shows a elliptical orbital from silicone to oxygen. This could be the 3p-2p bonding orbital.
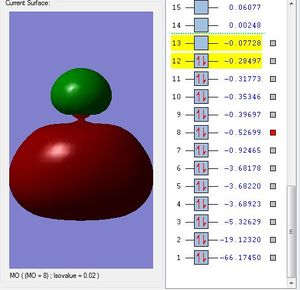
Molecular Orbital #8 shows a lobe of sp hybridized orbital and a indistinguishable of different phases. This could be the 3sp2-2p antibonding orbital.
Molecular Orbital #7 shows a lobe of sp hybridized orbital. This could be the 3sp2-2p bonding orbital.
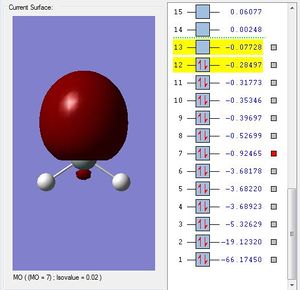
Molecular Orbital #4 shows s orbital on silicon.
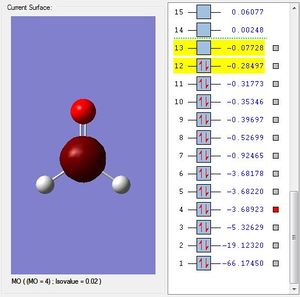
Molecular Orbital #2 shows s orbital on oxygen.